Abstract
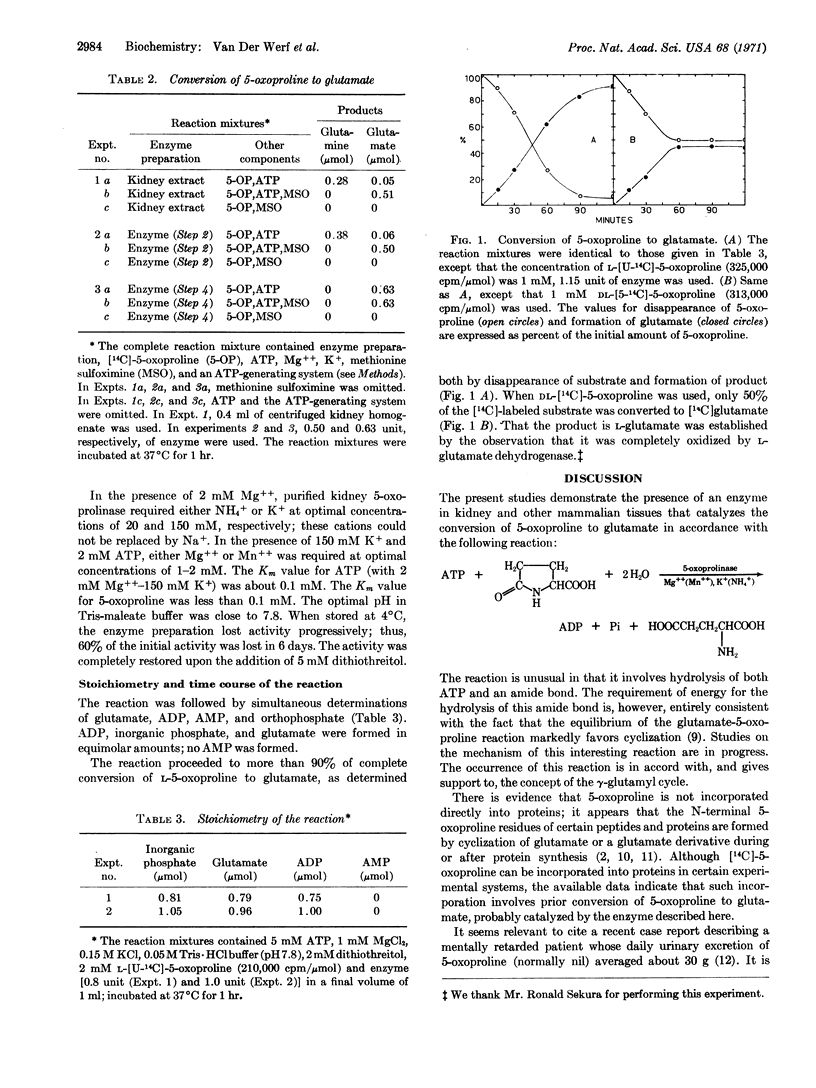
A new enzyme, 5-oxoprolinase, was found in rat kidney and in several other tissues; it catalyzes the conversion of 5-oxo-L-proline (L-5-oxo-pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid, L-2-pyrrolidone-5-carboxylic acid, L-pyroglutamic acid) to L-glutamic acid, with concomitant stoichiometric cleavage of ATP to ADP and orthophosphate. The reaction catalyzed by 5-oxoprolinase, in which 5-oxoproline formed from γ-glutamyl amino acids by the action of γ-glutamylcyclotransferase is converted to glutamate, appears to function in the γ-glutamyl cycle. 5-Oxoprolinase requires Mg++ (or Mn++) and K+ (or NH4+) for activity. The equilibrium is markedly in favor of glutamate formation at pH 7.8.
Keywords: kidney, amino-acid transport, pyroglutamic acid, 5-oxo-pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Jellum E., Kluge T., Börresen H. C., Stokke O., Eldjarn L. Pyroglutamic aciduria--a new inborn error of metabolism. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1970 Dec;26(4):327–335. doi: 10.3109/00365517009046241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Meister A. The gamma-glutamyl cycle: a possible transport system for amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1248–1255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishna M., Krishnaswamy P. R., Rao D. R. Metabolism of pyrrolidonecarboxylic acid in the rat. Biochem J. 1970 Aug;118(5):895–897. doi: 10.1042/bj1180895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronzio R. A., Wilk S., Rowe W. B., Meister A. Preparation and studies on the characterization of sheep brain glutamine synthetase. Biochemistry. 1969 Jun;8(6):2670–2674. doi: 10.1021/bi00834a064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rush E. A., McLaughlin C. L., Solomon A. The essentiality of decyclization of pyrrolidonecarboxylic acid prior to utilization in protein biosynthesis. Cancer Res. 1971 Aug;31(8):1134–1139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rush E. A., Starr J. L. The indirect incorporation of pyrrolidone carboxylic acid into transfer ribonucleic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jan 21;199(1):41–55. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90693-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



