Abstract
A structure consisting of poly(A) complexed with other components is released from polysomes by ribonuclease treatment. The poly(A) complex has a sedimentation value of 12-15, while the corresponding sedimentation value for free poly(A) is 4. The complex does not appear to represent an artifact formed by interaction of free poly(A) with either cytoplasmic or polysomal proteins. The polynucleotide released from the complex by treatment with sodium dodecyl sulfate shows the same electrophoretic mobility as that of poly(A) isolated from deproteinized polysomal RNA. The poly(A) in the complex is partially protected from digestion by T2 ribonuclease. At least part of the poly(A) is available for base pairing with poly(U). The components associated with the poly(A) cause it to bind to Millipore filters at low ionic strength. These components are removed from the complex by Pronase digestion. The findings indicate that the poly(A) segment in messenger RNA serves as a binding site for a particle. This particle appears to consist of proteins.
Keywords: protein-binding site on mRNA, polysome structure
Full text
PDF
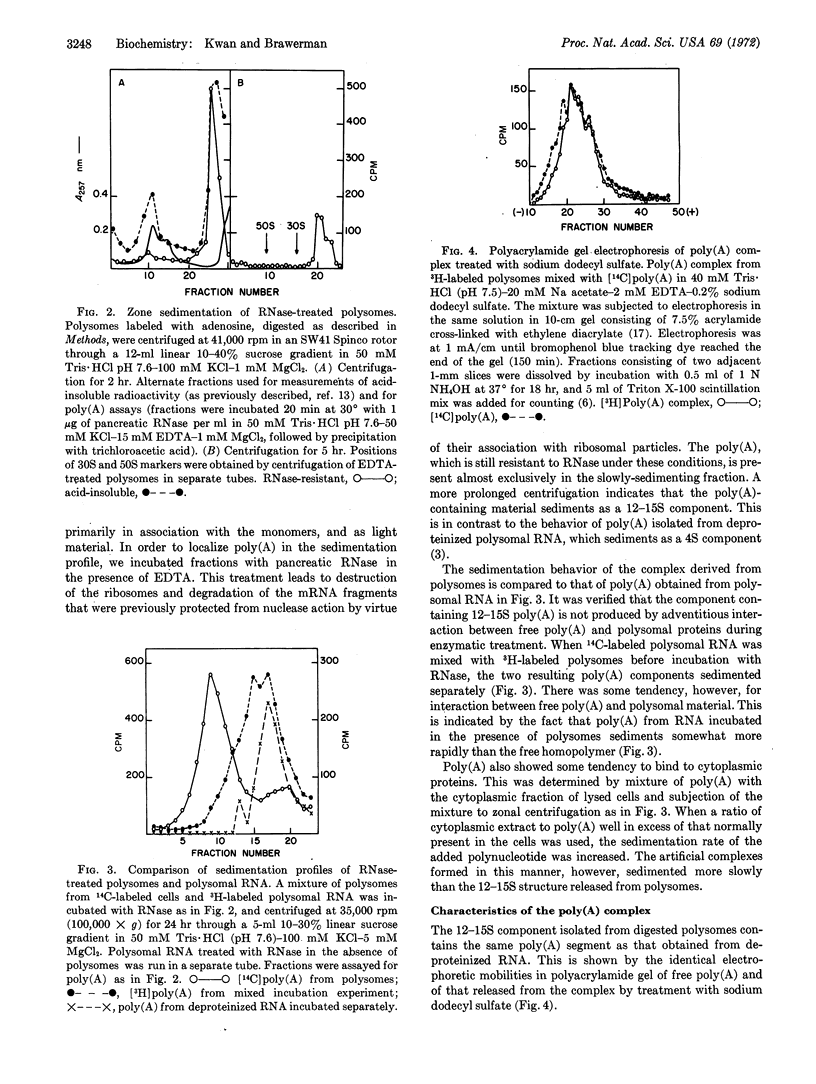
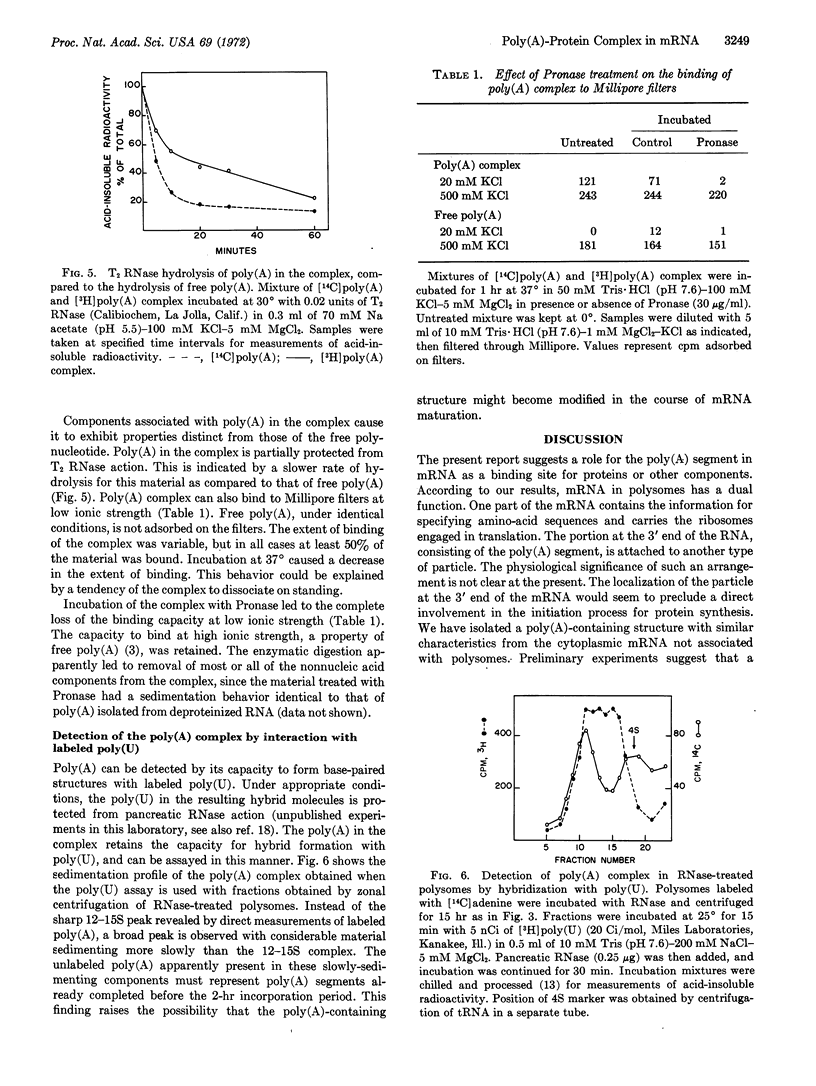

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brawerman G., Mendecki J., Lee S. Y. A procedure for the isolation of mammalian messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 15;11(4):637–641. doi: 10.1021/bi00754a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choules G. L., Zimm B. H. An acrylamide gel soluble in scintillation fluids: its application to electrophoresis at neutral and low pH. Anal Biochem. 1965 Nov;13(2):336–344. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90202-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Wall R., Tushinski R. J. An adenylic acid-rich sequence in messenger RNA of HeLa cells and its possible relationship to reiterated sites in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1321–1325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds M., Vaughan M. H., Jr, Nakazato H. Polyadenylic acid sequences in the heterogeneous nuclear RNA and rapidly-labeled polyribosomal RNA of HeLa cells: possible evidence for a precursor relationship. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1336–1340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henshaw E. C., Loebenstein J. Rapidly labeled, polydisperse RNA in rat-liver cytoplasm: evidence that it is contained in ribonucleoprotein particles of heterogeneous size. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 18;199(2):405–420. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henshaw E. C. Messenger RNA in rat liver polyribosomes: evidence that it exists as ribonucleoprotein particles. J Mol Biol. 1968 Sep 28;36(3):401–411. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90164-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. Y., Brawerman G. Pulse-labeled ribonucleic acid complexes released by dissociation of rat liver polysomes. Biochemistry. 1971 Feb 2;10(3):510–516. doi: 10.1021/bi00779a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. Y., Krsmanovic V., Brawerman G. Initiation of polysome formation in mouse sarcoma 180 ascites cells. Utilization of cytoplasmic messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 2;10(5):895–900. doi: 10.1021/bi00781a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. Y., Mendecki J., Brawerman G. A polynucleotide segment rich in adenylic acid in the rapidly-labeled polyribosomal RNA component of mouse sarcoma 180 ascites cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1331–1335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim L., Canellakis E. S. Adenine-rich polymer associated with rabbit reticulocyte messenger RNA. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):710–712. doi: 10.1038/227710a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendecki J., Lee S. Y., Brawerman G. Characteristics of the polyadenylic acid segment associated with messenger ribonucleic acid in mouse sarcoma 180 ascites cells. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 29;11(5):792–798. doi: 10.1021/bi00755a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S., Vesco C., Penman M. Localization and kinetics of formation of nuclear heterodisperse RNA, cytoplasmic heterodisperse RNA and polyribosome-associated messenger RNA in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1968 May 28;34(1):49–60. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90234-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., Kelley D. E. Buoyant densities of cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein particles of mammalian cells: distinctive character of ribosome subunits and the rapidly labeled components. J Mol Biol. 1966 Apr;16(2):255–268. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80171-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., Kelley D. E. Messenger RNA-protein complexes and newly synthesized ribosomal subunits: analysis of free particles and components of polyribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;35(1):37–59. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(68)80035-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryskov A. P., Farashyan V. R., Georgiev G. P. The localization of polyadenylic sequence at the 5'-end of light nuclear dRNA. FEBS Lett. 1972 Feb 15;20(3):355–358. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80106-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylber E., Vesco C., Penman S. Selective inhibition of the synthesis of mitochondria-associated RNA by ethidium bromide. J Mol Biol. 1969 Aug 28;44(1):195–204. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90414-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



