Abstract
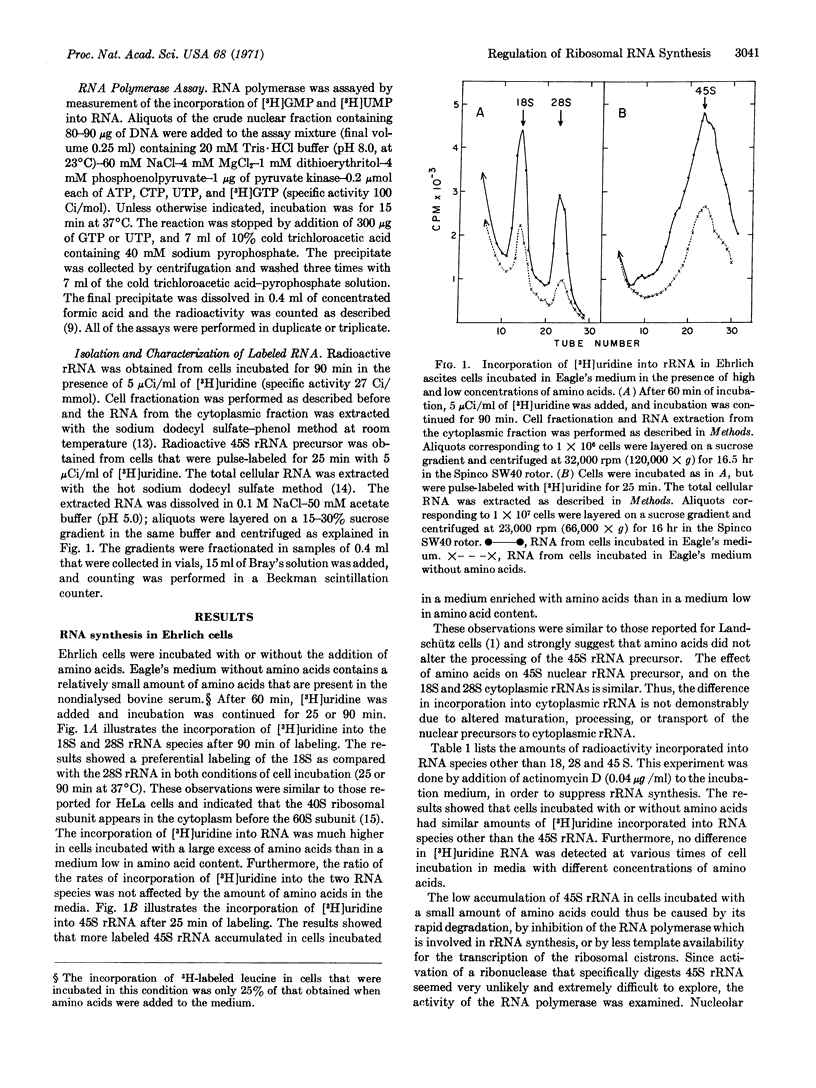
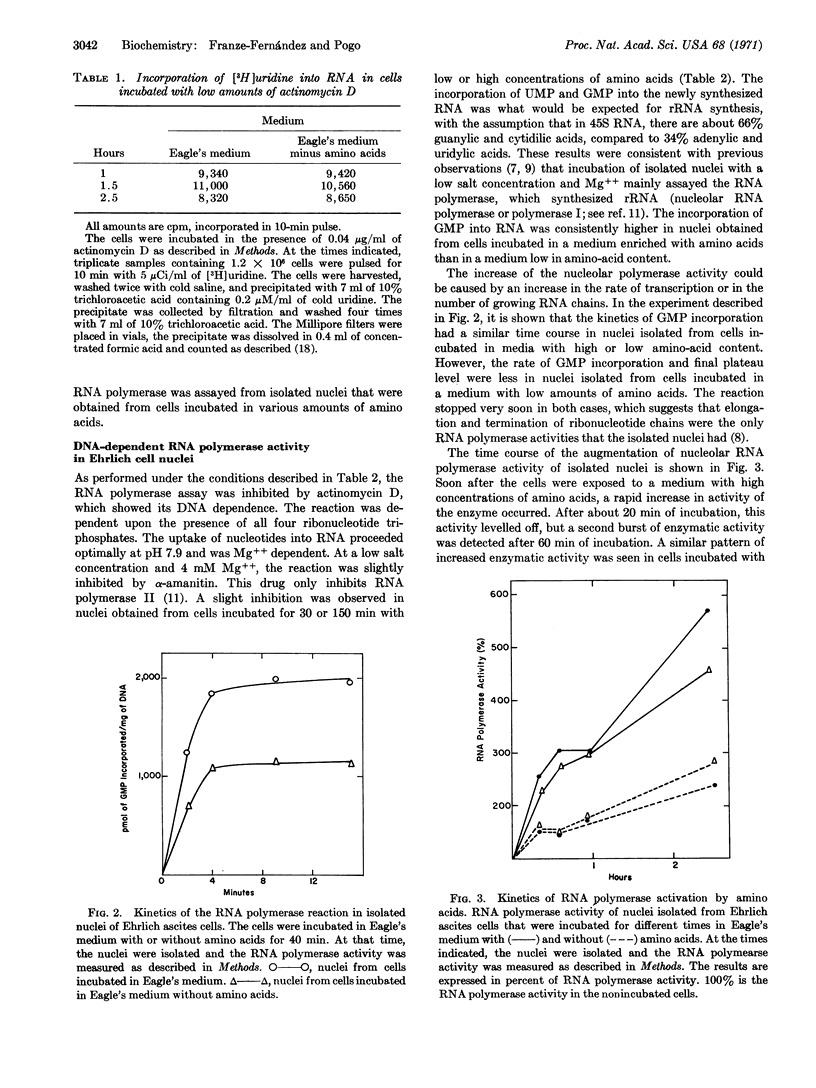
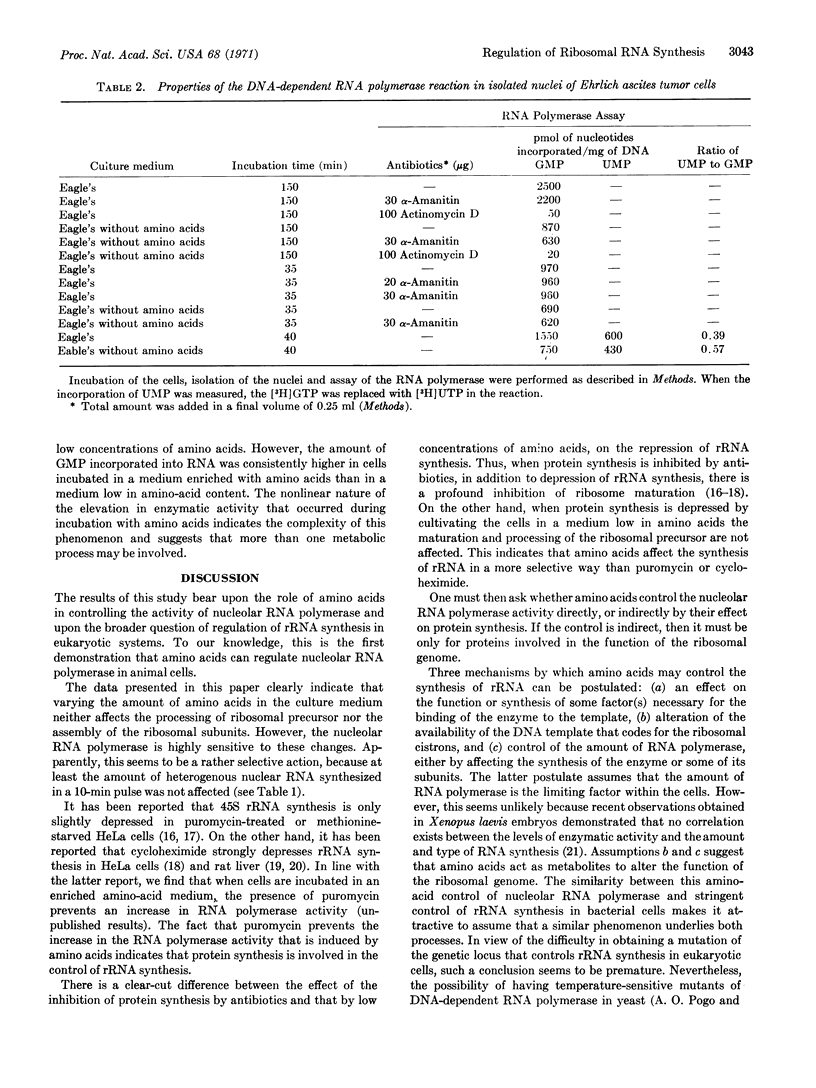
Experiments were performed to ascertain the degree to which the amount of amino acids might be one of the regulatory factors that control the activity of the nucleolar RNA polymerase. Assays of the enzymatic activity were done with isolated nuclei from cells incubated with low and high concentrations of amino acids. Soon after the cells were exposed to a medium enriched in amino acids, a rapid increase of nucleolar RNA polymerase activity occurred. A similar result was obtained in cells incubated with lower concentrations of amino acids. However, the rate of ribosomal RNA synthesized was regularly much higher in cells incubated in a medium enriched with amino acids than in a medium low in amino acids. Apparently, the amino acids only controlled ribosomal RNA synthesis. Thus, neither maturation, processing, and transport of nuclear precursors into cytoplasmic ribosomal RNA, nor the synthesis of rapidly labeled RNA was affected.
