Abstract
Acquisition of acetylcholine receptors during differentiation of a clonal myoblast cell line was monitored with a neurotoxin isolated from venom of the Indian Cobra Naja naja. Toxin bound specifically and reversibly to acetylcholine receptors of the differentiated cells. Specificity of the binding reaction was assayed by measurement of the ability of various cholinergic agonists and antagonists to compete with neurotoxin for its binding site. The rate of toxin binding paralleled the rate of inactivation of functional acetylcholine receptors, as measured by iontophoretic application of acetylcholine. Bound toxin was released from the cells with a half-life of about 7 hr. This release was not associated with a decrease in the total number of toxin-binding sites. A slow hyperpolarizing response to acetylcholine seen in myoblasts was insensitive to toxin; the appearance of toxin-binding sites parallels the appearance of fused fibers during differentiation of the muscle cells in tissue culture.
Keywords: snake venom, hyperpolarizing response, neurotoxin
Full text
PDF
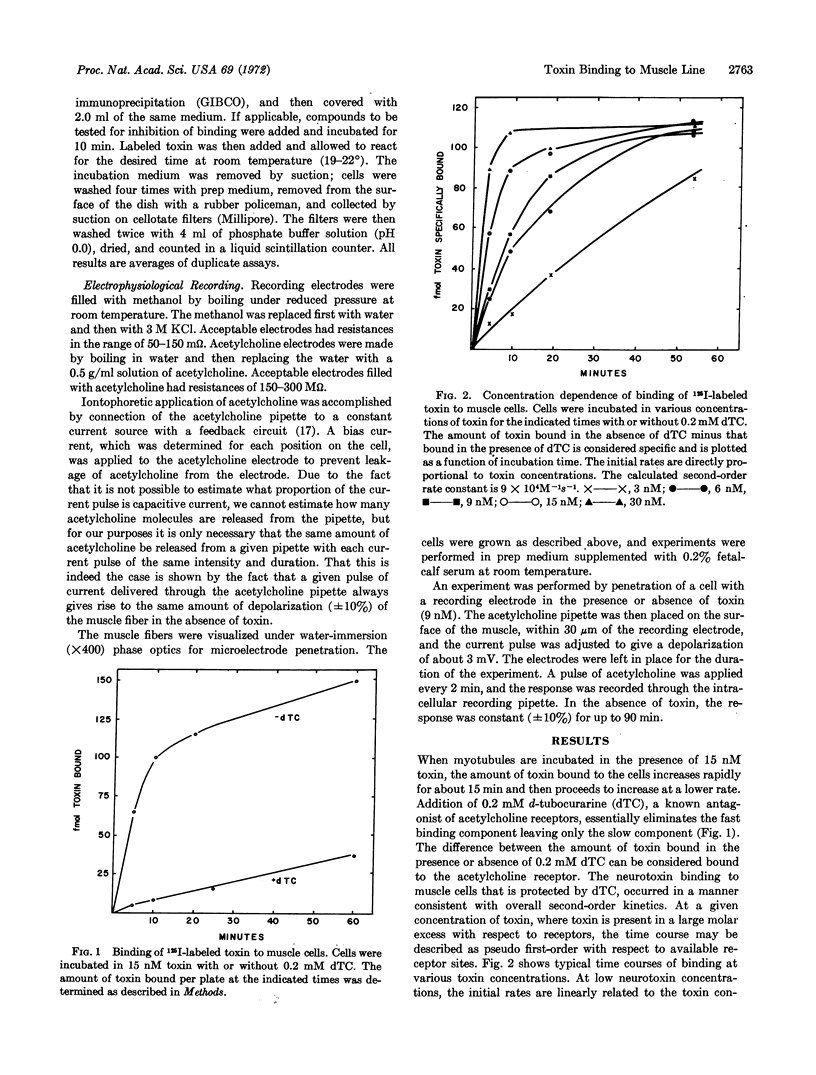
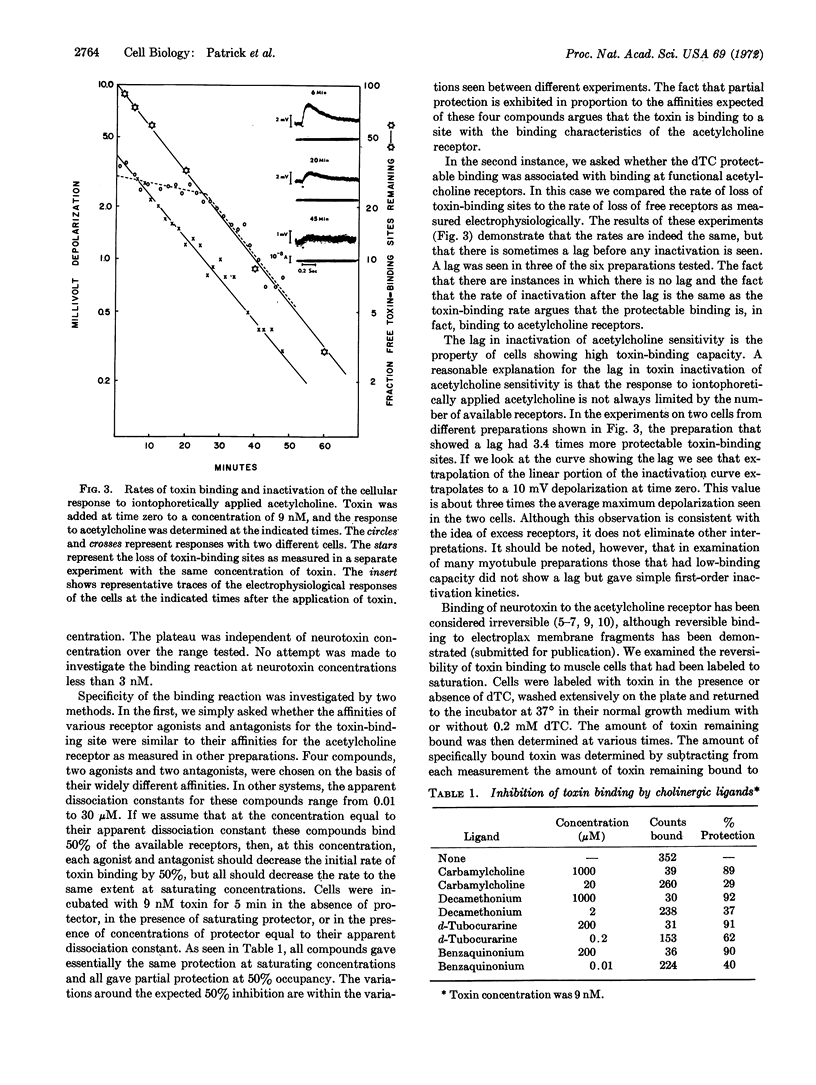
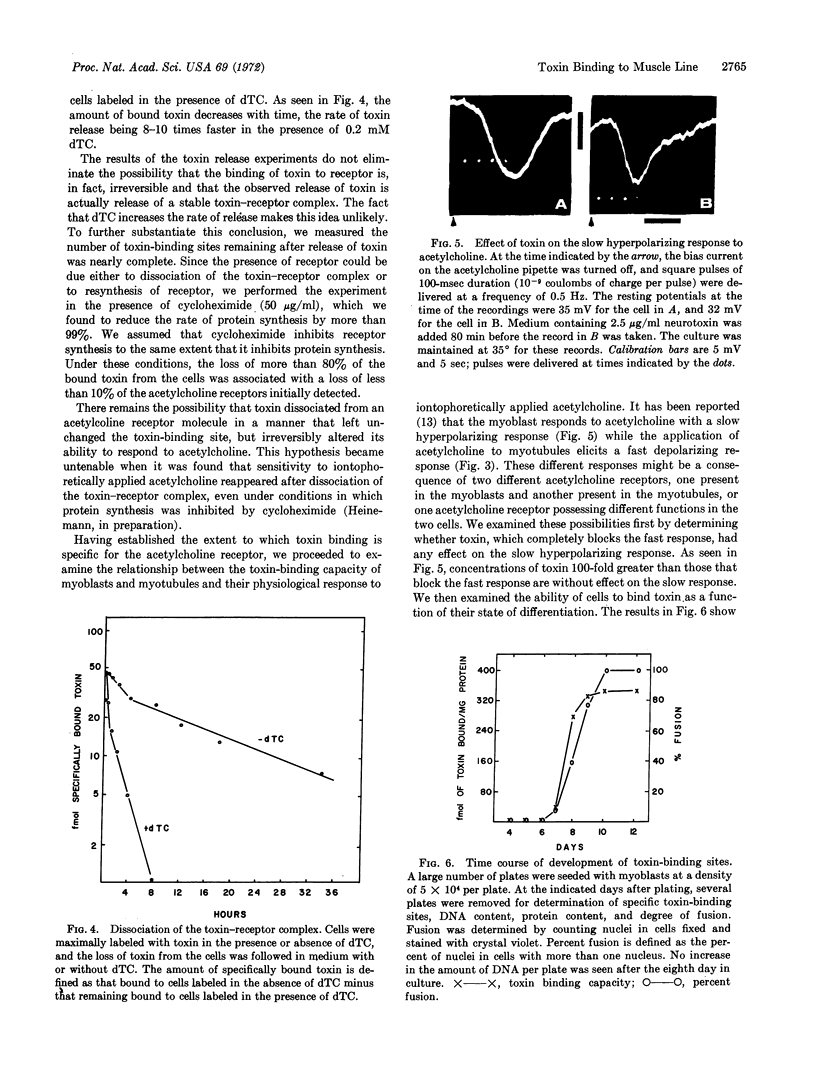

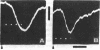
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnard E. A., Wieckowski J., Chiu T. H. Cholinergic receptor molecules and cholinesterase molecules at mouse skeletal muscle junctions. Nature. 1971 Nov 26;234(5326):207–209. doi: 10.1038/234207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosmann H. B. Acetylcholine receptor. I. Identification and biochemical characteristics of a cholinergic receptor of guinea pig cerebral cortex. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jan 10;247(1):130–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Kasai M., Lee C. Y. Use of a snake venom toxin to characterize the cholinergic receptor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1241–1247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M., Hartzell H. C. Acetylcholine receptors: number and distribution at neuromuscular junctions in rat diaphragm. Science. 1972 Apr 14;176(4031):189–191. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4031.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guth L. "Trophic" influences of nerve on muscle. Physiol Rev. 1968 Oct;48(4):645–687. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.4.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. J., Heinemann S., Schubert D., Tarakis H. Trophic interaction between cloned tissue culture lines of nerve and muscle. Nature. 1971 Jun 4;231(5301):296–301. doi: 10.1038/231296a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson E., Eaker D. L., Porath J. Purification of a neurotoxin from the venom of Naja nigricollis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Oct 31;127(2):505–520. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90404-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Chang C. C. Modes of actions of purified toxins from elapid venoms on neuromuscular transmission. Mem Inst Butantan. 1966;33(2):555–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILEDI R. Properties of regenerating neuromuscular synapses in the frog. J Physiol. 1960 Nov;154:190–205. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menez A., Morgat J. -L., Fromageot P., Ronseray A. -M., Boquet P., Changeux J. -P. Tritium labelling of the alpha-neurotoxin of Naja nigricollis. FEBS Lett. 1971 Oct 1;17(2):333–335. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier J. C., Olsen R. W., Menez A., Fromageot P., Boquet P., Changeux J. P. Some physical properties of the cholinergic receptor protein from Electrophorus electricus revealed by a tritiated alpha-toxin from Naja nigricollis venom. Biochemistry. 1972 Mar 28;11(7):1200–1210. doi: 10.1021/bi00757a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Molinoff P., Potter L. T. Isolation of the cholinergic receptor protein of Torpedo electric tissue. Nature. 1971 Feb 19;229(5286):554–557. doi: 10.1038/229554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Potter L. T. Acetylcholine receptors in muscle fibres. Nature. 1971 Oct 29;233(5322):599–603. doi: 10.1038/233599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima S., Onodera K. Membrane properties of the stretch receptor neurones of crayfish with particular reference to mechanisms of sensory adaptation. J Physiol. 1969 Jan;200(1):161–185. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGT M., DULBECCO R. Steps in the neoplastic transformation of hamster embryo cells by polyoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Feb 15;49:171–179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.2.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D. Retention of differentiation potentialities during prolonged cultivation of myogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):477–483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]