Abstract
Background
Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) are a family of inhibitory and activating receptors expressed by natural killer (NK) cells and regulate NK cell activity in the innate response against viral infections. The aim of this study was to determine the possibility of KIR genes and genotypes as a candidate for susceptibility to or protection against chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection or spontaneous remission of the infection in a Turkish cohort.
Material/Methods
The present study was carried out on 37 patients with chronic HBV infection, 36 patients in spontaneous remission of HBV infection, and 85 healthy subjects. Sequence-specific oligonucleotide probes analysis was used to investigate 16 KIR genes. All data were statistically analyzed by the Fisher exact test.
Results
The rate of inhibitory KIR2DL3 (p=0.0) and 3DS1 (p=0.0) were higher in the healthy group than the group composed of chronic HBV patients and patients with spontaneous remission. There were no statistically significant differences between the rate of AA and Bx genotypes of chronic HBV patients and patients with spontaneous remission and the control group (p>0.05).
Conclusions
Our results suggest that KIR2DL3 and KIR3DS1 genes could be protector genes for HBV infection and they could be important immuno-genetic markers in determining antiviral immunity in the Turkish population.
MeSH Keywords: KIR3DS1 Receptors, KIR2DL3 Receptors, Hepatitis B, Killer Immunoglobulin-Like Receptor (KIR) Family of Receptors
Background
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a hepatotrophic virus that causes a major global health problem. An estimated 2 billion individuals have been infected with HBV and approximately 350 million have the chronic disease [1]. Although the mechanism of HBV pathogenesis remains elusive, host genetic factors are proposed to govern the pathology of disease progression or regression, along with viral and environmental factors. NK cells are activated in the early response to infection, and there is substantial population variability in the rates of HBV infection [2]. Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) are members of the group of cell-surface molecules that activate or inhibit NK cell interaction with HLA class I molecules on the surface of target cells [3,4]. Although detailed genetic and functional analyses exploring KIR influences on HBV in large cohorts are lacking, accumulating evidence supports that NK cell activation contributes to inflammation and liver injury during HBV infection both in HBV transgenic mice and in HBV infected patients [5–8].
KIRs are members of the immunoglobulin superfamily of receptors and are encoded on chromosome 19q13.4. The KIR gene cluster comprises up to 16 highly homologous and closely linked genes and pseudogenes [3,4]. Fourteen of them encode receptors triggering either inhibition (3DL1–3, 2DL1–3, 2DL5) or activation (3DS1, 2DS1–5) and/or both (2DL4), and 2 pseudogenes (2DP1 and 3DP1) do not encode cell-surface receptors [3]. KIR2DS4 has 12 alleles, of which 9 have nucleotide changes in coding regions. Only 2DS4*00101, *00102, and *00103 encode for cell-surface receptors, while the remaining alleles, 2DS4*003/4/6/7/8/9, carry a 22-base pair deletion in exon 5, which causes a frame shift, yielding a truncated KIR2DS4 protein with loss of the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains of the full-length KIR2DS4 protein [9]. Additionally, different combinations of KIR genes generate inherited haplotypes that can be divided into 2 basic groups – A and B – on the basis of their gene content [3].
Polymorphic KIRs, which interact with HLA class 1, are largely inhibitory and exhibit substantial genetic diversity. The result is a significant variation of NK cell repertoire between individuals and also between populations [10,11]. As each KIR-ligand interaction may have differential effects on NK cell activation and inhibition, this diversity has important potential influences on the host response to infections. Genetic studies have demonstrated associations between specific KIR-ligand combinations and the pathogenesis and progression of diverse viral infectious diseases [12–17]. There is still limited data on the relationship of KIR genes and chronic HBV infection in the literature. Additionally, to our knowledge, no analogous study has been performed in our population thus far. The aim of this study was to analyze whether inhibiting or activatory KIR genes and different KIR genotypes have an association in the progression of HBV infection in a Turkish population. This may help to explore some of the possible immune genes that could be important in predisposition to chronic HBV infection.
