Abstract
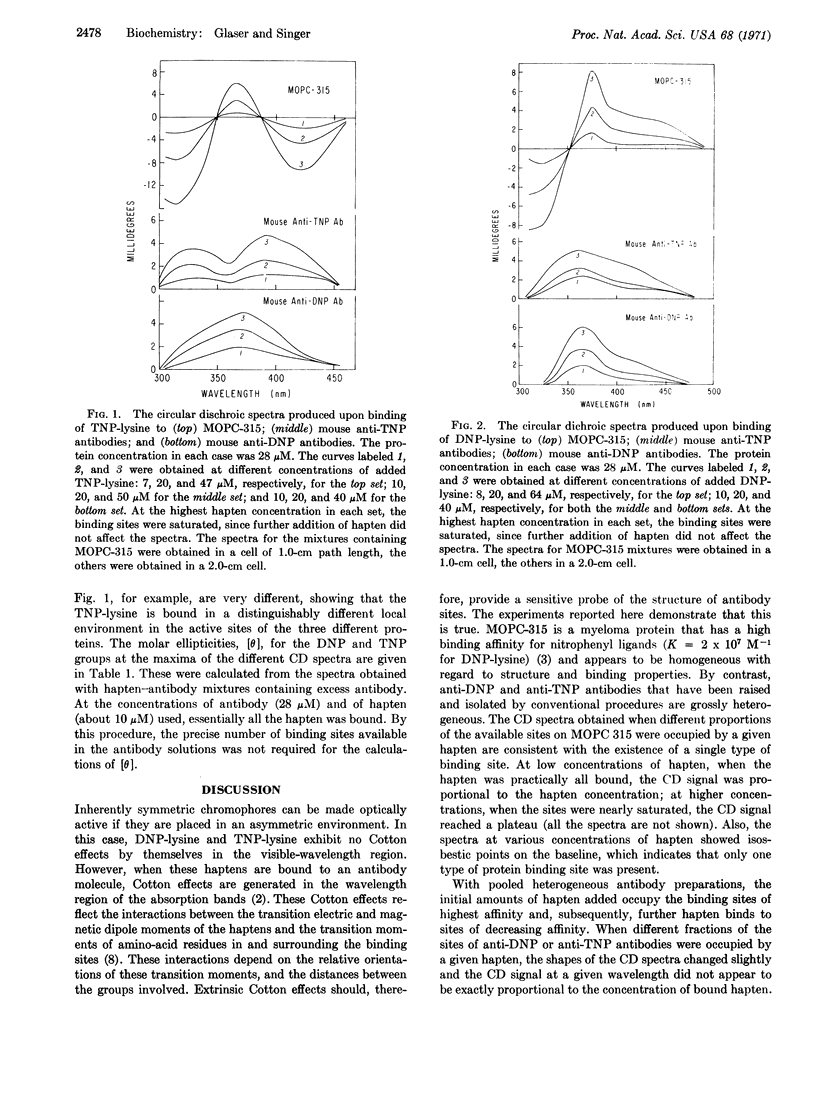
The reversible binding of the haptens 2,4-dinitrophenyllysine (DNP-lysine) and 2,4,6-trinitrophenyllysine (TNP-lysine) to either the nitrophenyl-binding myeloma protein MOPC-315 or to pooled mouse anti-DNP or anti-TNP antibodies produces large and characteristic extrinsic Cotton effects (in the circular dichroic spectra). Despite the similarities in binding characteristics of the three proteins, the circular dichroic spectra produced by the haptens bound to the active sites of these proteins were markedly different. Extrinsic Cotton effects, therefore, provide a powerful new probe of the structure of the reversible complex formed between a hapten and an antibody active site.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Conway-Jacobs A., Schechter B., Sela M. Extrinsic Cotton effect and immunological properties of the p-azobenzenearsonate hapten attached to a helical amino acid copolymer. Biochemistry. 1970 Dec 8;9(25):4870–4875. doi: 10.1021/bi00827a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISEN H. N., SISKIND G. W. VARIATIONS IN AFFINITIES OF ANTIBODIES DURING THE IMMUNE RESPONSE. Biochemistry. 1964 Jul;3:996–1008. doi: 10.1021/bi00895a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen H. N., Little J. R., Steiner L. A., Simms E. S., Gray W. Degeneracy in the secondary immune response: stimulation of antibody formation by cross-reacting antigens. Isr J Med Sci. 1969 May-Jun;5(3):338–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen H. N., Simms E. S., Potter M. Mouse myeloma proteins with antihapten antibody acitivity. The protein produced by plasma cell tumor MOPC-315. Biochemistry. 1968 Nov;7(11):4126–4134. doi: 10.1021/bi00851a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennel S. J., Singer S. J. Affinity labeling of rabbit antibodies to the 2,4,6 trinitrophenyl determinant. Immunochemistry. 1970 Feb;7(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90159-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. R., Eisen H. N. Physical and chemical differences between rabbit antibodies to the 2,4-dinitrophenyl and the 2,4,6-trinitrophenyl groups. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):711–720. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. R., Eisen H. N. Preparation and characterization of antibodies specific for the 2,4,6-trinitrophenyl group. Biochemistry. 1966 Nov;5(11):3385–3395. doi: 10.1021/bi00875a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. R., Eisen H. N. Specificity of the immune response to the 2,4-dinitrophenyl and 2,4,6-trinitrophenyl groups. Ligand binding and fluorescence properties of cross-reacting antibodies. J Exp Med. 1969 Feb 1;129(2):247–265. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.2.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid V., Glaser M., Kennett R., Singer S. J. Extrinsic Cotton effects in hapten--carrier and hapten--antibody interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1184–1187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rockey J. M., Dorrington K. J., Montgomery K. J. Induced optical activity of 2,4-dinitrophenyl-lysine specifically bound to mouse MOPC-315 myeloma protein. Nature. 1971 Jul 16;232(5307):192–194. doi: 10.1038/232192a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner L. A., Eisen H. N. The relative affinity of antibodies synthesized in the secondary response. J Exp Med. 1967 Dec 1;126(6):1185–1205. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.6.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe N. O., Singer S. J. The affinity-labeled residues in antibody active sites. II. Nearest-neighbor analyses. Biochemistry. 1969 Nov;8(11):4523–4534. doi: 10.1021/bi00839a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



