Abstract
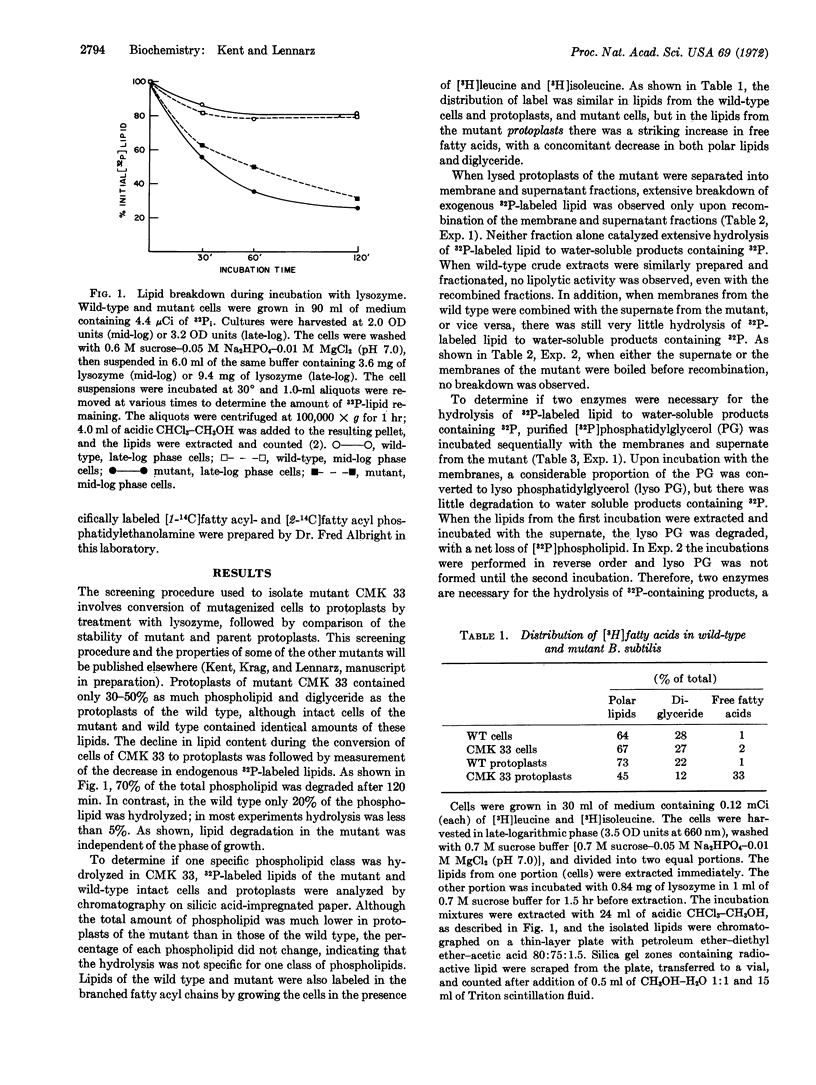
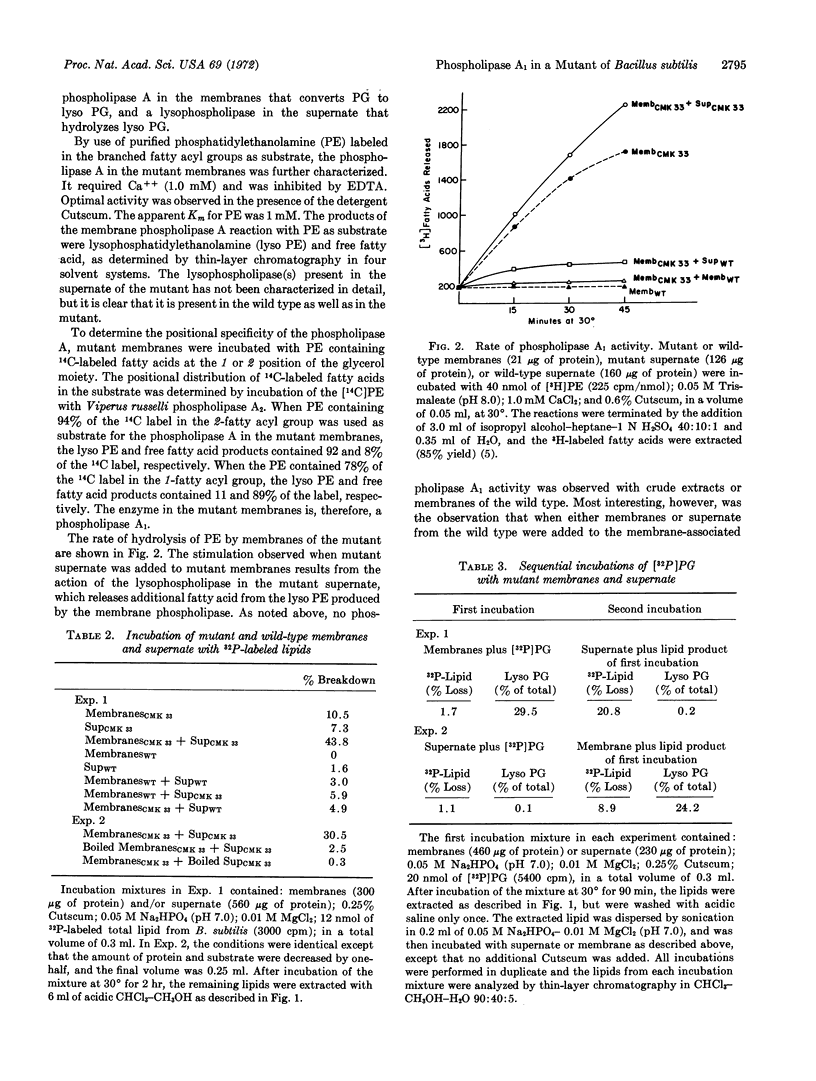
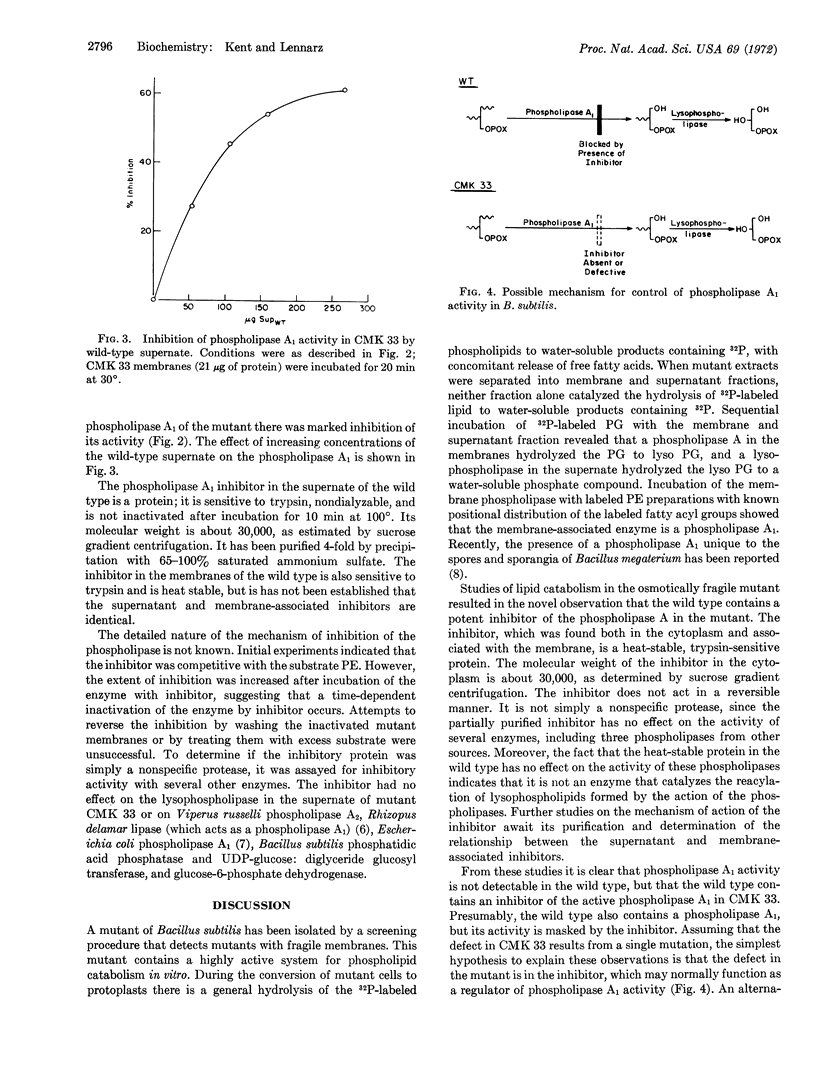
By use of a newly developed procedure for the isolation of mutants with osmotically fragile protoplasts, a mutant of Bacillus subtilis was isolated that has a very active enzyme system for the catabolism of phospholipids via the sequential action of a phospholipase A1 (EC 3.1.1.4) and a lysophospholipase (EC 3.1.1.5). The wild-type bacteria contain no detectable phospholipase A1 activity, but do contain a protein that specifically inhibits the phospholipase A1 in the mutant. This protein may play an important role in the control of phospholipid catabolism.
Keywords: protoplasts, lysophospholipase, phospholipase A1 inhibitor
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gould R. M., Lennarz W. J. Metabolism of Phosphatidylglycerol and Lysyl Phosphatidylglycerol in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1135–1144. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1135-1144.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raybin D. M., Bertsch L. L., Kornberg A. A phospholipase in Bacillus megaterium unique to spores and sporangia. Biochemistry. 1972 May 9;11(10):1754–1760. doi: 10.1021/bi00760a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scandella C. J., Kornberg A. A membrane-bound phospholipase A1 purified from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov 23;10(24):4447–4456. doi: 10.1021/bi00800a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipski V. P., Peterson R. F., Barclay M. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids by thin-layer chromatography. Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):374–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0900374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOSHIKAWA H., SUEOKA N. Sequential replication of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. II. Isotopic transfer experiments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jun;49:806–813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.6.806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