Material and Methods
Study subjects and samples
The patient groups consisted of 37 patients (17 male, 20 female) with chronic HBV infection and 36 patients (15 male, 21 female) in spontaneous remission state of HBV infection diagnosed at the Department of Infectious Diseases of the Cukurova University, Balcalı Hospital. The diagnostic criterion for chronic HBV adopted in this study was previously described [18]. The control group consisted of 85 healthy subjects (38 males and 47 females). The ages ranged from 18 to 70 years (mean, 43 years) for the patients with chronic HBV, from 19 to 78 years (mean, 42.6 years) for the patients with spontaneous remission, and from 19 to 74 years (mean, 42.5 years) for the control group. All individuals included in this study were from the Cukurova region of Turkey and they were all matched for ethnicity. They were also unrelated and randomly selected. All the enrolled subjects had no serological evidence of hepatitis C virus, hepatitis D virus, and HIV infections, and had no other diseases such as diabetes, malignant tumor, or autoimmune diseases. Samples were collected after informed written consent that was obtained from all participants, and the study was approved by the Cukurova University Ethics Committee.
Laboratory diagnosis of patients with chronic HBV infection
Diagnosis of chronic HBV infection was based on seropositivity for anti-HBV antibody using electrochemiluminescence immunoassay (Roche Diagnostics, GmbH, Mannheim, Germany) and the confirmation of HBV DNA using Light Cycler 2.0 real-time polymerase chain reaction (Roche Diagnostics, GmbH, Mannheim, Germany).
KIR genotyping
DNA from a venous blood sample of each subject was extracted by DNA isolation kit (QIAamp DNA blood mini kit, cat no: 51104, QIAGEN Vertriebs GmbH, Vienna, Austria). Genotyping of KIR genes was performed using the multiplex KIR-SSO typing kit from Tepnel Lifecodes Corporation (Ref: 545110R, CT, USA). This product consists of a mixture of locus-specific oligonucleotide probes coupled to color-coded microspheres (Luminex Corp) and 2 PCR reactions for the amplification of KIR-exons 4, 5, 7, 8, and 9. To type each sample, PCR was performed and the product was hybridized with the SSO-probe mixture using the manufacturer’s protocol. After hybridization, the sample plate was placed in a Luminex instrument for analysis.
Prediction of group-A/-B KIR haplotypes
Frequencies of group-A and -B KIR haplotypes were deduced from the genotype data [19]. In individuals carrying only KIR3DL3, 2DL3, 2DL1, 2DP1, 3DP1, 2DL4, 3DL1, 2DS4 and 3DL2, a fixed-gene content characteristic of group-A haplotypes was considered carrying 2 copies of group-A KIR haplotypes (AA genotypes). If any of genes KIR2DL2, 2DL5, 3DS1, 2DS1, 2DS2, 2DS3 and/or 2DS5 were present, then the genotype was considered as having B haplotype (Bx) [19].
Statistics
The percentage of each KIR gene in the patient and control groups was determined by direct counting (individuals positive for the gene/individuals tested per population×100). Data analysis was performed with the statistical software Minitab Version 15. Differences between 2 groups in the distribution of each KIR gene were estimated by 2-tailed Fisher’s exact test and p<0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
Results
Distribution of KIR genes and genotypes in chronic HBV patients
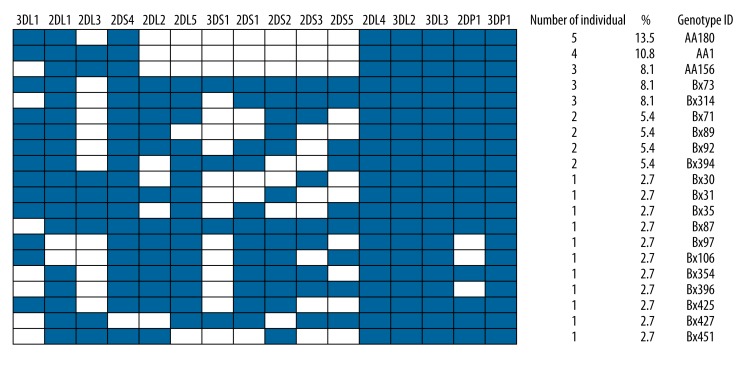
Framework genes KIR2DL4, 3DL2, 3DL3, and 3DP1 were present in all of the samples (Figure 1). Among inhibitory KIR genes, 2DL1 and 3DL1 had higher frequencies in all samples of chronic HBV patients, which were more than 78.4%. With the exception of KIR2DS4, frequencies of the remaining activating genes were all lower than 54.1% (Table 1). Twenty different genotypes were found in 37 patients with chronic HBV. The most frequent genotype, found in 13.5% of patients, was AA180 genotype, which consists of only 1 activating gene – 2DS4. Additionally, 2 more AA genotypes were found in the patient group – AA1 (10.8%) and AA156 (8.1%) (Figure 1). Other patients demonstrated the presence of more than 1 activating gene and thus were considered as Bx (67.6%). Eleven genotypes were seen only once (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
KIR genotype profiles of patients with chronic HBV. Twenty genotypes that differed from each other by the presence (shaded box) and absence (white box) of 16 KIR genes were observed. The figure consisted the percentage frequency and defined the number of individuals carrying the genotype. Genotype ID refers to genotype classification according to www.allelefrequencies.net (43).
