Abstract
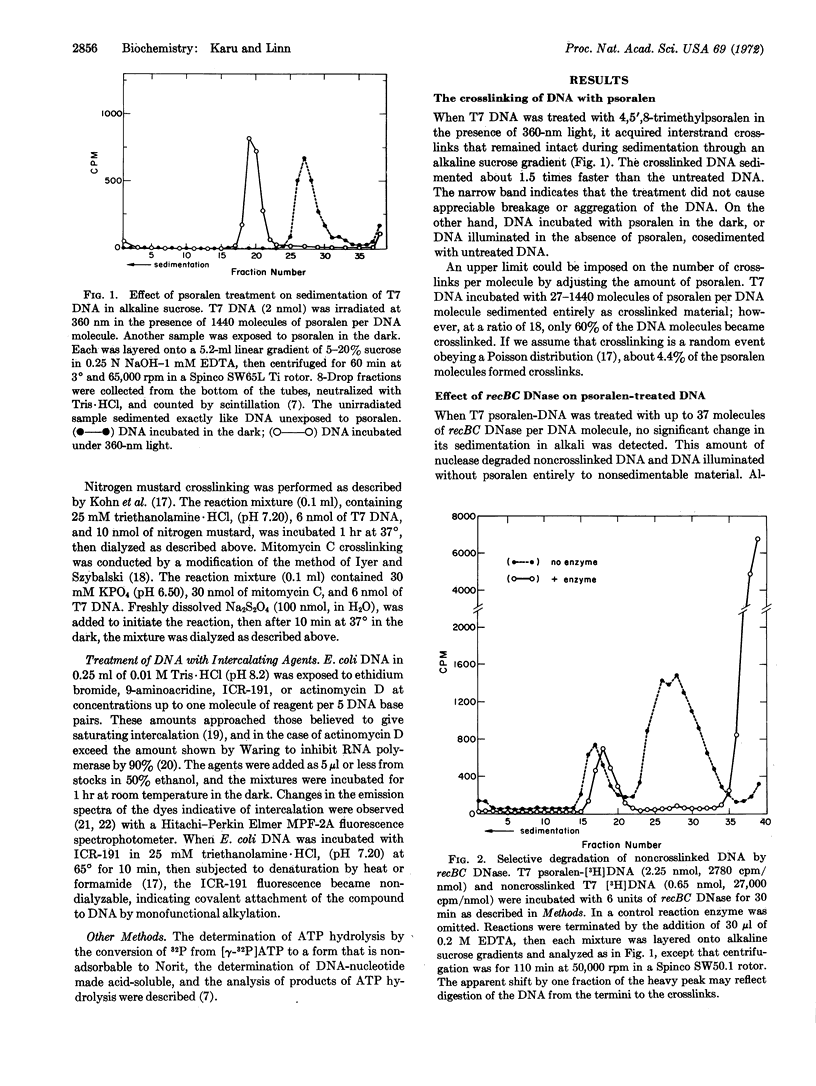
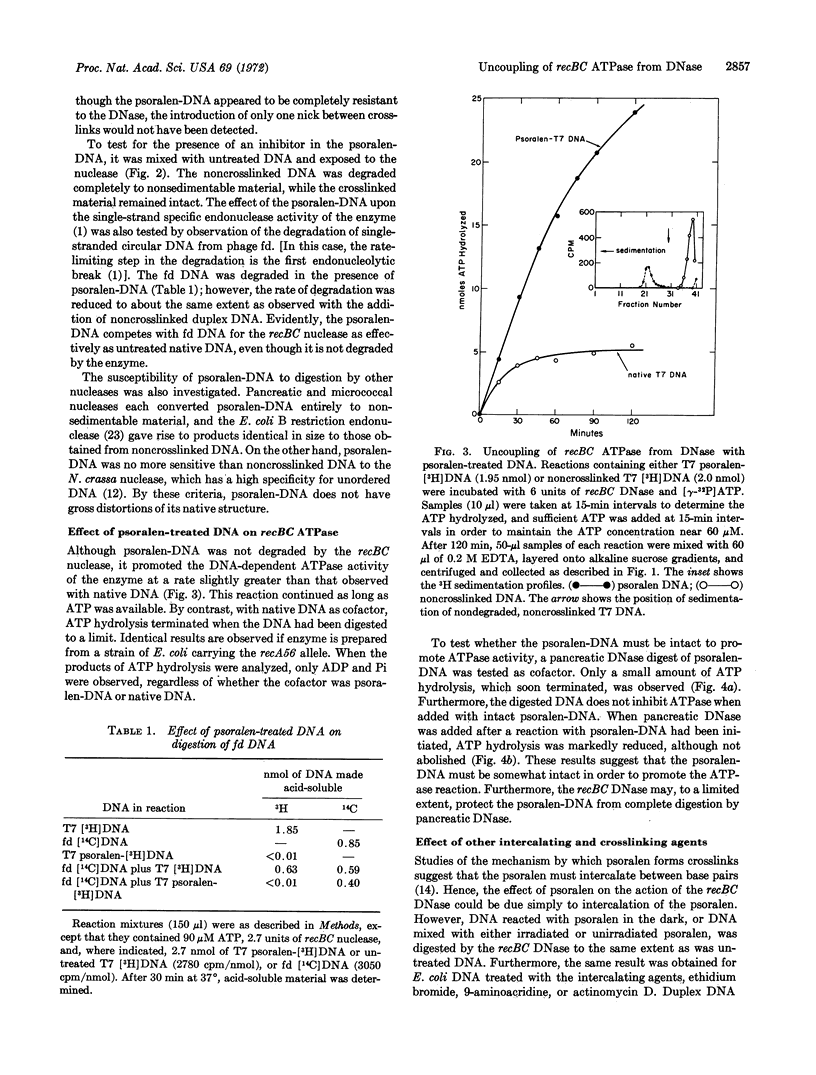
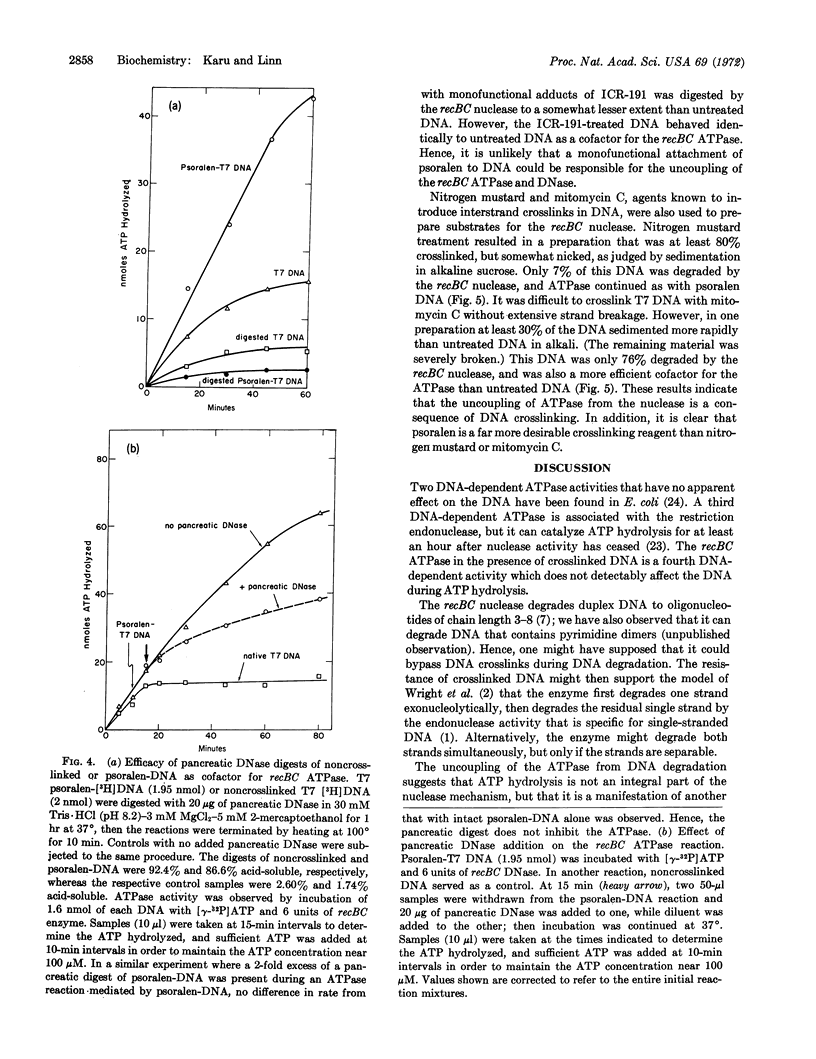
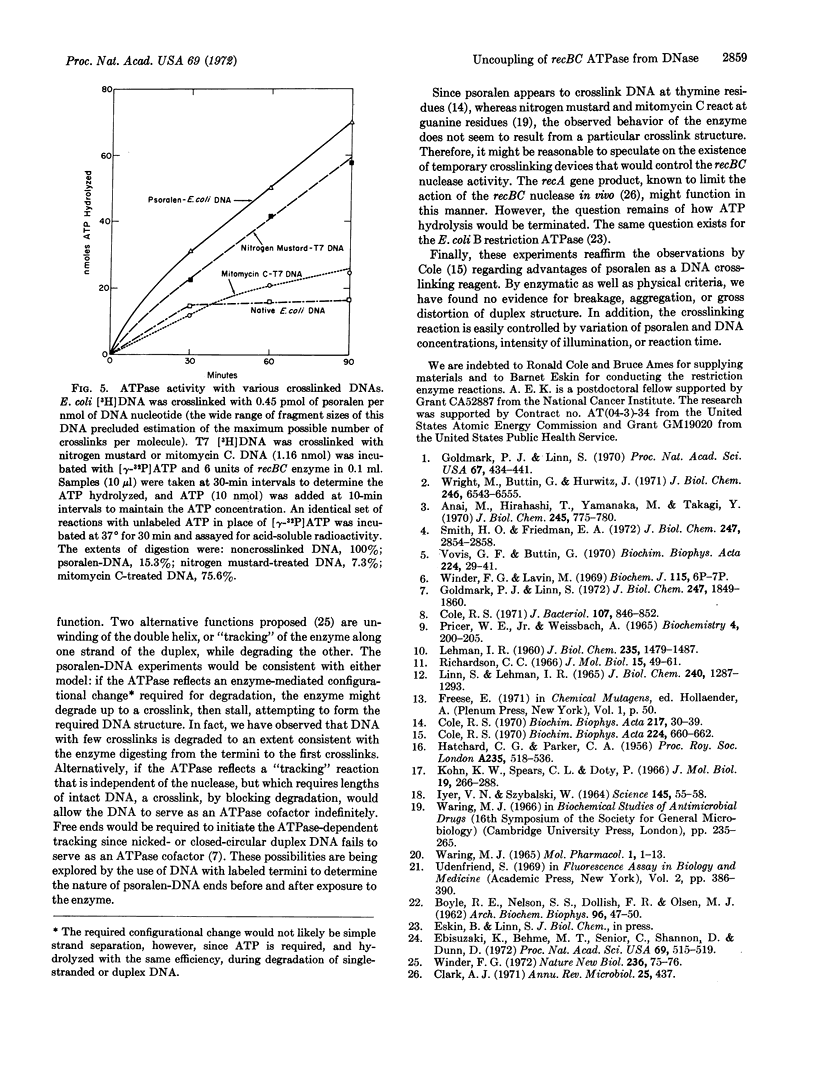
Exonucleolytic cleavage of DNA by the recBC DNase is accompained by a DNA-dependent ATP hydrolysis that ceases when the DNA that has been digested to a limit. On the other hand, DNA that has been crosslinked by 4,5′,8-trimethylpsoralen in the presence of 360-nm light remains an effective cofactor in the ATPase reaction, but is resistant to digestion by the enzyme. Psoralentreated DNA is degraded by pancreatic DNase, micrococcal nuclease, and Escherichia coli B restriction enzyme, but not by Neurospora crassa nuclease, suggesting that crosslinking did not grossly distort the duplex structure of the DNA. The psoralen-DNA is not a potent inhibitor, but competes with single-stranded DNA from bacteriophage fd for the recBC DNase to roughly the same extent as does normal duplex DNA. DNA treated with psoralen in the dark, exposed to 360-nm light in the absence of psoralen, or treated with the intercalating agents ethidium bromide, 9-aminoacridine, ICR-191, or actinomycin D, responds to the enzyme no differently from untreated DNA. However, DNA crosslinked with mitomycin C or nitrogen mustard behaves similarly to psoralen-treated DNA. The relationship of these findings to models for the function and control of the recBC ATPase and nuclease, and the advantages of psoralen as a DNA crosslinking agent, are discussed.
