Abstract
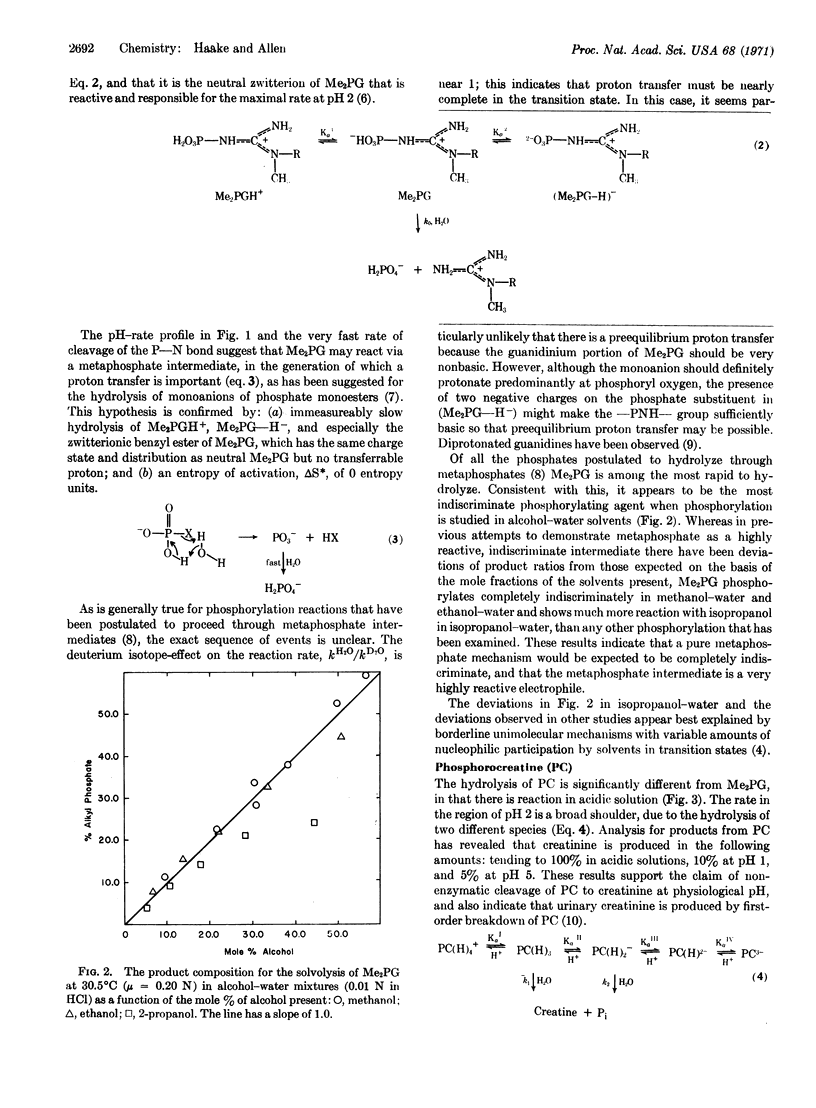
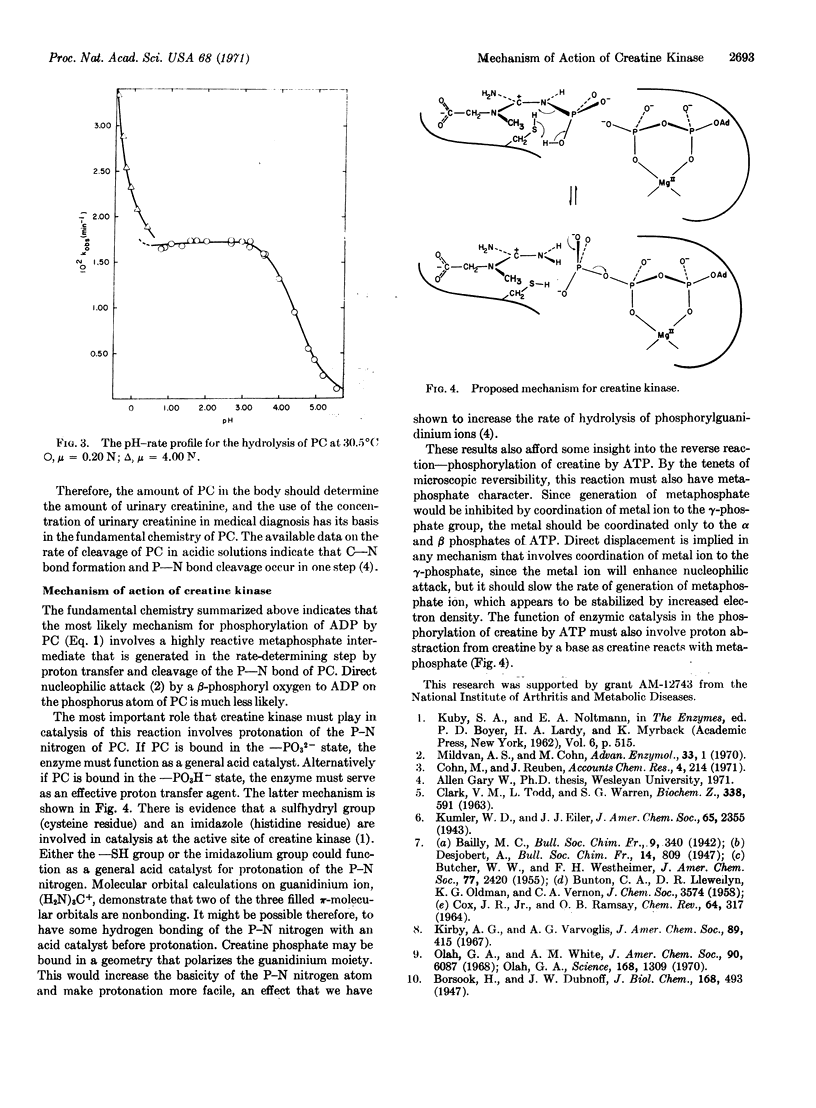
The solvolyses of phosphorocreatine (creatine phosphate) and models for phosphorocreatine have been investigated and the results are applied to the mechanism of action of creatine kinase (EC 2.7.3.2). A metaphosphate intermediate appears to be involved.