Table 1.
Frequencies of killer immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) genes in chronic HBV patients (n=37) and patients with spontaneous remission (n=36).
| Gene | Chronic HBV patients | Patients with spontaneous remission | p value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | |||
| Inhibitory KIRs | 2DL1 | 35 | 94.6 | 34 | 94.4 | 1.000 |
| 2DL2 | 20 | 54.1 | 24 | 66.7 | 0.341 | |
| 2DL3 | 13 | 35.1 | 10 | 27.8 | 0.616 | |
| 2DL4 | 37 | 100.0 | 36 | 100.0 | 1.000 | |
| 2DL5 | 22 | 59.5 | 17 | 47.2 | 0.352 | |
| 3DL1 | 26 | 78.4 | 29 | 80.6 | 0.417 | |
| 3DL2 | 37 | 100.0 | 36 | 100.0 | 1.000 | |
| 3DL3 | 37 | 100.0 | 36 | 100.0 | 1.000 | |
| Activating KIRs | 2DS1 | 18 | 48.6 | 15 | 41.7 | 0.640 |
| 2DS2 | 20 | 54.1 | 23 | 63.9 | 0.478 | |
| 2DS3 | 14 | 37.8 | 9 | 25.0 | 0.315 | |
| 2DS4 | 36 | 97.3 | 34 | 94.4 | 0.615 | |
| 2DS5 | 15 | 40.5 | 12 | 33.3 | 0.63 | |
| 3DS1 | 7 | 18.9 | 8 | 22.2 | 0.778 | |
| Pseudogene | 2DP1 | 34 | 91.9 | 34 | 94.4 | 1.000 |
| 3DP1 | 37 | 100.0 | 36 | 100.0 | 1.000 | |
Distribution of KIR genes and genotypes in patients with spontaneous remission
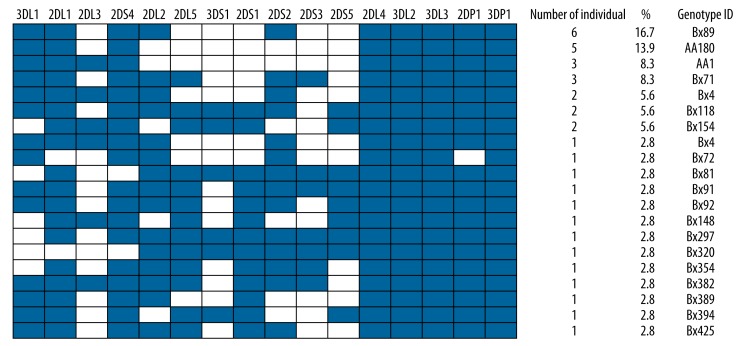
Twenty different genotypes were found in 36 patients with spontaneous remission. The most frequent genotype, found in 16.7% of patients, was Bx89 genotype. Two different AA genotypes – AA180 (13.9%) and AA1 (8.3%) – were found in the spontaneous remission group, which consists of only one activating gene – KIR2DS4 (Figure 2). Other individuals in this group demonstrated the presence of more than 1 activating gene and thus were considered as Bx (76.8%). Thirteen genotypes were seen only once (Figure 2). Framework genes KIR2DL4, 3DL2, 3DL3, and 3DP1 were also present in all of the samples (Figure 2). Among inhibitory KIR genes, 2DL1 and 3DL1 had higher frequencies in all samples of chronic HBV patients, which were more than 80.6%. With the exception of KIR2DS4, frequencies of the remaining activating genes were all lower than 63.9% (Table 1).
Figure 2.
