Abstract
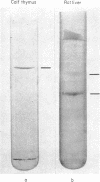
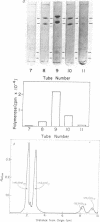
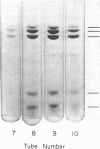
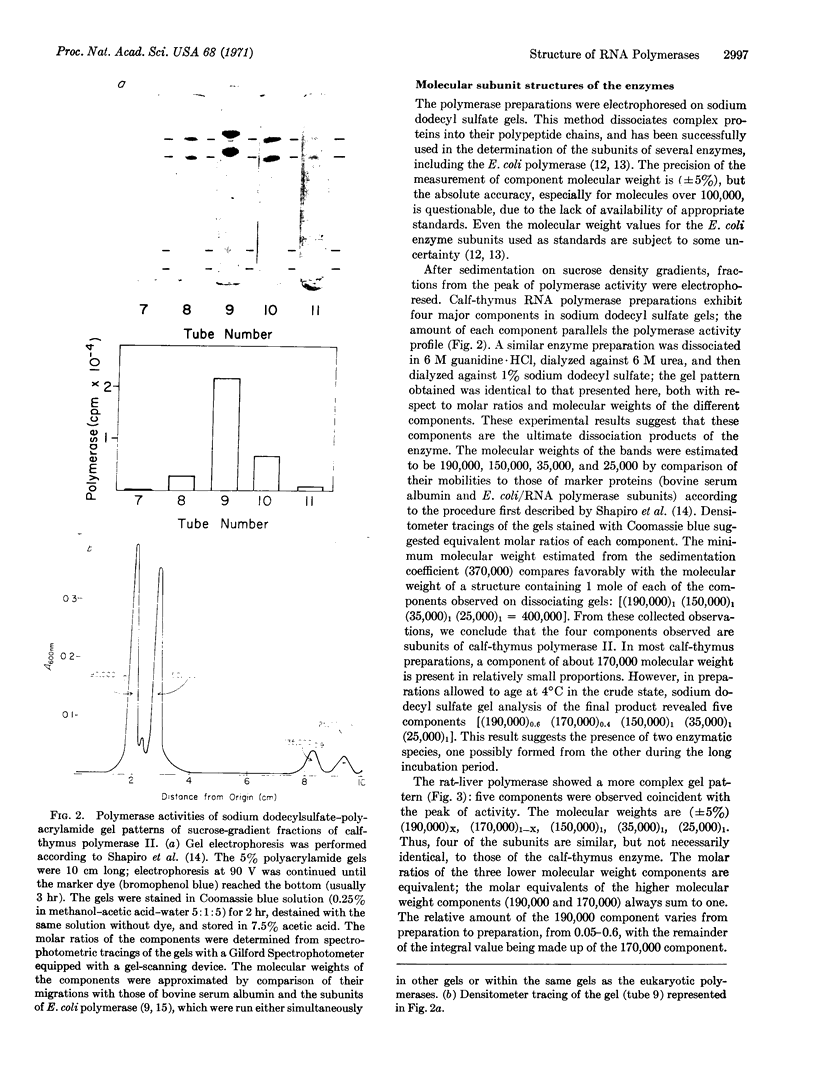
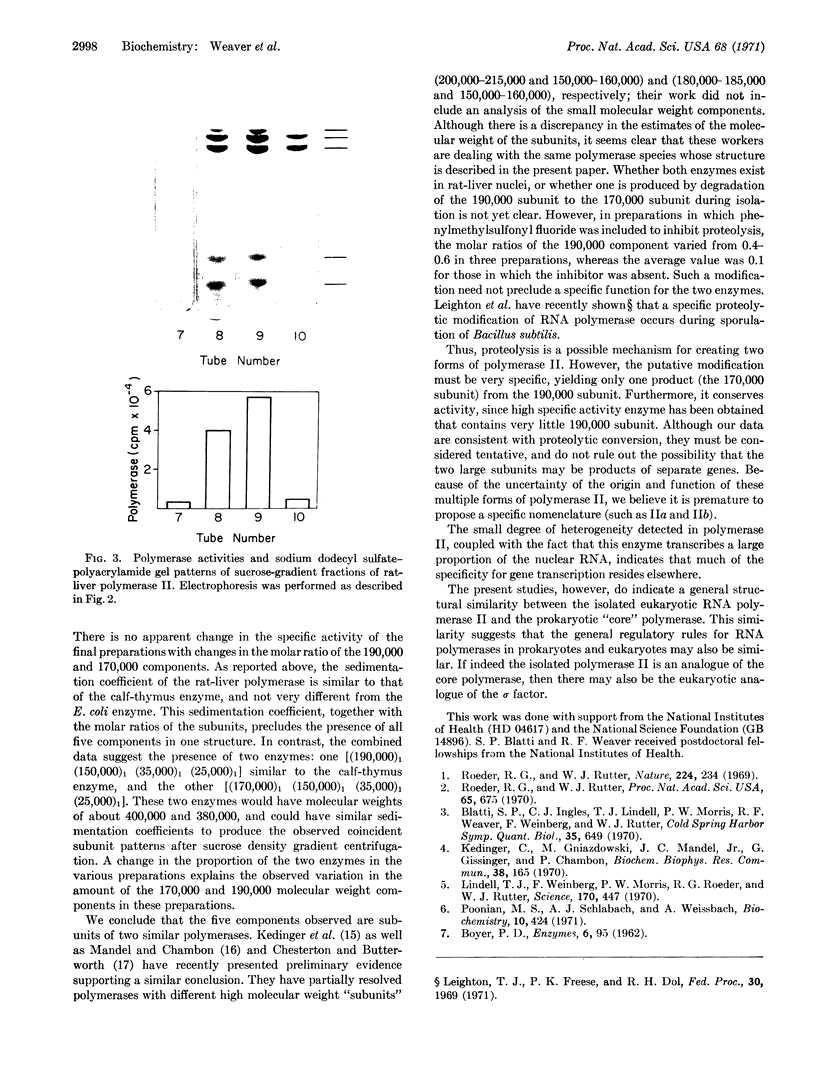
DNA-dependent RNA polymerase II has been purified to high specific activity and apparent homogeneity from both calf thymus and rat liver. Two form II enzymes are present in rat-liver preparations, one with the molecular structure [(190,000)1(150,000)1(35,000)1(25,000)1], the other with a molecular structure of [(170,000)1(150,000)1(35,000)1(25,000)1] (molecular weights are within ±5% but the absolute values are approximate). Inclusion of a proteolytic inhibitor during the isolation procedure decreases the proportion of the molecule containing the 170,000 subunit. Calf-thymus RNA polymerase preparations typically exhibit four components on polyacrylamide gels that contain sodium dodecyl sulfate, with an apparent molecular structure of [(190,000)1(150,000)1(35,000)1(25,000)1]. In addition, some calf-thymus polymerase II preparations contain small quantities of the [(170,000)1(150,000)1(35,000)1(25,000)1] species; the quantity of this species may also be increased from less than 5% in the normal preparation to at least 40% in an “aged” preparation. Thus, the 170,000 subunit may be derived from the 190,000 subunit in both tissues. Until unequivocal evidence is obtained on this point, however, the possibility that the large subunits are unique species should not be eliminated. The general structural similarity of the eukaryotic RNA polymerase II with that of the prokaryotic polymerase suggests that the modes of action and regulation may be analogous.
Keywords: acrylamide gel electrophoresis, sodium dodecyl sulfate, subunits, polymerase II
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg D., Chamberlin M. Physical studies on ribonucleic acid polymerase from Escherichia coli B. Biochemistry. 