Keywords: solvolyses, creatinine, dimethylphosphoroguanidinate, methylbenzylphosphoroguanidinate, reaction kinetics
Full text
PDF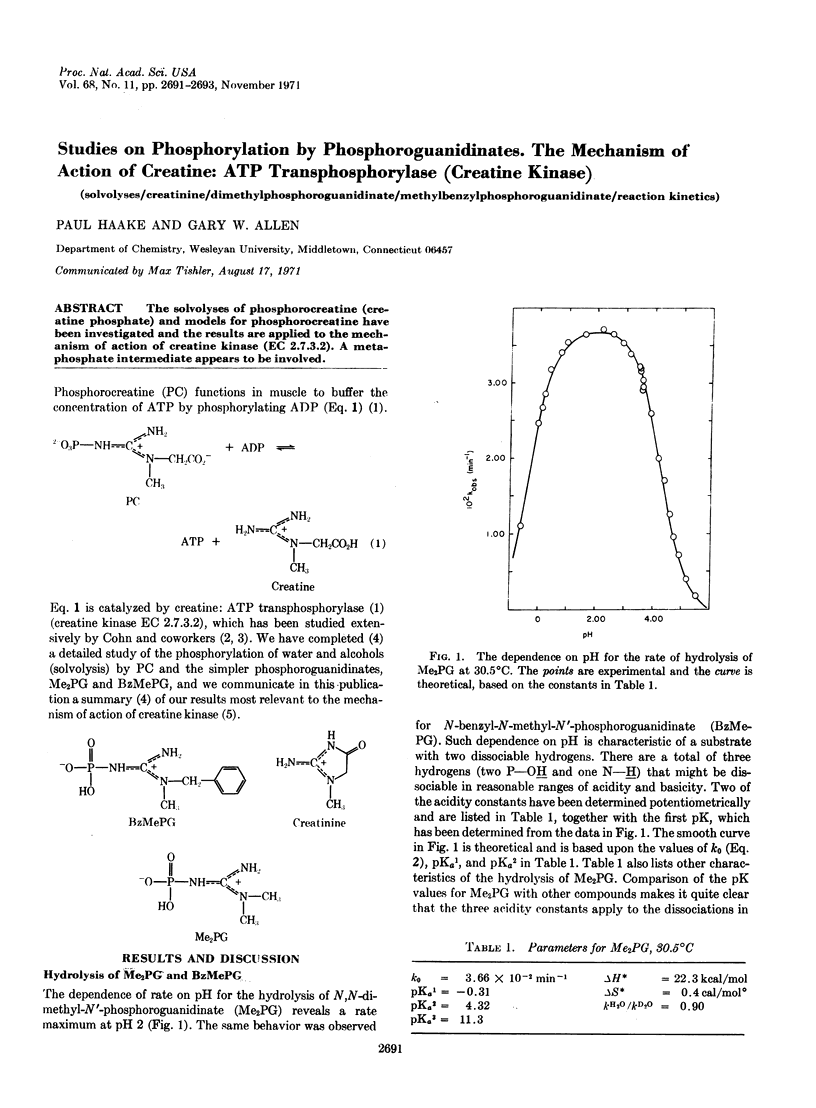
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CLARK V. M., TODD L., WARREN S. G. STUDIES ON PHOSPHORYLATION. XXV. METAL ION CATALYSED REACTIONS OF PHOSPHAGENS. Biochem Z. 1963;338:591–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mildvan A. S., Cohn M. Aspects of enzyme mechanisms studies by nuclear spin relazation induced by paramagnetic probes. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1970;33:1–70. doi: 10.1002/9780470122785.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