KIR genotype profiles of patients with spontaneous remission. Twenty genotypes that differed from each other by the presence (shaded box) and absence (white box) of 16 KIR genes were observed. The figure consisted the percentage frequency and defined the number of individuals carrying the genotype. Genotype ID refers to genotype classification according to www.allelefrequencies.net (43).
Relationship of KIR genes and genotypes with HBV infection
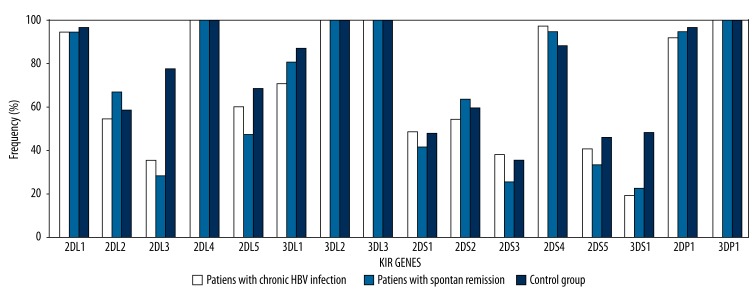
In the first step, frequencies of individual KIR genes were compared between chronic HBV patients and patients with spontaneous remission (Table 1). All 16 KIR genes were compared by Fisher’s exact test. There were no statistically significant differences between these 2 groups. In the second step, frequencies of individual KIR genes were compared between the control group and the group composed of chronic HBV patients and patients with spontaneous remission (Table 2, Figure 3). The rate of inhibitory KIR2DL3 (p=0.0) and 3DS1 (p=0.0) were higher in the healthy group than the group composed of chronic HBV patients and patients with spontaneous remission. Since the methods used for KIR genotyping permitted distinguishing groups of alleles of activating KIR2DS4, we found that there were no statistically significant differences for 2DS4*001 (full-length exon 5) and 2DS4*003/4/6/7/8/9 (deletion in exon 5) alleles between the 2 groups (p>0.05). Additionally, there were no statistically significant differences between the rate of AA and Bx genotypes of chronic HBV patients and patients with spontaneous remission and the control group (p>0.05).
Table 2.
Frequencies of killer immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) genes in the control group (n=85) and the group composed of chronic HBV patients and patients with spontaneous remission (n=73). Statistically significant genes are indicated in bold characters.
| Gene | Patients with chronic HBV and spontaneous remission | Control group | p value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | |||
| Inhibitory KIRs | 2DL1 | 69 | 94.5 | 82 | 96.5 | 0.705 |
| 2DL2 | 44 | 60.3 | 50 | 58.8 | 0.872 | |
| 2DL3 | 23 | 31.5 | 66 | 77.6 | 0* | |
| 2DL4 | 73 | 100.0 | 85 | 100 | 0.212 | |
| 2DL5 | 39 | 53.4 | 58 | 68.2 | 0.072 | |
| 3DL1 | 55 | 79.5 | 74 | 87.1 | 0.066 | |
| 3DL2 | 73 | 100.0 | 85 | 100.0 | 1.000 | |
| 3DL3 | 73 | 100.0 | 85 | 100.0 | 1.000 | |
| Activating KIRs | 2DS1 | 33 | 45.2 | 41 | 48.2 | 0.750 |
| 2DS2 | 43 | 58.9 | 51 | 60.0 | 1.000 | |
| 2DS3 | 23 | 31.5 | 30 | 35.3 | 0.736 | |
| 2DS4 | 70 | 95.9 | 75 | 88.2 | 0.091 | |
| 2DS5 | 27 | 37.0 | 39 | 45.9 | 0.332 | |
| 3DS1 | 15 | 20.5 | 41 | 48.2 | 0* | |
| Pseudogene | 2DP1 | 68 | 93.2 | 82 | 96.5 | 0.472 |
| 3DP1 | 73 | 100.0 | 85 | 100.0 | 1.000 | |
Figure 3.
Distrubition of KIR gene frequencies of chronic HBV patients, patients with spontaneous remission and controls.
Discussion
NK cells express multiple cell surface receptors, and during different infections different receptors are likely to be important. Many of these receptors are monomorphic and are expressed on all NK cells. KIRs have a variegated expression pattern, and their complex genetics indicate that they are involved in generating population diversity in antiviral immune response. Previous studies have demonstrated several associations between various KIR genes and/or their HLA class I ligands in clinical progression of HBV infection [20–22] and in the progression of this infection to hepatocellular carcinoma [23]. These associations could be due to the capacity of interactions of HLA class I molecules -especially HLA-C and HLA-B- with KIRs and activation of NK cells.
