Abstract
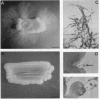
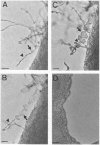
Cryptococcus neoformans is a major opportunistic fungal pathogen in AIDS and other immunosuppressed patients. We have shown that wild-type haploid C. neoformans can develop an extensive hyphal phase under appropriate conditions. Hyphae produced under these conditions are monokaryotic, possess unfused clamp connections, and develop basidia with viable basidiospores. The ability to undergo this transition is determined by the presence of the alpha-mating type locus and is independent of serotype. The association of the hyphal phase with the alpha-mating type may explain the preponderance of this mating type in the environment and the nature of the infectious propagule of C. neoformans.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe K., Kusaka I., Fukui S. Morphological change in the early stages of the mating process of Rhodosporidium toruloides. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):710–718. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.710-718.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banuett F. Genetics of Ustilago maydis, a fungal pathogen that induces tumors in maize. Annu Rev Genet. 1995;29:179–208. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.29.120195.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulmer G. S. Twenty-five years with Cryptococcus neoformans. Mycopathologia. 1990 Feb;109(2):111–122. doi: 10.1007/BF00436791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erke K. H. Light microscopy of basidia, basidiospores, and nuclei in spores and hyphae of Filobasidiella neoformans (Cryptococcus neoformans). J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):445–455. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.445-455.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farhi F., Bulmer G. S., Tacker J. R. Cryptococcus neoformans IV. The Not-So-Encapsulated Yeast. Infect Immun. 1970 Jun;1(6):526–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.6.526-531.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer R., Timberlake W. E. Aspergillus nidulans apsA (anucleate primary sterigmata) encodes a coiled-coil protein required for nuclear positioning and completion of asexual development. J Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;128(4):485–498. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.4.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimeno C. J., Fink G. R. The logic of cell division in the life cycle of yeast. Science. 1992 Jul 31;257(5070):626–626. doi: 10.1126/science.1496375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimeno C. J., Ljungdahl P. O., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. Unipolar cell divisions in the yeast S. cerevisiae lead to filamentous growth: regulation by starvation and RAS. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1077–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90079-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HATCH T. F. Distribution and deposition of inhaled particles in respiratory tract. Bacteriol Rev. 1961 Sep;25:237–240. doi: 10.1128/br.25.3.237-240.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jong S. C., Bulmer G. S., Ruiz A. Serologic grouping and sexual compatibility of airborne Cryptococcus neoformans. Mycopathologia. 1982 Sep 17;79(3):185–188. doi: 10.1007/BF01837197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J. A new genus, filobasidiella, the perfect state of Cryptococcus neoformans. Mycologia. 1975 Nov-Dec;67(6):1197–1200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J. A new species of Filobasidiella, the sexual state of Cryptococcus neoformans B and C serotypes. Mycologia. 1976 Jul-Aug;68(4):943–946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Bennett J. E. Distribution of alpha and alpha mating types of Cryptococcus neoformans among natural and clinical isolates. Am J Epidemiol. 1978 Oct;108(4):337–340. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Edman J. C., Wickes B. L. Genetic association of mating types and virulence in Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):602–605. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.602-605.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J. Nuclear genotypes of spore chains in Filobasidiella neoformans (Cryptococcus neoformans). Mycologia. 1980 Mar-Apr;72(2):418–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Wickes B. L., Stockman L., Roberts G. D., Ellis D., Howard D. H. Virulence, serotype, and molecular characteristics of environmental strains of Cryptococcus neoformans var. gattii. Infect Immun. 1992 May;60(5):1869–1874. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.5.1869-1874.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lurie H. I., Shadomy H. J. Morphological variations of a hypha-forming strain of Cryptococcus neoformans (Coward strain) in tissues of mice. Sabouraudia. 1971 Mar;9(1):10–14. doi: 10.1080/00362177185190041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore T. D., Edman J. C. The alpha-mating type locus of Cryptococcus neoformans contains a peptide pheromone gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1962–1970. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson J. B., Fromtling R. A., Bulmer G. S. Cryptococcus neoformans: size range of infectious particles from aerosolized soil. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):634–638. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.634-638.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rippon J. W. Dimorphism in pathogenic fungi. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1980;8(1):49–97. doi: 10.3109/10408418009085078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz A., Neilson J. B., Bulmer G. S. A one year study on the viability of Cryptococcus neoformans in nature. Mycopathologia. 1982 Feb 19;77(2):117–122. doi: 10.1007/BF00437394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- San-Blas G., San-Blas F. Molecular aspects of fungal dimorphism. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1984;11(2):101–127. doi: 10.3109/10408418409105474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmeding K. A., Jong S. C., Hugh R. Biochemical variation of Cryptococcus neoformans. Mycopathologia. 1984 Feb 15;84(2-3):121–131. doi: 10.1007/BF00436523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadomy H. J., Utz J. P. Preliminary studies on a hyphaforming mutant of Cryptococcus neoformans. Mycologia. 1966 May-Jun;58(3):383–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd M. G. Morphogenetic transformation of fungi. Curr Top Med Mycol. 1988;2:278–304. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-3730-3_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Guererro H., Edman J. C. Melanin-deficient mutants of Cryptococcus neoformans. J Med Vet Mycol. 1994;32(4):303–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]