Keywords: nuclear ribosomal RNA precursor, cytoplasmic ribosomal RNA, nuclear rapidly labeled RNA
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Darnell J. E., Jr Ribonucleic acids from animal cells. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Sep;32(3):262–290. doi: 10.1128/br.32.3.262-290.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faiferman I., Hamilton M. G., Pogo A. O. Nucleoplasmic ribonucleoprotein particles of rat liver. I. Selective degradation by nuclear nucleases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Apr 15;204(2):550–563. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi K., Matsuhisa T., Kitao A., Sakamoto Y. Selective suppression of nucleolar RNA metabolism in the absence of protein synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 24;166(2):388–393. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90226-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindell T. J., Weinberg F., Morris P. W., Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Specific inhibition of nuclear RNA polymerase II by alpha-amanitin. Science. 1970 Oct 23;170(3956):447–449. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3956.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden B. E., Vaughan M. H., Warner J. R., Darnell J. E. Effects of valine deprivation on ribosome formation in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1969 Oct 28;45(2):265–275. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90104-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maul G. G., Hamilton T. H. The intranuclear localization of two DNA-dependent RNA polymerase activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1371–1378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu M., Shimada N., Higashinakagawa T. Effect of cycloheximide on the nucleolar RNA synthesis in rat liver. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):91–106. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90047-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogo A. O., Littau V. C., Allfrey V. G., Mirsky A. E. Modification of ribonucleic Acid synthesis in nuclei isolated from normal and regenerating liver: some effects of salt and specific divalent cations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Mar;57(3):743–750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.3.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pogo A. O. Modification of ribonucleic acid synthesis in isolated rat liver nuclei by low alt concentrations and specific divalent cations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 May 20;182(1):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90520-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeder R. G., Rutter W. J. Specific nucleolar and nucleoplasmic RNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Mar;65(3):675–682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.3.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields R., Korner A. Regulation of mammalian ribosome synthesis by amino acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Apr 15;204(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90172-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smulson M. Amino acid deprivation of human cells: effects on RNA synthesis, RNA polymerase, and ribonucleoside phosphorylation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 18;199(2):537–540. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan M. H., Jr, Soeiro R., Warner J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr The effects of methionine deprivation on ribosome synthesis in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1527–1534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R., Girard M., Latham H., Darnell J. E. Ribosome formation in HeLa cells in the absence of protein synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(2):373–382. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R., Soeiro R., Birnboim H. C., Girard M., Darnell J. E. Rapidly labeled HeLa cell nuclear RNA. I. Identification by zone sedimentation of a heterogeneous fraction separate from ribosomal precursor RNA. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(2):349–361. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R. The assembly of ribosomes in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(2):383–398. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widnell C. C., Tata J. R. Studies on the stimulation by ammonium sulphate of the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of isolated rat-liver nuclei. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Sep;123(3):478–492. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90216-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems M., Penman M., Penman S. The regulation of RNA synthesis and processing in the nucleolus during inhibition of protein synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1969 Apr;41(1):177–187. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