In the present study, we examined the genes encoding KIR receptors and KIR genotypes in chronic HBV patients, patients with spontaneous remission, and healthy controls in a Turkish cohort. Our results showed that the frequencies of both KIR2DL3 and KIR3DS1 genes were much higher in healthy controls than in chronic HBV patients and patients with spontaneous remission. This might indicate that the inhibitory KIR2DL3 and activating KIR3DS1 were possibly protector genes for HBV infection. Similarly, Gao et al, in their study comparing 182 chronic HBV patients with 140 healthy controls, reported that KIR2DL3: HLA-C1 homozygosity was protective against HBV infection [22] and that KIR2DL1: HLA-C2 was associated with susceptibility to HBV infection. In contrast, Zhi-ming et al showed that KIR2DS2 and KIR2DS3 are HBV-susceptive genes, whereas KIR2DS1, KIR3DS1, and KIR2DL5 may be protective genes that facilitate the clearance of HBV [21] in a Han Chinese population. Population genetic analyses have revealed that the frequency and distribution of KIR genes and haplotypes vary with ethnicity [19]. Although Zhi-Ming’s study and ours were done in different populations, the KIR3DS1 gene was found as a protector gene in both studies.
In a wider study, Lu et al analyzed KIR genes in 150 patients with chronic HBV infection, 251 spontaneous resolvers, and 451 healthy controls. They found a lower frequency of the A haplotype and higher frequency of the B haplotype in patients exposed to HBV infection compared with healthy controls, implying a susceptibility effect of the B haplotype [20]. In our study, there were no statistically significant differences between the rate of AA and Bx genotypes of chronic HBV patients and patients with spontaneous remission and the control group. Additionally, in a recent study, Pan et al suggested the association of a combination of full-length form and 22 bp-deleted form of KIR2DS4 (KIR2DS4/1D) with hepatocellular carcinoma incidence in patients with chronic HBV [23].
Previous studies showed that there are important similarities between inhibitory and activating KIR frequencies of patients with hepatitis C and HBV infections, despite these viruses being phylogenetically unrelated. Khakoo et al reported that genes encoding the inhibitory NK cell receptor KIR2DL3 and its ligand, HLA-C1, influence resolution of hepatitis C virus infection in Caucasians and African Americans with expected low infectious doses of HCV but not in those with high-dose exposure [12]. These findings have been confirmed in several studies [14,20,24,25].
Conclusions
Chronic HBV patients, patients with spontaneous remission of HBV infection, and healthy controls in our population demonstrate that KIR2DL3 and KIR3DS1 are important immuno-genetic markers in determining antiviral immunity. To explore the role of KIRs in HBV infections, the interrelation between KIR genes, genotypes, and chronic HBV infection should be investigated in many different populations. Models based on both activating and inhibitory receptors and their ligand interactions could be generated for detailed genetic studies in wider groups. The present study was merely performed in a small group in Turkey. Thus, in order to confirm the present general results obtained in this study, functional studies and investigations in different populations are still needed to better understand this mechanism.
