Abstract
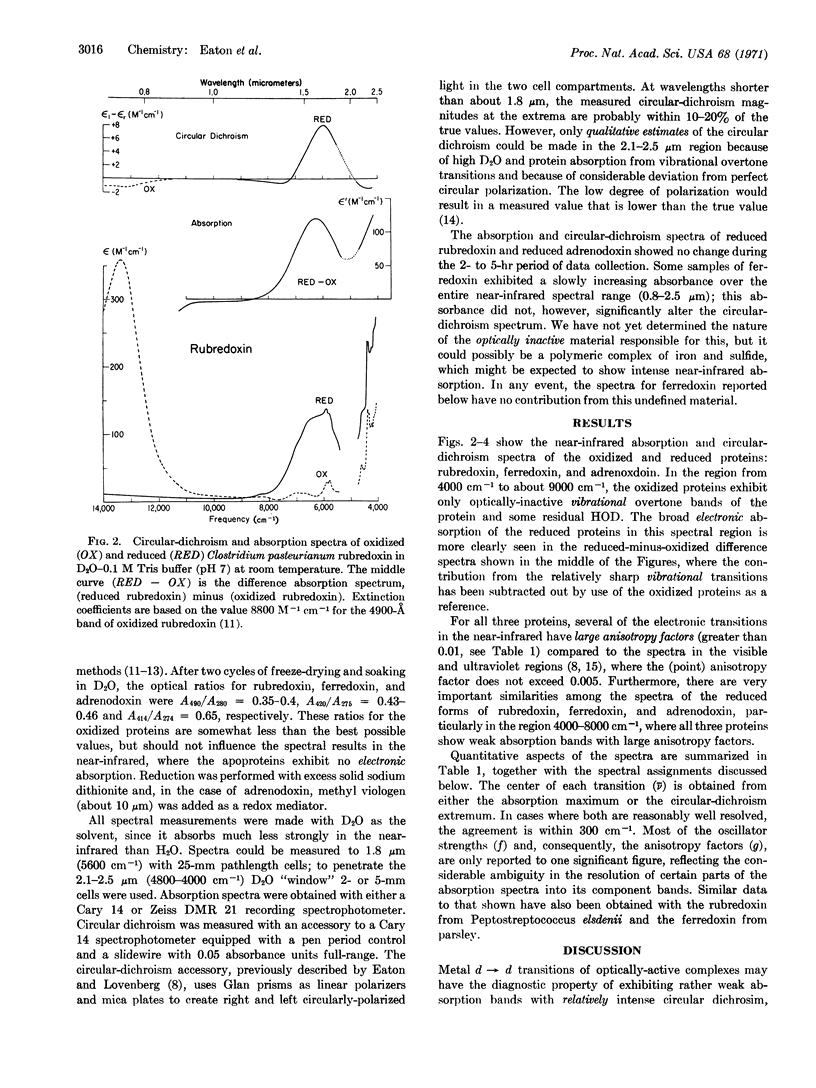
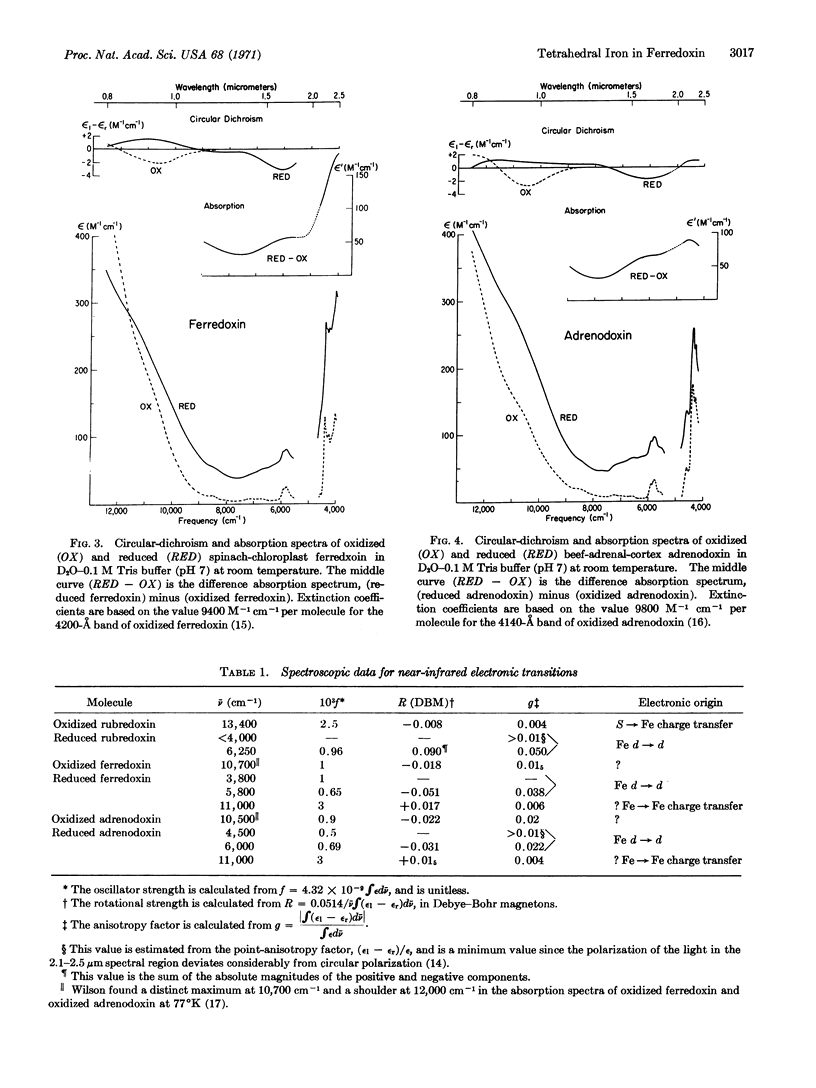
The coordination structure of the iron-sulfur complex in spinach ferredoxin and adrenodoxin is investigated by optical spectroscopy. The circular-dichroism and absorption spectra of these two-iron iron-sulfur proteins reveal weak electronic transitions in the near-infrared wavelength range, 0.8-2.5 μm (12,500-4000 cm-1). On the basis of the low absorption intensities and large anisotropy factors, d → d transitions of the iron can be identified in the reduced proteins at about 4000 cm-1 and 6000 cm-1. The low energy of these one-center ligand-field transitions, together with the similarity to the ligand-field spectrum of the one-iron protein rubredoxin, leads to the conclusion that the reduced two-iron iron-sulfur proteins also contain a high-spin ferrous ion in a distorted tetrahedral site.
Keywords: iron-sulfur proteins, rubredoxin, near-infrared circular dichroism, ligand-field spectrum, EPR
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brintzinger H., Palmer G., Sands R. H. On the ligand field of iron in ferredoxin from spinach chloroplasts and related nonheme iron enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Feb;55(2):397–404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.2.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton W. A., Charney E. Near-infrared absorption and circular dichroism spectra of ferrocytochrome c: d-d transitions. J Chem Phys. 1969 Nov 15;51(10):4502–4505. doi: 10.1063/1.1671818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton W. A., Lovenberg W. Near-infrared circular dichroism of an iron-sulfur protein. D leads to d transitions in rubredoxin. J Am Chem Soc. 1970 Dec 2;92(24):7195–7198. doi: 10.1021/ja00727a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fee J. A., Palmer G. The properties of parsley ferredoxin and its selenium-containing homolog. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 6;245(1):175–195. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90020-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson J. F., Hall D. O., Thornley J. H., Whatley F. R. The iron complex in spinach ferredoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):987–990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herriott J. R., Sieker L. C., Jensen L. H., Lovenberg W. Structure of rubredoxin: an x-ray study to 2.5 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jun 14;50(2):391–406. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90200-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura T., Huang J. J. Studies on adrenal steroid hydroxylases: optical absorption spectroscopy of adrenal iron-sulfur protein (adrenodoxin) and its apoprotein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Apr;137(2):357–364. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90449-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovenberg W., Williams W. M. Further observations on the chemical nature of rubredoxin from Clostridium pasteurianum. Biochemistry. 1969 Jan;8(1):141–148. doi: 10.1021/bi00829a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer G., Brintzinger H., Estabrook R. W. Spectroscopic studies on spinach ferredoxin and adrenodoxin. Biochemistry. 1967 Jun;6(6):1658–1664. doi: 10.1021/bi00858a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer G., Dunham W. R., Fee J. A., Sands R. H., Iizuka T., Yonetani T. The magnetic susceptibility of spinach ferredoxin from 77-250 degrees K: a measurement of the antiferromagnetic coupling between the two iron atoms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 6;245(1):201–207. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(71)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer G., Sands R. H. On the magnetic resonance of spinach ferredoxin. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 10;241(1):253–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petering D. H., Palmer G. Properties of spinach ferredoxin in anaerobic urea solution: a comparison with the native protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Dec;141(2):456–464. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips W. D., Poe M., Weiher J. F., McDonald C. C., Lovenberg W. Proton magnetic resonance, magnetic susceptibility and Mössbauer studies of Clostridium pasteurianum rubredoxin. Nature. 1970 Aug 8;227(5258):574–577. doi: 10.1038/227574a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watari H., Kimura T. Study of the adrenal non-heme iron protein (adrenodoxin) by electron spin resonance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jul 6;24(1):106–112. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90417-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. F. The near infra-red electronic spectra of non-heme iron proteins at minus 196 degrees. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Oct;122(1):254–256. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



