Abstract
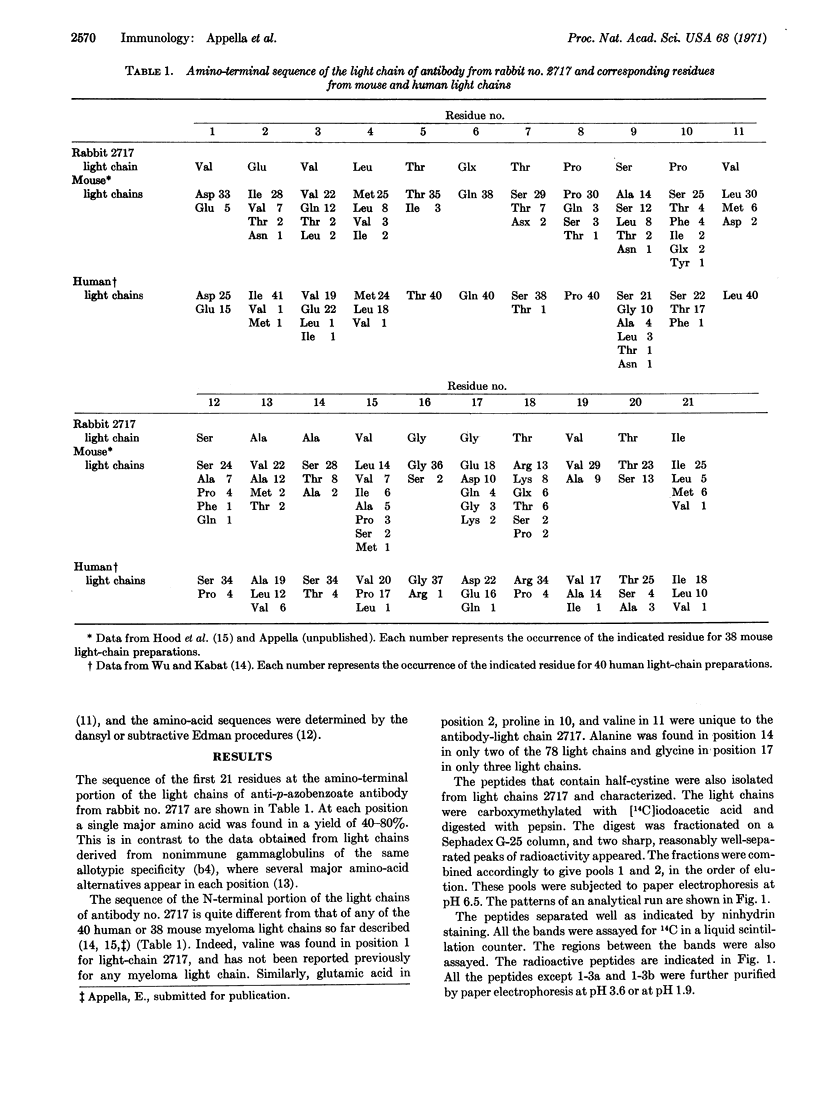
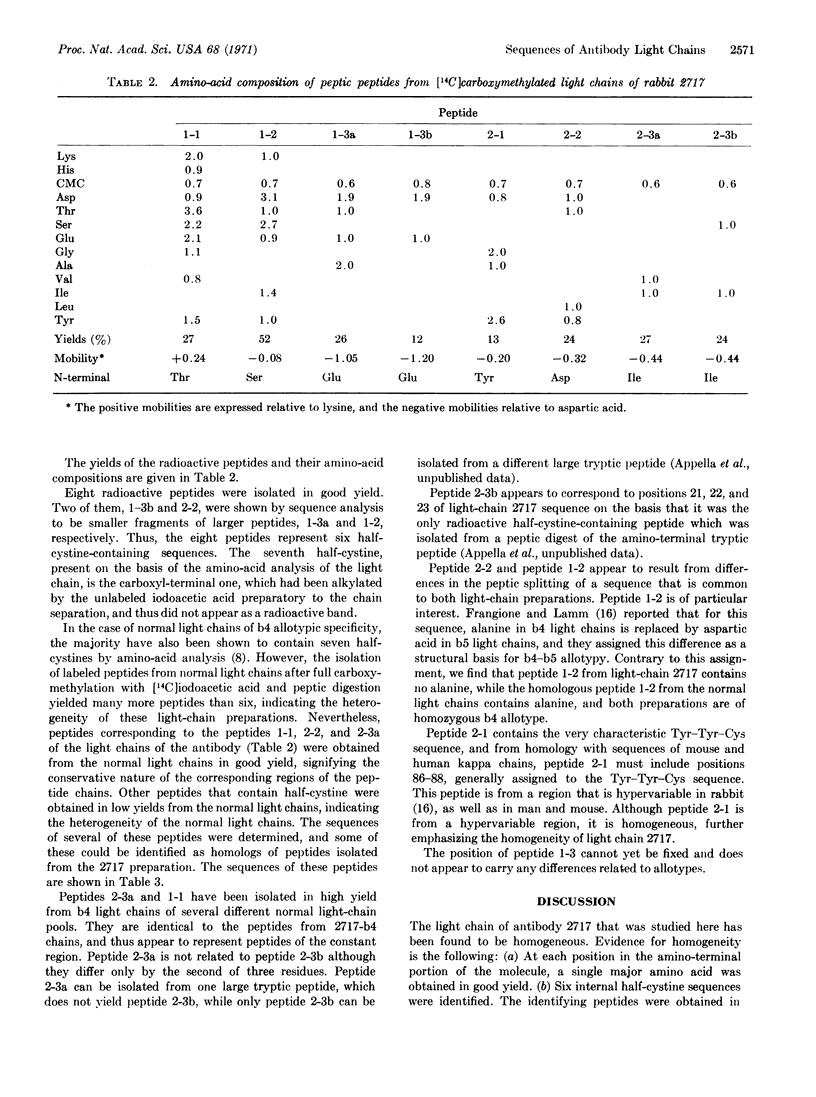
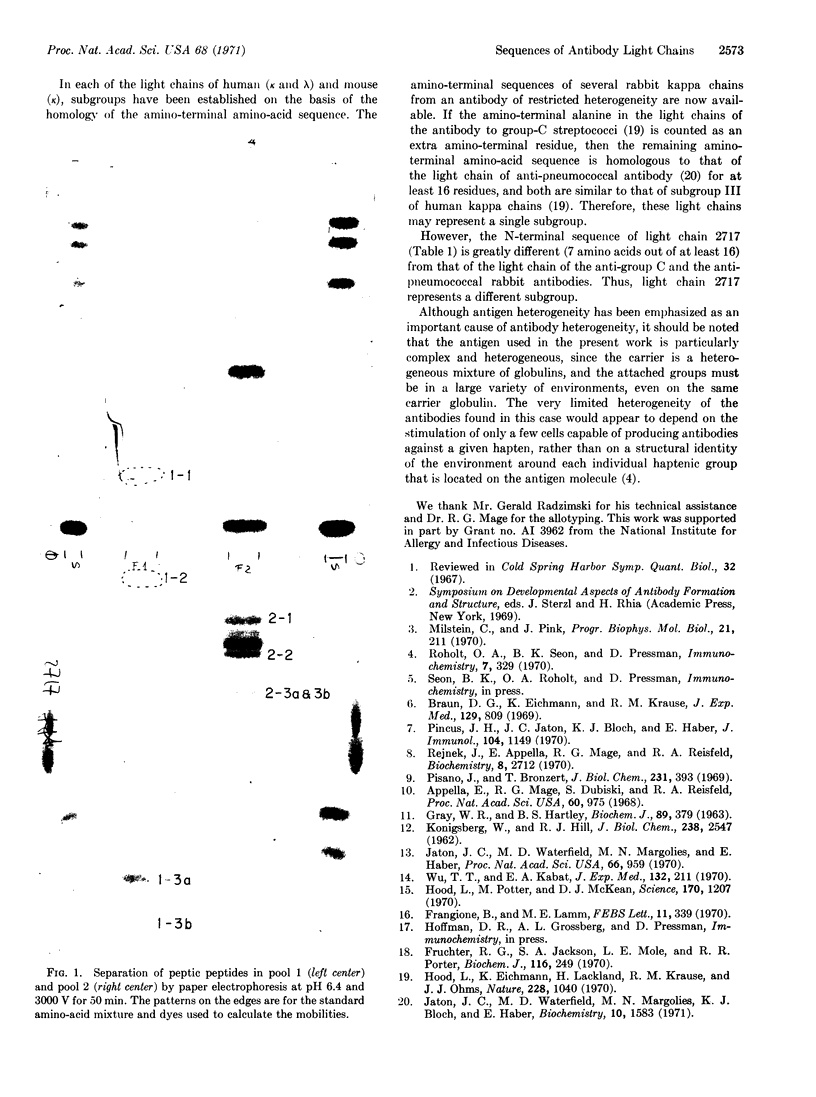
Half-cystine peptic peptides representing the intrachain disulfide bonds of the light chain from an apparently homogeneous rabbit anti-p-azobenzoate antibody were isolated in good yields after reduction and alkylation with [14C]iodoacetate, and their sequences were determined. The sequence of the first 21 amino-terminal residues was also determined. The good yields of these peptides, the fact that no variants of any of them were found, and the cleanness of the amino-terminal sequence determination confirm the high degree of homogeneity of this light-chain preparation. Previous evidence for the homogeneity of the light chain includes the appearance of only a single band upon analysis by disc electrophoresis, a relatively unique amino-acid composition, and a simple tryptic peptide map. The whole antibody shows a homogeneity of the hapten-binding constant. The antigen used in the present work is complex, since the attached hapten groups are in a large variety of environments, particularly since the carrier is a heterogeneous mixture of globulins. The very limited heterogeneity of the antibodies found in this case would appear to depend on the stimulation of only a few of the cells capable of producing antibody against a given hapten, rather than on a structural identity of the environment around each individual hapten group that is located on the antigen molecule.
Keywords: half-cystine peptic peptides, rabbit, N-terminal residues, hapten, bovine gammaglobulin
