Abstract
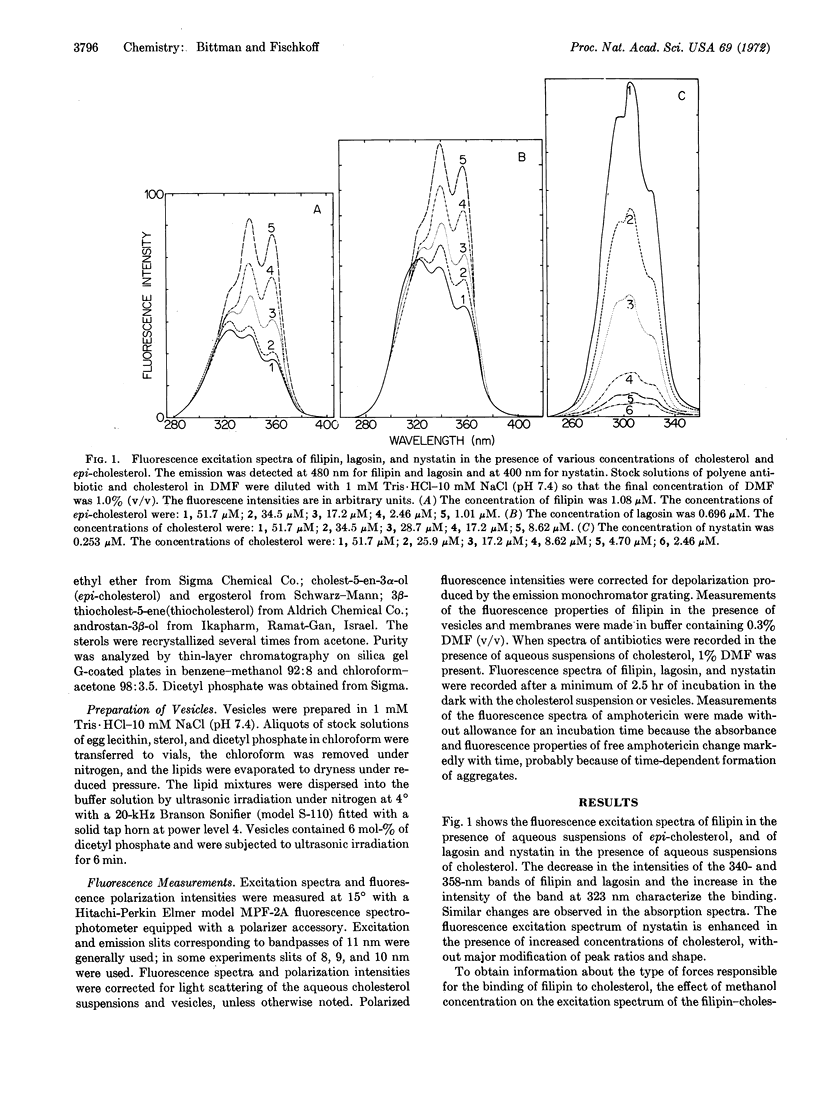
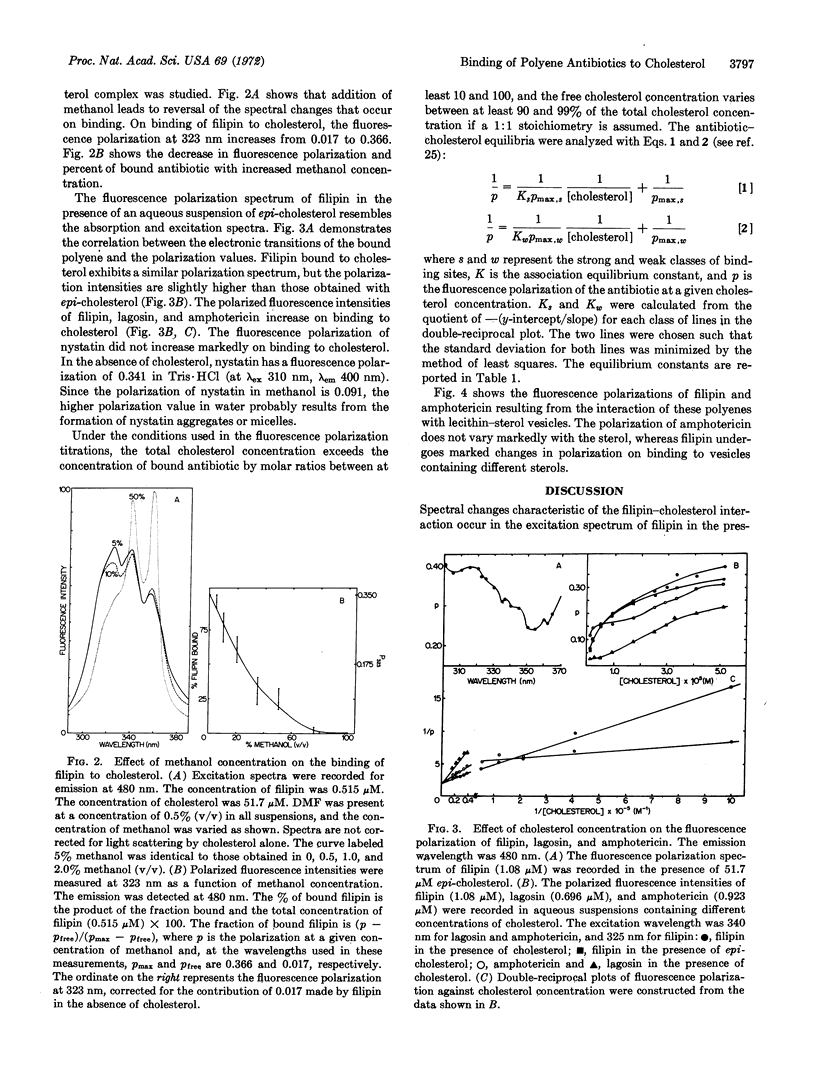
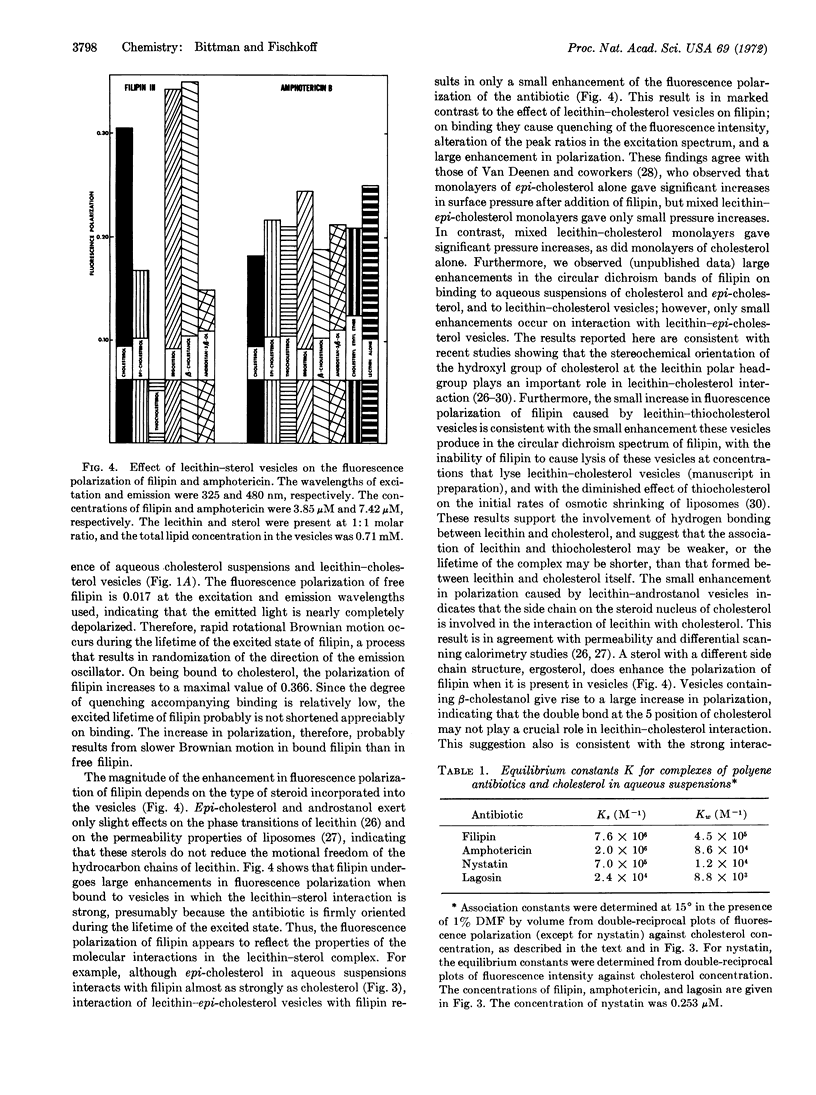
The interactions of filipin III, amphotericin B, nystatin, and lagosin with sterols in aqueous suspension and in vesicles were followed by fluorescence excitation spectra and by measurement of polarized fluorescence intensities. The equilibrium constants for association of the polyene antibiotics with aqueous suspensions of cholesterol follow the order filipin III > amphotericin B > nystatin > lagosin, in agreement with the order reported for the extent of damage these antibiotics cause in natural and model membranes. Fluorescence polarization measurements show that hydrophobic forces are primarily responsible for the formation of the complexes. Filipin III undergoes a large enhancement in fluorescence polarization on binding to aqueous suspensions of cholesterol and epi-cholesterol, and to vesicles of lecithin-cholesterol, lecithin-β-cholestanol, and lecithinergosterol. Small increases in polarization occur on interaction of filipin III with vesicles derived from lecithin and epi-cholesterol, thiocholesterol, and androstan-3β-ol. Amphotericin B undergoes a relatively constant enhancement in fluorescence polarization on interaction with the various lecithin-sterol vesicles used and does not display the selectivity exhibited by filipin III. It is suggested that filipin III serves as a probe of lecithin-sterol interaction.
Keywords: membranes, vesicles, lecithin, probe
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergy M. E., Eble T. E. The filipin complex. Biochemistry. 1968 Feb;7(2):653–659. doi: 10.1021/bi00842a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner D. P., Mechlinski W., Schaffner C. P. Polyene macrolide derivatives. 3. Biological properties of polyene macrolide ester salts. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Apr;25(4):261–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowski E., Zieliński J., Ziminski T., Falkowski L., Kolodziejczyk P., Golik J., Jereczek E. Chemical studies with amphotericin B. 3. The complete structure of the antibiotic. Tetrahedron Lett. 1970 Sep;(45):3909–3914. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4039(01)98622-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CIRILLO V. P., HARSCH M., LAMPEN J. O. ACTION OF THE POLYENE ANTIBIOTICS FILIPIN, NYSTATIN AND N-ACETYLCANDIDIN ON THE YEAST CELL MEMBRANE. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 May;35:249–259. doi: 10.1099/00221287-35-2-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cass A., Finkelstein A., Krespi V. The ion permeability induced in thin lipid membranes by the polyene antibiotics nystatin and amphotericin B. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jul;56(1):100–124. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong C. N., Rickards R. W. Macrolide antibiotic studies. XVI. The structure of nystatin. Tetrahedron Lett. 1970 Dec;(59):5145–5148. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4039(00)96962-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demel R. A., Bruckdorfer K. R., van Deenen L. L. Structural requirements of sterols for the interaction with lecithin at the air water interface. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 17;255(1):311–320. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90030-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demel R. A., Bruckdorfer K. R., van Deenen L. L. The effect of sterol structure on the permeability of lipomes to glucose, glycerol and Rb + . Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 17;255(1):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher H., Griminger P., Schaffner C. P. Effect of polyene macrolides on cholesterol metabolism of the chick. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Oct;132(1):253–255. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganis P., Avitabile G., Mechlinski W., Schaffner C. P. Polyene macrolide antibiotic amphotericin B. Crystal structure of the N-iodoacetyl derivative. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Sep 8;93(18):4560–4564. doi: 10.1021/ja00747a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon H. W., Schaffner C. P. The effect of polyene macrolides on the prostate gland and canine prostatic hyperplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1201–1208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAZEN E. L., BROWN R. Two antifungal agents produced by a soil actinomycete. Science. 1950 Oct 13;112(2911):423–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KINSKY S. C. COMPARATIVE RESPONSES OF MAMMALIAN ERYTHROCYTES AND MICROBIAL PROTOPLASTS TO POLYENE ANTIBIOTICS AND VITAMIN A. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Aug;102:180–188. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90169-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KINSKY S. C. Effect of polyene antibiotics on protoplasts of Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol. 1962 Feb;83:351–358. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.2.351-358.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsky S. C., Luse S. A., Zopf D., van Deenen L. L., Haxby J. Interaction of filipin and derivatives with erythrocyte membranes and lipid dispersions: electron microscopic observations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967;135(5):844–861. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(67)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMPEN J. O., ARNOW P. M., SAFFERMAN R. S. Mechanism of protection by sterols against polyene antibiotics. J Bacteriol. 1960 Aug;80:200–206. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.2.200-206.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUCY J. A., GLAUERT A. M. STRUCTURE AND ASSEMBLY OF MACROMOLECULAR LIPID COMPLEXES COMPOSED OF GLOBULAR MICELLES. J Mol Biol. 1964 May;8:727–748. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80121-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manwaring D. C., Rickards R. W., Golding B. T. The structure of the aglycone of the macrolide antibiotic nystatin. Tetrahedron Lett. 1969 Dec;(60):5319–5322. doi: 10.1016/s0040-4039(01)88953-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman A. W., Demel R. A., de Kruyff B., van Deenen L. L. Studies on the biological properties of polyene antibiotics. Evidence for the direct interaction of filipin with cholesterol. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 25;247(6):1918–1929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey R. C., Narasimhachari N., Rinehart K. L., Jr, Millington D. S. Polyene antibiotics. IV. Structure of chainin. J Am Chem Soc. 1972 Jun 14;94(12):4306–4310. doi: 10.1021/ja00767a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey R. C., Rinehart K. L., Jr Polyene antibiotics. V. Characterization of components of the filipin complex by mass spectrometry. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1970 Aug;23(8):414–417. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.23.414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGLETON W. S., GRAY M. S., BROWN M. L., WHITE J. L. CHROMATOGRAPHICALLY HOMOGENEOUS LECITHIN FROM EGG PHOSPHOLIPIDS. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1965 Jan;42:53–56. doi: 10.1007/BF02558256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarma R. H., Woronick C. L. Electronic, hydrophobic, and steric effects of binding of inhibitors to the horse liver alcohol dehydrogenase-reduced pyridine coenzyme binary complex. Biochemistry. 1972 Jan 18;11(2):170–179. doi: 10.1021/bi00752a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner C. P., Gordon H. W. The hypocholesterolemic activity of orally administered polyene macrolides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):36–41. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder F., Bieber L. L. Effects of Filipin and cholesterol on housefly, Musca domestica L., and wax moth, Galleria mellonella L. Chem Biol Interact. 1972 Mar;4(4):239–249. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(72)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sessa G., Weissmann G. Effects of four components of the polyene antibiotic, filipin, on phospholipid spherules (liposomes) and erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1968 Aug 25;243(16):4364–4371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweeley C. C., O Connor J. D., Bieber L. L. Effect of polyene macrolides on growth and reproduction of Musca domestica and on the uptake of cholesterol in Galleria mellonella larvae. Chem Biol Interact. 1970 Oct;2(3):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(70)90027-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kruyff B., Demel R. A., van Deenen L. L. The effect of cholesterol and epicholesterol incorporation on the permeability and on the phase transition of intact Acholeplasma laidlawii cell membranes and derived liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 17;255(1):331–347. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zutphen H., Demel R. A., Norman A. W., van Deenen L. L. The action of polyene antibiotics on lipid bilayer membranes in the presence of several cations and anions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 13;241(2):310–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