Footnotes
Source of support: This study was funded by BAP of Cukurova University, Adana, Turkey (Grant Number: TF-2013-BAP-13)
References
- 1.World Health Organization. Fact Sheet 204. 2008. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs204/en/
- 2.Custer B, Sullivan SD, Hazlet TK, et al. Global epidemiology of hepatitis B virus. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2004;38:158–68. doi: 10.1097/00004836-200411003-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Vilches C, Parham P. KIR: diverse, rapidly evolving receptors of innate and adaptive immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:217–51. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.20.092501.134942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Middleton D, Williams F, Halfpenny IA. KIR genes. Transp Immunol. 2005;14:135–42. doi: 10.1016/j.trim.2005.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dunn C, Brunetto M, Reynolds G, et al. Cytokines induced during chronic hepatitis B virus infection promote a pathway for NK cell-mediated liver damage. J Exp Med. 2007;204:667–80. doi: 10.1084/jem.20061287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chen Y, Sun R, Jiang W, et al. Liver-specific HBsAg transgenic mice are over-sensitive to Poly(I: C)-induced liver injury in NK cell- and IFNgamma-dependent manner. J Hepatol. 2007;47:183–90. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2007.02.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kakimi K, Lane TE, Wieland S, et al. Blocking chemokine responsive to gamma-2/interferon (IFN)-gamma inducible protein and monokine induced by IFN-gamma activity in vivo reduces the pathogenetic but not the antiviral potential of hepatitis B virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 2001;194:1755–66. doi: 10.1084/jem.194.12.1755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chen Y, Wei H, Sun R, et al. Increased susceptibility to liver injury in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice involves NKG2D-ligand interaction and natural killer cells. Hepatology. 2007;46:706–15. doi: 10.1002/hep.21872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bao X, Hou L, Sun A, et al. An allelic typing method for 2DS4 variant used in study of haplotypes of killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor gene. Int J Lab Hematol. 2010;32:625–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-553X.2010.01234.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hsu KC, Chida S, Geraghty DE, Dupont B. The killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) genomic region: geneorder, haplotypes and allelic polymorphism. Immunol Rev. 2002;190:40–52. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2002.19004.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Uhrberg M, Valiante NM, Shum BP, et al. Human diversity in killer cell inhibitory receptor genes. Immunity. 1997;7:753–63. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80394-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Khakoo SI, Thio CL, Martin MP, et al. HLA and NK cell inhibitory receptor genes in resolving hepatitis C virus infection. Science. 2004;305:872–74. doi: 10.1126/science.1097670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Romero V, Azocar J, Zuniga J, et al. Interaction of NK inhibitory receptor genes with HLA-C and MHC class II alleles in hepatitis C virus infection outcome. Mol Immunol. 2008;45:2429–36. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2008.01.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Knapp S, Warshow U, Hegazy D, et al. Consistent beneficial effects of killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 2DL3 and group 1 human leukocyte antigen-C following exposure to hepatitis c virus. Hepatology. 2010;51:1168–75. doi: 10.1002/hep.23477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Martin MP, Gao X, Lee JH, et al. Epistatic interaction between KIR3DS1 and HLA-B delays the progression to AIDS. Nat Genet. 2002;31:429–34. doi: 10.1038/ng934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Estefanía E, Gómez-Lozano N, Portero F, et al. Influence of KIR gene diversity on the course of HSV-1 infection: resistance to the disease is associated with the absence of KIR2DL2 and KIR2DS2. Tissue Antigens. 2007;70:34–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.2007.00844.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Stern M, Hadaya K, Hönger G, et al. Telomeric Rather than Centromeric Activating KIR Genes Protect from Cytomegalovirus Infection after Kidney Transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2011;11:1302–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2011.03516.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lok AS, McMahon BJ. Chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2001;34:1225–41. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2001.29401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Middleton D, Menchaca L, Rood H, Komerofsky R. New allele frequency database. Tissue Antigens. 2003;61:403–7. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-0039.2003.00062.x. http://www.allelefrequencies.net. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lu Z, Zhang B, Chen S, et al. Association of KIR genotypes and haplotypes with susceptibility to chronic hepatitis B virus infection in Chinese Han population. Cell Mol Immunol. 2008;5:457–63. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2008.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Zhi-ming L, Yu-lian J, Zhao-lei F, et al. Polymorphisms of killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor gene: possible association with susceptibility to or clearance of hepatitis B virus infection in Chinese Han population. Croat Med J. 2007;48:800–6. doi: 10.3325/cmj.2007.6.800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gao X, Jiao Y, Wang L, et al. Inhibitory KIR and specific HLA-C gene combinations confer susceptibility to or protection against chronic hepatitis B. Clin Immunol. 2010;137:139–46. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2010.05.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Pan N, Jiang W, Sun H, et al. KIR and HLA Loci Are Associated with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development in Patients with Hepatitis B Virus Infection: A Case-Control Study. PLoS One. 2011;6:e25682. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zúñiga J, Romero V, Azocar J, et al. Protective KIR-HLA interactions for HCV infection in intravenous drug users. Mol Immunol. 2009;46:2723–27. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2009.05.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Thio CL, Gao X, Goedert JJ, et al. HLA-Cw*04 and hepatitis C virus persistence. J Virol. 2002;76:4792–97. doi: 10.1128/JVI.76.10.4792-4797.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]