Abstract
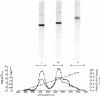
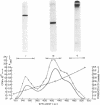
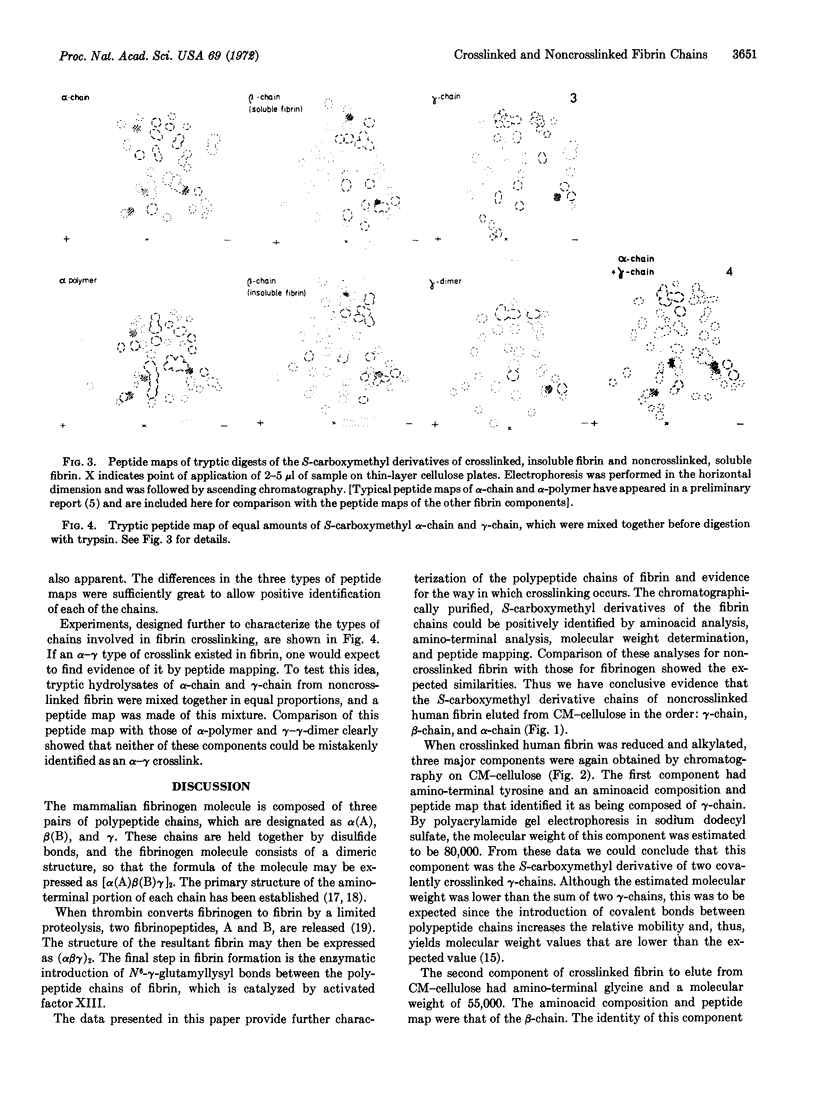
The S-carboxymethyl derivative chains of crosslinked and noncrosslinked fibrins were prepared from purified human fibrinogen. For crosslinked fibrin, fibrinogen was clotted with thrombin in the presence of calcium and purified human factor XIII. For noncrosslinked fibrin, ethylenediaminetetraacetate was substituted for factor XIII and calcium. After reduction with dithiothrcitol and alkylation with tritiated iodoacetic acid, the derivative chains were separated on carboxymethyl cellulose in a sodium acetate-pH gradient that contained 8 M urea. Purity of the separated chains was determined by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis at acid and at neutral pH. The derivative chains of noncrosslinked fibrin were eluted from carboxymethyl cellulose in the order: γ-chain, β-chain, and α-chain. Each of the purified derivative chains was characterized and identified by amino-terminal aminoacid analysis, aminoacid composition, tryptic peptide mapping, and molecular weight estimation by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in sodium dodecyl sulfate. In like manner, the derivative components of crosslinked fibrin were eluted from carboxymethyl cellulose in the order: γ-γ-dimer, β-chain, and α-polymer. Application of the same analytical criteria and comparision with the derivatives of noncrosslinked fibrin confirmed the identity of these components. These data provide conclusive evidence that crosslinking of human fibrin involves formation of peptide bonds between two γ-chains to form γ-γ-dimer and between multiple α-chains to form high molecular weight polymers of α-chains.
Keywords: factor XIII, fibrin stabilization
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blombäck B., Blombäck M., Edman P., Hessel B. Human fibrinopeptides. Isolation, characterization and structure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 28;115(2):371–396. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90437-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blombäck B., Hessel B., Iwanaga S., Reuterby J., Blombäck M. Primary structure of human fibrinogen and fibrin. I. Clevage of fibrinogen with cyanogen bromide. Isolation and characterization of NH 2 -terminal fragments of the ("A") chain. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 10;247(5):1496–1512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blombäck M., Blombäck B., Mammen E. F., Prasad A. S. Fibrinogen Detroit--a molecular defect in the N-terminal disulphide knot of human fibrinogen? Nature. 1968 Apr 13;218(5137):134–137. doi: 10.1038/218134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brummel M. C., Montgomery R. Acrylamide gel electrophoresis of the S-sulfo derivatives of fibrinogen. Anal Biochem. 1970 Jan;33(1):28–35. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90435-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R., Doolittle R. F. - cross-linking sites in human and bovine fibrin. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov 23;10(24):4487–4491. doi: 10.1021/bi00800a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edman P. Sequence determination. Mol Biol Biochem Biophys. 1970;8:211–255. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-12834-3_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henschen A., Edman P. Large scale preparation of S-carboxymethylated chains of human fibrin and fibrinogen and the occurrence of -chain variants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 15;263(2):351–367. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90088-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorand L., Chenoweth D., Domanik R. A. Chain pairs in the crosslinking of fibrin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Oct 8;37(2):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90722-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh J., Messel H., McDonagh R. P., Jr, Murano G., Blombäck B. Molecular weight analysis of fibrinogen and fibrin chains by an improved sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis method. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 26;257(1):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90262-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonagh R. P., McDonagh J., Blombäck M., Blombäck B. Crosslinking of human fibrin: Evidence for intermolecular crosslinking involving alpha-chains. FEBS Lett. 1971 Apr 12;14(1):33–36. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee P. A., Mattock P., Hill R. L. Subunit structure of human fibrinogen, soluble fibrin, and cross-linked insoluble fibrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):738–744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murano G., Wiman B., Blombäck M., Blombäck B. Preparation and isolation of the S-carboxymethyl derivative chains of human fibrinogen. FEBS Lett. 1971 Apr 12;14(1):37–41. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisano J. J., Finlayson J. S., Peyton M. P. Chemical and enzymic detection of protein cross-links. Measurement of epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)lysine in fibrin polymerized by factor XIII. Biochemistry. 1969 Mar;8(3):871–876. doi: 10.1021/bi00831a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]