Abstract
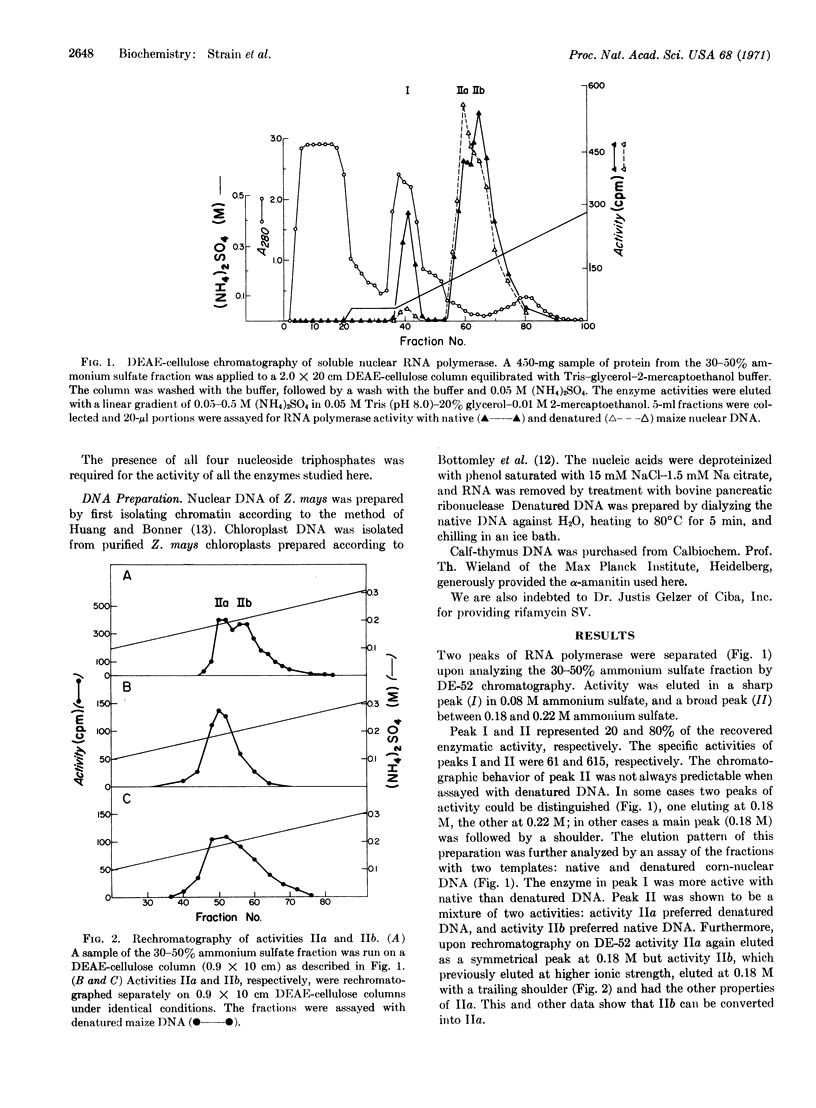
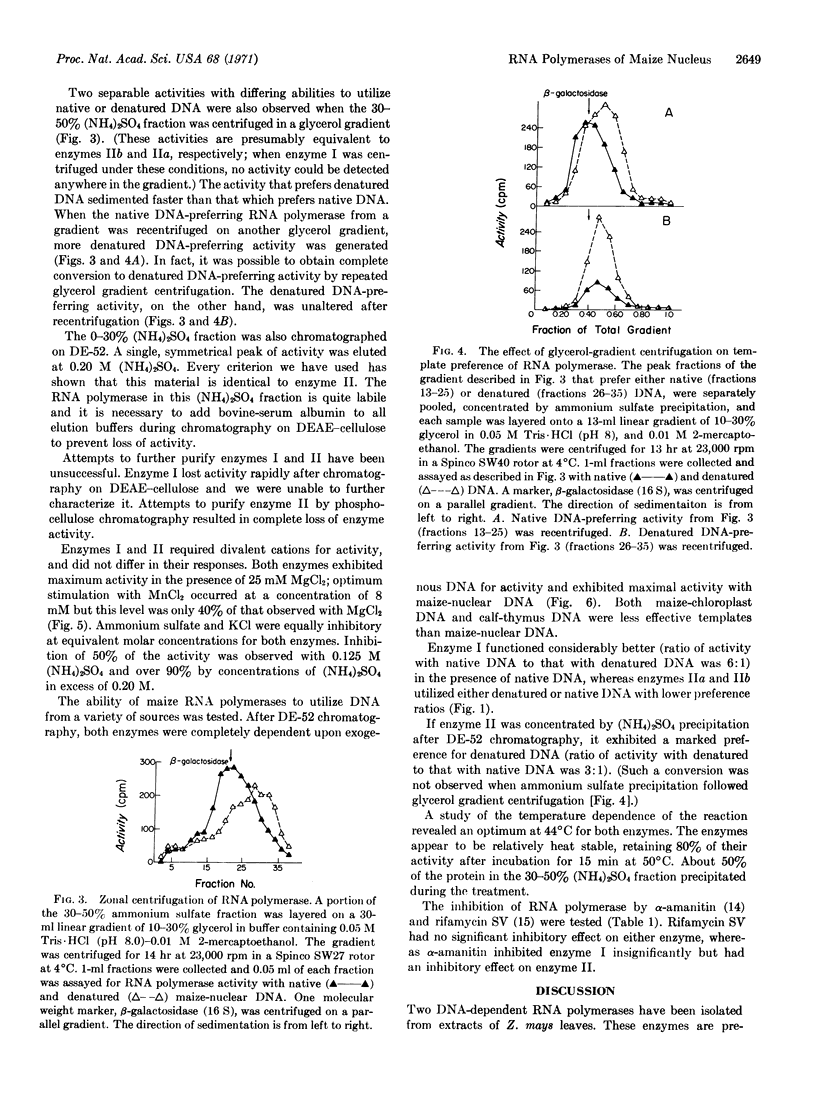
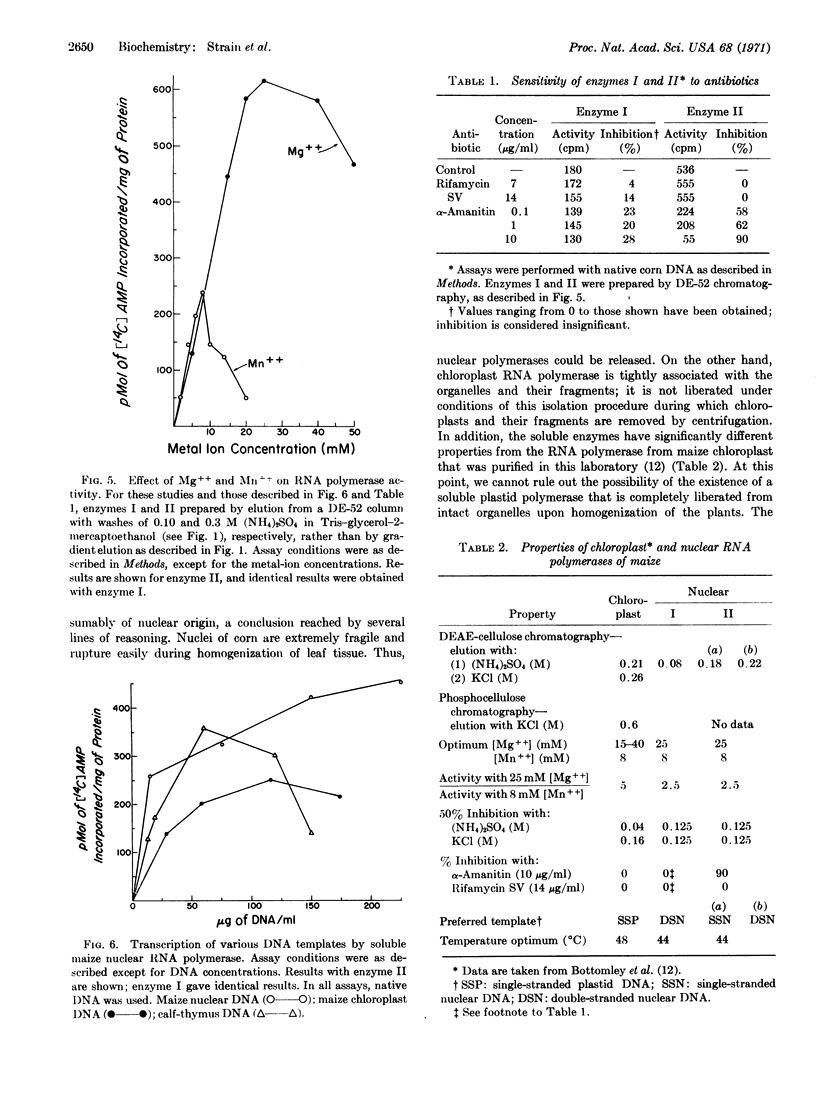
Two DNA-dependent RNA polymerases of nuclear origin have been purified from leaves of Zea mays. The two enzymes can be separated on DEAE-cellulose columns. Enzymes I and II are eluted with 0.08 and 0.20 M (NH4)2SO4, respectively. Both enzymes prefer maize nuclear DNA as a template; they are also more active in the presence of Mg++ than Mn++ and are inhibited by (NH4)2-SO4 or KCl. Neither enzyme is inhibited by rifamycin SV. Enzyme II is strongly inhibited by α-amanitin, whereas enzyme I is not significantly affected. Their ability to use native and denatured DNA as templates varies according to the extent and method of purification of the polymerase. Furthermore, enzyme II can be resolved by DEAE-chromatography or glycerol-gradient centrifugation into two components, one of which prefers native DNA, while the other prefers denatured DNA.
Keywords: Zea mays, rifamycin SV, α-amanitin, native and denatured DNA, Mg++, Mn++
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bottomley W., Smith H. J., Bogorad L. RNA polymerases of maize: partial purification and properties of the chloroplast enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2412–2416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R. A new