Abstract
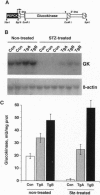
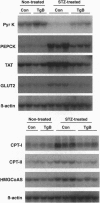
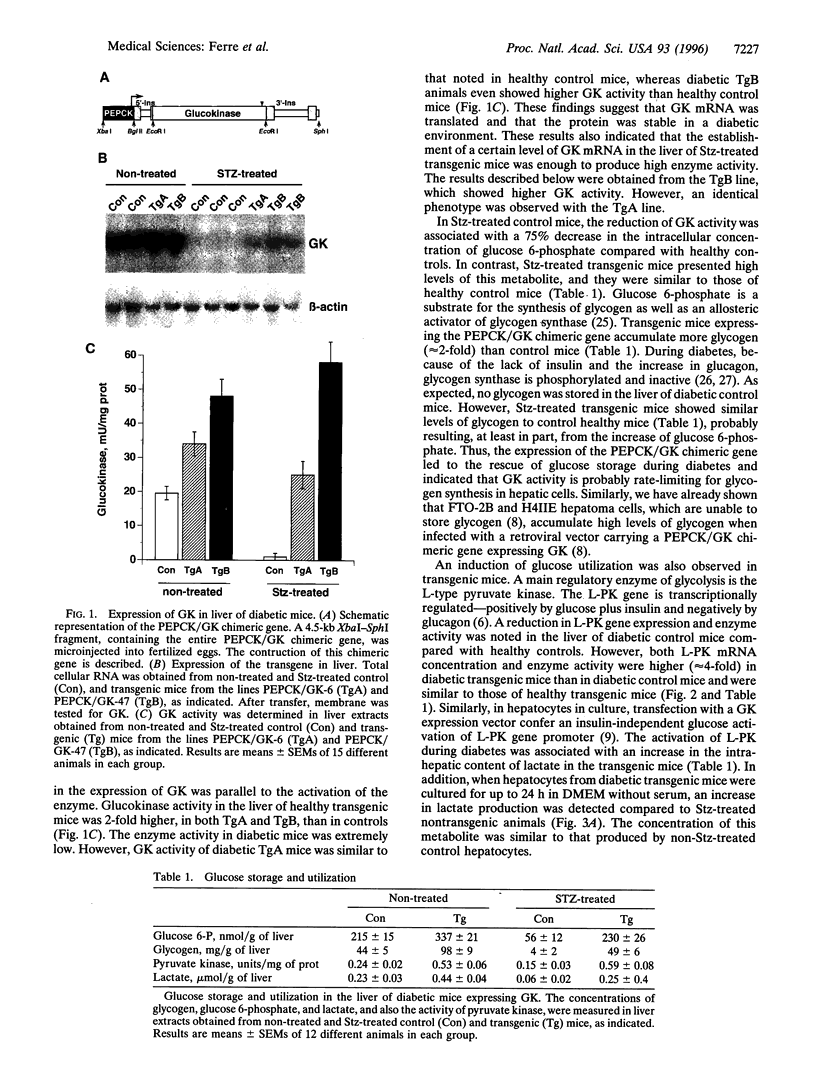
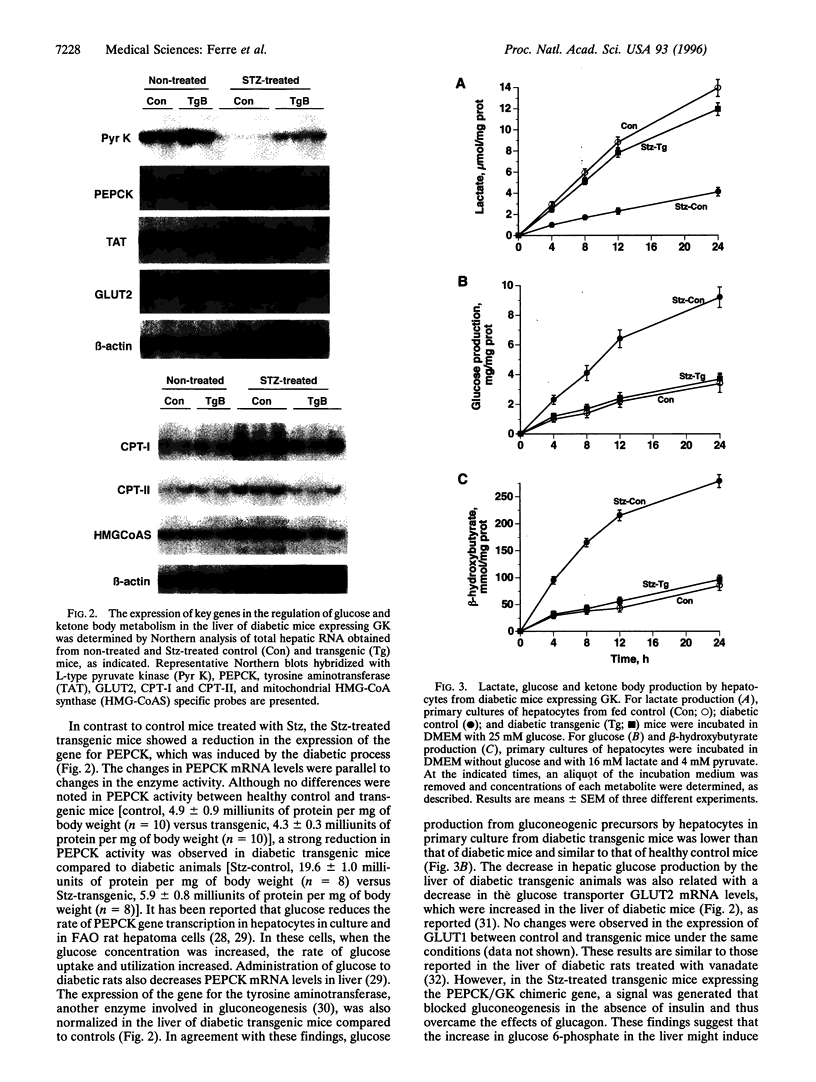
Hyperglycemia is a common feature of diabetes mellitus. It results from a decrease in glucose utilization by the liver and peripheral tissues and an increase in hepatic glucose production. Glucose phosphorylation by glucokinase is an initial event in glucose metabolism by the liver. However, glucokinase gene expression is very low in diabetic animals. Transgenic mice expressing the P-enolpyruvate carboxykinase/glucokinase chimeric gene were generated to study whether the return of the expression of glucokinase in the liver of diabetic mice might prevent metabolic alterations. In contrast to nontransgenic mice treated with streptozotocin, mice with the transgene previously treated with streptozotocin showed high levels of both glucokinase mRNA and its enzyme activity in the liver, which were associated with an increase in intracellular levels of glucose 6-phosphate and glycogen. The liver of these mice also showed an increase in pyruvate kinase activity and lactate production. Furthermore, normalization of both the expression of genes involved in gluconeogenesis and ketogenesis in the liver and the production of glucose and ketone body by hepatocytes in primary culture were observed in streptozotocin-treated transgenic mice. Thus, glycolysis was induced while gluconeogenesis and ketogenesis were blocked in the liver of diabetic mice expressing glucokinase. This was associated with normalization of blood glucose, ketone bodies, triglycerides, and free fatty acids even in the absence of insulin. These results suggest that the expression of glucokinase during diabetes might be a new approach to the normalization of hyperglycemia.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelrod J. D., Pilch P. F. Unique cytochalasin B binding characteristics of the hepatic glucose carrier. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 26;22(9):2222–2227. doi: 10.1021/bi00278a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Burant C. F., Takeda J., Gould G. W. Structure and function of mammalian facilitative sugar transporters. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19161–19164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casals N., Roca N., Guerrero M., Gil-Gómez G., Ayté J., Ciudad C. J., Hegardt F. G. Regulation of the expression of the mitochondrial 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase gene. Its role in the control of ketogenesis. Biochem J. 1992 Apr 1;283(Pt 1):261–264. doi: 10.1042/bj2830261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. C., Lane M. D. The enzymatic carboxylation of phosphoenolpyruvate. II. Purification and properties of liver mitochondrial phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2413–2420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson A. L., Arion W. J. Factors underlying significant underestimations of glucokinase activity in crude liver extracts: physiological implications of higher cellular activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Feb 15;253(1):156–167. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90648-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decaux J. F., Marcillat O., Pichard A. L., Henry J., Kahn A. Glucose-dependent and -independent effect of insulin on gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3432–3438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doiron B., Cuif M. H., Kahn A., Diaz-Guerra M. J. Respective roles of glucose, fructose, and insulin in the regulation of the liver-specific pyruvate kinase gene promoter. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10213–10216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esser V., Britton C. H., Weis B. C., Foster D. W., McGarry J. D. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of a cDNA encoding rat liver carnitine palmitoyltransferase I. Direct evidence that a single polypeptide is involved in inhibitor interaction and catalytic function. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5817–5822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felíu J. E., Hue L., Hers H. G. Regulation in vitro and in vivo of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent inactivation of rat-liver pyruvate kinase type L. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Dec;81(3):609–617. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto S., Schmid W., Schütz G. Transcriptional activation of the rat liver tyrosine aminotransferase gene by cAMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6637–6641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iynedjian P. B. Mammalian glucokinase and its gene. Biochem J. 1993 Jul 1;293(Pt 1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2930001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Lauris V., Koch S., Crettaz M., Granner D. K. Acute and chronic regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase mRNA by insulin and glucose. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 May;3(5):840–845. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-5-840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner J. Insulin and the stimulation of glycogen synthesis. The road from glycogen structure to glycogen synthase to cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase to insulin mediators. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1990;63:173–231. doi: 10.1002/9780470123096.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Cam A., Guillouzo A., Freychet P. Ultrastructual and biochemical studies of isolated adult rat hepatocytes prepared under hypoxic conditions. Cryopreservation of hepatocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Mar 15;98(2):382–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90448-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J. S., Park E. A., Gurney A. L., Roesler W. J., Hanson R. W. Cyclic AMP induction of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) gene transcription is mediated by multiple promoter elements. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):19095–19102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGarry J. D., Foster D. W. Regulation of hepatic fatty acid oxidation and ketone body production. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:395–420. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGarry J. D. What if Minkowski had been ageusic? An alternative angle on diabetes. Science. 1992 Oct 30;258(5083):766–770. doi: 10.1126/science.1439783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrane M. M., Yun J. S., Moorman A. F., Lamers W. H., Hendrick G. K., Arafah B. M., Park E. A., Wagner T. E., Hanson R. W. Metabolic effects of developmental, tissue-, and cell-specific expression of a chimeric phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP)/bovine growth hormone gene in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22371–22379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer S., Höppner W., Seitz H. J. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional effects of glucose on liver phosphoenolpyruvate-carboxykinase gene expression. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Dec 18;202(3):985–991. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16460.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. M., Lucas P. C., Forest C. D., Magnuson M. A., Granner D. K. Identification of a sequence in the PEPCK gene that mediates a negative effect of insulin on transcription. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):533–537. doi: 10.1126/science.2166335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka Y., Asano T., Shibasaki Y., Lin J. L., Tsukuda K., Akanuma Y., Takaku F. Increased liver glucose-transporter protein and mRNA in streptozocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1990 Apr;39(4):441–446. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.4.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilkis S. J., Granner D. K. Molecular physiology of the regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis and glycolysis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:885–909. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.004321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Printz R. L., Magnuson M. A., Granner D. K. Mammalian glucokinase. Annu Rev Nutr. 1993;13:463–496. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.13.070193.002335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Gil J. E., Gómez-Foix A. M., Ariño J., Guinovart J. J., Bosch F. Control of glycogen synthase and phosphorylase in hepatocytes from diabetic rats. Effects of glucagon, vasopressin, and vanadate. Diabetes. 1989 Jun;38(6):793–798. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.6.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short M. K., Clouthier D. E., Schaefer I. M., Hammer R. E., Magnuson M. A., Beale E. G. Tissue-specific, developmental, hormonal, and dietary regulation of rat phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase-human growth hormone fusion genes in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1007–1020. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R., Agius L. The biochemistry of diabetes. Biochem J. 1988 Mar 15;250(3):625–640. doi: 10.1042/bj2500625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valera A., Bosch F. Glucokinase expression in rat hepatoma cells induces glucose uptake and is rate limiting in glucose utilization. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Jun 1;222(2):533–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18895.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valera A., Fillat C., Costa C., Sabater J., Visa J., Pujol A., Bosch F. Regulated expression of human insulin in the liver of transgenic mice corrects diabetic alterations. FASEB J. 1994 Apr 1;8(6):440–447. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.6.8168695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valera A., Pelegrin M., Asins G., Fillat C., Sabater J., Pujol A., Hegardt F. G., Bosch F. Overexpression of mitochondrial 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA synthase in transgenic mice causes hepatic hyperketogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6267–6270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valera A., Pujol A., Gregori X., Riu E., Visa J., Bosch F. Evidence from transgenic mice that myc regulates hepatic glycolysis. FASEB J. 1995 Aug;9(11):1067–1078. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.9.11.7649406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valera A., Rodriguez-Gil J. E., Bosch F. Vanadate treatment restores the expression of genes for key enzymes in the glucose and ketone bodies metabolism in the liver of diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jul;92(1):4–11. doi: 10.1172/JCI116580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaulont S., Kahn A. Transcriptional control of metabolic regulation genes by carbohydrates. FASEB J. 1994 Jan;8(1):28–35. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.1.8299888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woeltje K. F., Esser V., Weis B. C., Cox W. F., Schroeder J. G., Liao S. T., Foster D. W., McGarry J. D. Inter-tissue and inter-species characteristics of the mitochondrial carnitine palmitoyltransferase enzyme system. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10714–10719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]