Abstract
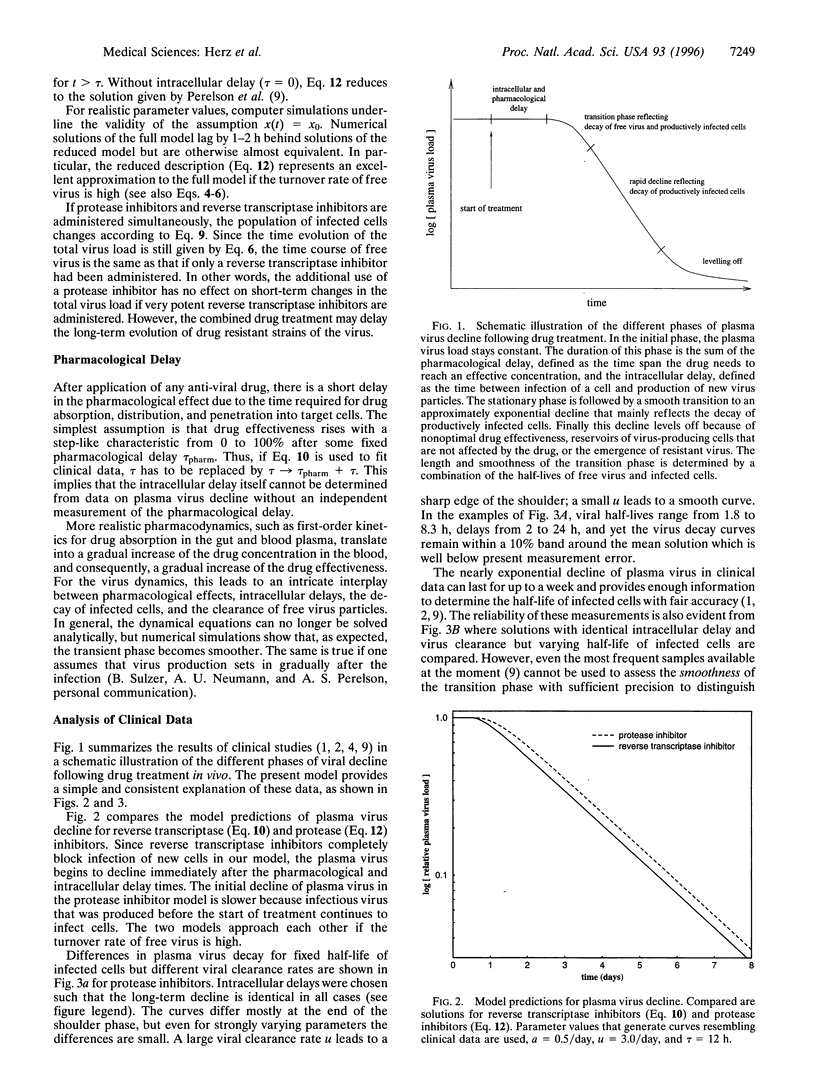
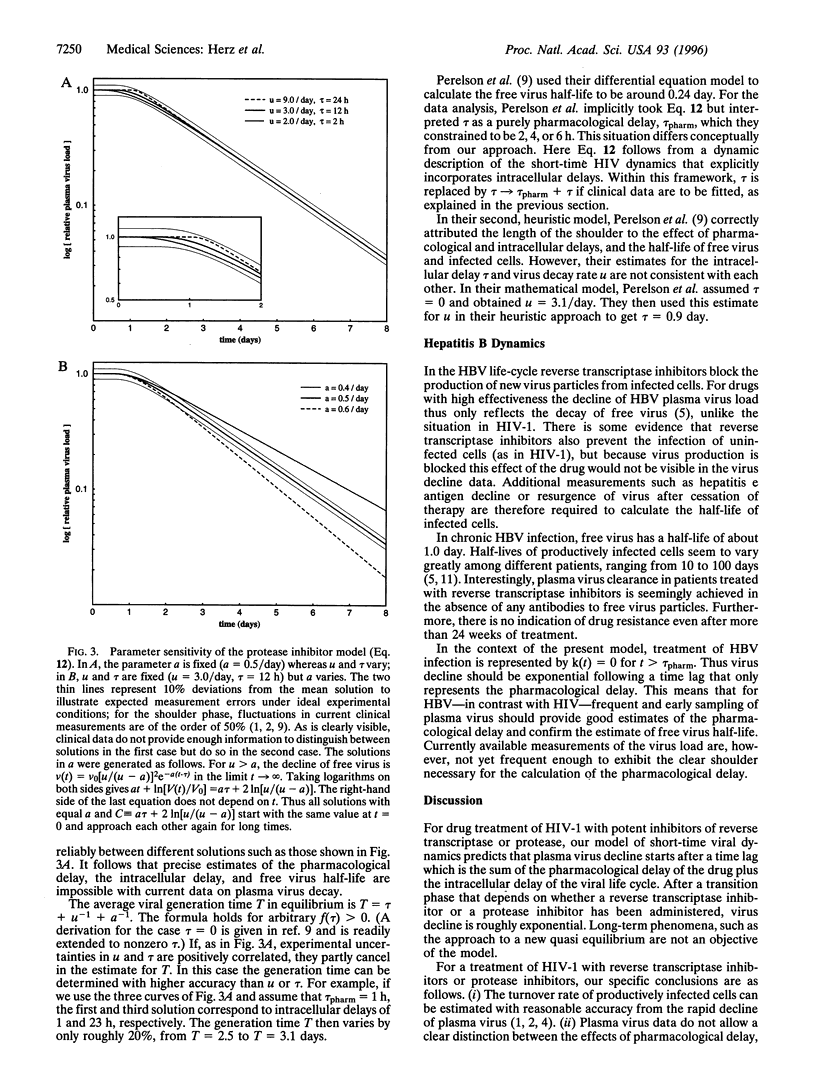
Anti-viral drug treatment of human immunodeficiency virus type I (HIV-1) and hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections causes rapid reduction in plasma virus load. Viral decline occurs in several phases and provides information on important kinetic constants of virus replication in vivo and pharmacodynamical properties. We develop a mathematical model that takes into account the intracellular phase of the viral life-cycle, defined as the time between infection of a cell and production of new virus particles. We derive analytic solutions for the dynamics following treatment with reverse transcriptase inhibitors, protease inhibitors, or a combination of both. For HIV-1, our results show that the phase of rapid decay in plasma virus (days 2-7) allows precise estimates for the turnover rate of productively infected cells. The initial quasi-stationary phase (days 0-1) and the transition phase (days 1-2) are explained by the combined effects of pharmacological and intracellular delays, the clearance of free virus particles, and the decay of infected cells. Reliable estimates of the first three quantities are not possible from data on virus load only; such estimates require additional measurements. In contrast with HIV-1, for HBV our model predicts that frequent early sampling of plasma virus will lead to reliable estimates of the free virus half-life and the pharmacological properties of the administered drug. On the other hand, for HBV the half-life of infected cells cannot be estimated from plasma virus decay.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coffin J. M. HIV population dynamics in vivo: implications for genetic variation, pathogenesis, and therapy. Science. 1995 Jan 27;267(5197):483–489. doi: 10.1126/science.7824947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Neumann A. U., Perelson A. S., Chen W., Leonard J. M., Markowitz M. Rapid turnover of plasma virions and CD4 lymphocytes in HIV-1 infection. Nature. 1995 Jan 12;373(6510):123–126. doi: 10.1038/373123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Darby G., Richman D. D. HIV with reduced sensitivity to zidovudine (AZT) isolated during prolonged therapy. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1731–1734. doi: 10.1126/science.2467383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchuk G. I., Petrov R. V., Romanyukha A. A., Bocharov G. A. Mathematical model of antiviral immune response. I. Data analysis, generalized picture construction and parameters evaluation for hepatitis B. J Theor Biol. 1991 Jul 7;151(1):1–40. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(05)80142-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean A. R., Nowak M. A. Competition between zidovudine-sensitive and zidovudine-resistant strains of HIV. AIDS. 1992 Jan;6(1):71–79. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199201000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean A. R., Nowak M. A. Models of interactions between HIV and other pathogens. J Theor Biol. 1992 Mar 7;155(1):69–86. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(05)80549-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak M. A., Anderson R. M., McLean A. R., Wolfs T. F., Goudsmit J., May R. M. Antigenic diversity thresholds and the development of AIDS. Science. 1991 Nov 15;254(5034):963–969. doi: 10.1126/science.1683006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak M. A., Bonhoeffer S., Hill A. M., Boehme R., Thomas H. C., McDade H. Viral dynamics in hepatitis B virus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Apr 30;93(9):4398–4402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.9.4398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak M. A., Bonhoeffer S., Loveday C., Balfe P., Semple M., Kaye S., Tenant-Flowers M., Tedder R. HIV results in the frame. Results confirmed. Nature. 1995 May 18;375(6528):193–193. doi: 10.1038/375193a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne R. J., Nowak M. A., Blumberg B. S. A cellular model to explain the pathogenesis of infection by the hepatitis B virus. Math Biosci. 1994 Sep;123(1):25–58. doi: 10.1016/0025-5564(94)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perelson A. S., Kirschner D. E., De Boer R. Dynamics of HIV infection of CD4+ T cells. Math Biosci. 1993 Mar;114(1):81–125. doi: 10.1016/0025-5564(93)90043-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perelson A. S., Neumann A. U., Markowitz M., Leonard J. M., Ho D. D. HIV-1 dynamics in vivo: virion clearance rate, infected cell life-span, and viral generation time. Science. 1996 Mar 15;271(5255):1582–1586. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5255.1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuurman R., Nijhuis M., van Leeuwen R., Schipper P., de Jong D., Collis P., Danner S. A., Mulder J., Loveday C., Christopherson C. Rapid changes in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA load and appearance of drug-resistant virus populations in persons treated with lamivudine (3TC). J Infect Dis. 1995 Jun;171(6):1411–1419. doi: 10.1093/infdis/171.6.1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei X., Ghosh S. K., Taylor M. E., Johnson V. A., Emini E. A., Deutsch P., Lifson J. D., Bonhoeffer S., Nowak M. A., Hahn B. H. Viral dynamics in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Nature. 1995 Jan 12;373(6510):117–122. doi: 10.1038/373117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winslow D. L., Otto M. J. HIV protease inhibitors. AIDS. 1995;9 (Suppl A):S183–S192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