method for the large scale purification of Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6160–6167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Travers A. A., Dunn J. J., Bautz E. K. Factor stimulating transcription by RNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 Jan 4;221(5175):43–46. doi: 10.1038/221043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUANG R. C., BONNER J. Histone, a suppressor of chromosomal RNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jul 15;48:1216–1222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.7.1216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausen P., Stein H. Ribonuclease H. An enzyme degrading the RNA moiety of DNA-RNA hybrids. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jun;14(2):278–283. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horgen P. A., Griffin D. H. Specific inhibitors of the three RNA polymerases from the aquatic fungus Blastocladiella emersonii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):338–341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno S., Yamazaki H., Nitta K., Umezawa H. Inhibition of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase reaction of Escherichia coli by an antimicrobial antibiotic, streptovaricin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 22;157(2):322–332. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90086-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondal H., Mandal R. K., Biswas B. B. Factors and rifampicin influencing RNA polymerase isolated from chromatin of eukaryotic cell. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Sep 10;40(5):1194–1200. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90922-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Multiple forms of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in eukaryotic organisms. Nature. 1969 Oct 18;224(5216):234–237. doi: 10.1038/224234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Specific nucleolar and nucleoplasmic RNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):675–682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Hausen P. A factor from calf thymus stimulating DNA-dependent RNA polymerase isolated from this tissue. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jun;14(2):270–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00286.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirpe F., Fiume L. Studies on the pathogenesis of liver necrosis by alpha-amanitin. Effect of alpha-amanitin on ribonucleic acid synthesis and on ribonucleic acid polymerase in mouse liver nuclei. Biochem J. 1967 Nov;105(2):779–782. doi: 10.1042/bj1050779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