Keywords: DNA-dependent ATPase, DNA intercalating agents, exonuclease V, E. coli
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anai M., Hirahashi T., Yamanaka M., Takagi Y. A deoxyribonuclease which requires nucleoside triphosphate from Micrococcus lysodeikticus. II. Studies on the role of nucleoside triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1970 Feb 25;245(4):775–780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYLE R. E., NELSON S. S., DOLLISH F. R., OLSEN M. J. The interaction of deoxyribonucleic acid and acridine orange. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Jan;96:47–50. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(62)90448-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J. Toward a metabolic interpretation of genetic recombination of E. coli and its phages. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1971;25:437–464. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.25.100171.002253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole R. S. Inactivation of Escherichia coli, F' episomes at transfer, and bacteriophage lambda by psoralen plus 360-nm light: significance of deoxyribonucleic acid cross-links. J Bacteriol. 1971 Sep;107(3):846–852. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.3.846-852.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole R. S. Light-induced cross-linking of DNA in the presence of a furocoumarin (psoralen). Studies with phage lambda, Escherichia coli, and mouse leukemia cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 17;217(1):30–39. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole R. S., Zusman D. Sedimentation properties of phage DNA molecules containing light-induced psoralen cross-links. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 14;224(2):660–662. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90607-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebisuzaki K., Behme M. T., Senior C., Shannon D., Dunn D. An alternative approach to the study of new enzymatic reactions involving DNA (DNA-dependent ATPases-purification-properties-E. coli). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):515–519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldmark P. J., Linn S. An endonuclease activity from Escherichia coli absent from certain rec- strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):434–441. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldmark P. J., Linn S. Purification and properties of the recBC DNase of Escherichia coli K-12. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 25;247(6):1849–1860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IYER V. N., SZYBALSKI W. MITOMYCINS AND PORFIROMYCIN: CHEMICAL MECHANISM OF ACTIVATION AND CROSS-LINKING OF DNA. Science. 1964 Jul 3;145(3627):55–58. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3627.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn K. W., Spears C. L., Doty P. Inter-strand crosslinking of DNA by nitrogen mustard. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(2):266–288. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEHMAN I. R. The deoxyribonucleases of Escherichia coli. I. Purification and properties of a phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1960 May;235:1479–1487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINN S., LEHMAN I. R. AN ENDONUCLEASE FROM NEUROSPORA CRASSA SPECIFIC FOR POLYNUCLEOTIDES LACKING AN ORDERED STRUCTURE. I. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF THE ENZYME. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1287–1293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C. C. The 5'-terminal nucleotides of T7 bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jan;15(1):49–61. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80208-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Friedman E. A. An adenosine triphosphate-dependent deoxyribonuclease from Hemophilus influenzae Rd. II. Adenosine triphosphatase properties. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2854–2858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vovis G. F., Buttin G. An ATP-dependent deoxyribonuclease from diplococcus pneumoniae. I. Partial purification and some biochemical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 12;224(1):29–41. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90617-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring M. J. The effects of antimicrobial agents on ribonucleic acid polymerase. Mol Pharmacol. 1965 Jul;1(1):1–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winder F. G., Lavin M. The reaction catalysed by a partially prufied nucleoside triphosphate-dependent deoxyribonucleic acid-breakdown system from Mycobacterium smegmatis. Biochem J. 1969 Nov;115(3):6P–7P. doi: 10.1042/bj1150006pb. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winder F. G. Role of ATP in ATP-dependent deoxyribonuclease activity. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 22;236(64):75–76. doi: 10.1038/newbio236075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright M., Buttin G., Hurwitz J. The isolation and characterization from Escherichia coli of an adenosine triphosphate-dependent deoxyribonuclease directed by rec B, C genes. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov;246(21):6543–6555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