1970 Dec 22;9(26):5055–5064. doi: 10.1021/bi00828a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R. A new method for the large scale purification of Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6160–6167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R. Separation and characterization of the subunits of ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6168–6176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesterton C. J., Butterworth P. H.W. Purification of the rat liver form B DNA-dependent RNA polymerases. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 24;15(3):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80307-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedinger C., Gniazdowski M., Mandel J. L., Jr, Gissinger F., Chambon P. Alpha-amanitin: a specific inhibitor of one of two DNA-pendent RNA polymerase activities from calf thymus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jan 6;38(1):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedinger C., Nuret P., Chambon P. Structural evidence for two alpha-amanitin sensitive RNA polymerases in calf thymus. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 24;15(3):169–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindell T. J., Weinberg F., Morris P. W., Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Specific inhibition of nuclear RNA polymerase II by alpha-amanitin. Science. 1970 Oct 23;170(3956):447–449. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3956.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel J. L., Chambon P. Purification of RNA polymerase B activity from rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1971 Jun 24;15(3):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80306-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poonian M. S., Schlabach A. J., Weissbach A. Covalent attachment of nucleic acids to agarose for affinity chromatography. Biochemistry. 1971 Feb 2;10(3):424–427. doi: 10.1021/bi00779a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Multiple forms of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in eukaryotic organisms. Nature. 1969 Oct 18;224(5216):234–237. doi: 10.1038/224234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Specific nucleolar and nucleoplasmic RNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):675–682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]