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appella E., Mage R. G., Dubiski S., Reisfeld R. A. Chemical and immunochemical evidence for different classes of rabbit light polypeptide chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):975–981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun D. G., Eichmann K., Krause R. M. Rabbit antibodies to streptococcal carbohydrates. Influence of primary and secondary immunization and of possible genetic factors on the antibody response. J Exp Med. 1969 Apr 1;129(4):809–830. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.4.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangione B., Lamm M. E. Expression of allelic and non-allelic genes in immunoglobulin light chains from homozygous rabbits. FEBS Lett. 1970 Dec 18;11(5):339–341. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80563-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruchter R. G., Jackson S. A., Mole L. E., Porter R. R. Sequence studies of the Fd section of the heavy chain of rabbit immunoglobulin G. Biochem J. 1970 Jan;116(2):249–259. doi: 10.1042/bj1160249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY W. R., HARTLEY B. S. THE STRUCTURE OF A CHYMOTRYPTIC PEPTIDE FROM PSEUDOMONAS CYTOCHROME C-551. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89:379–380. doi: 10.1042/bj0890379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L. E., Potter M., McKean D. J. Immunoglobulin structure: amino terminal sequences of kappa chains from genetically similar mice (BALB/c). Science. 1970 Dec 11;170(3963):1207–1210. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3963.1207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Eichmann K., Lackland H., Krause R. M., Ohms J. J. Rabbit antibody light chains and gene evolution. Nature. 1970 Dec 12;228(5276):1040–1044. doi: 10.1038/2281040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaton J. C., Waterfield M. D., Margolies M. N., Bloch K. J., Haber E. Variation in the primary structure of antibodies during the course of immunization. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 27;10(9):1583–1587. doi: 10.1021/bi00785a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaton J. C., Waterfield M. D., Margolies M. N., Haber E. Isolation and characterization of structurally homogeneous antibodies from antipneumococcal sera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):959–966. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONIGSBERG W., HILL R. J. The structure of human hemoglobin. III. The sequence of amino acids in the tryptic peptides of the alpha chain. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2547–2561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus J. H., Jaton J. C., Bloch K. J., Haber E. Properties of structurally restricted antibody to type VIII pneumococcal polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1970 May;104(5):1149–1154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rejnek J., Appella E., Mage R. G., Reisfeld R. A. Subtypes of rabbit kappa light polypeptide chains associated with the beta locus. Biochemistry. 1969 Jul;8(7):2712–2718. doi: 10.1021/bi00835a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roholt O. A., Seon B. K., Pressman D. Antibodies of limited heterogeneity: L chains of a single mobility. Immunochemistry. 1970 Apr;7(4):329–340. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90236-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T., Kabat E. A. An analysis of the sequences of the variable regions of Bence Jones proteins and myeloma light chains and their implications for antibody complementarity. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):211–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]