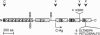Abstract
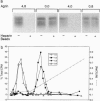
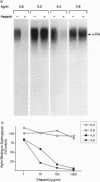
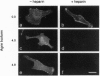
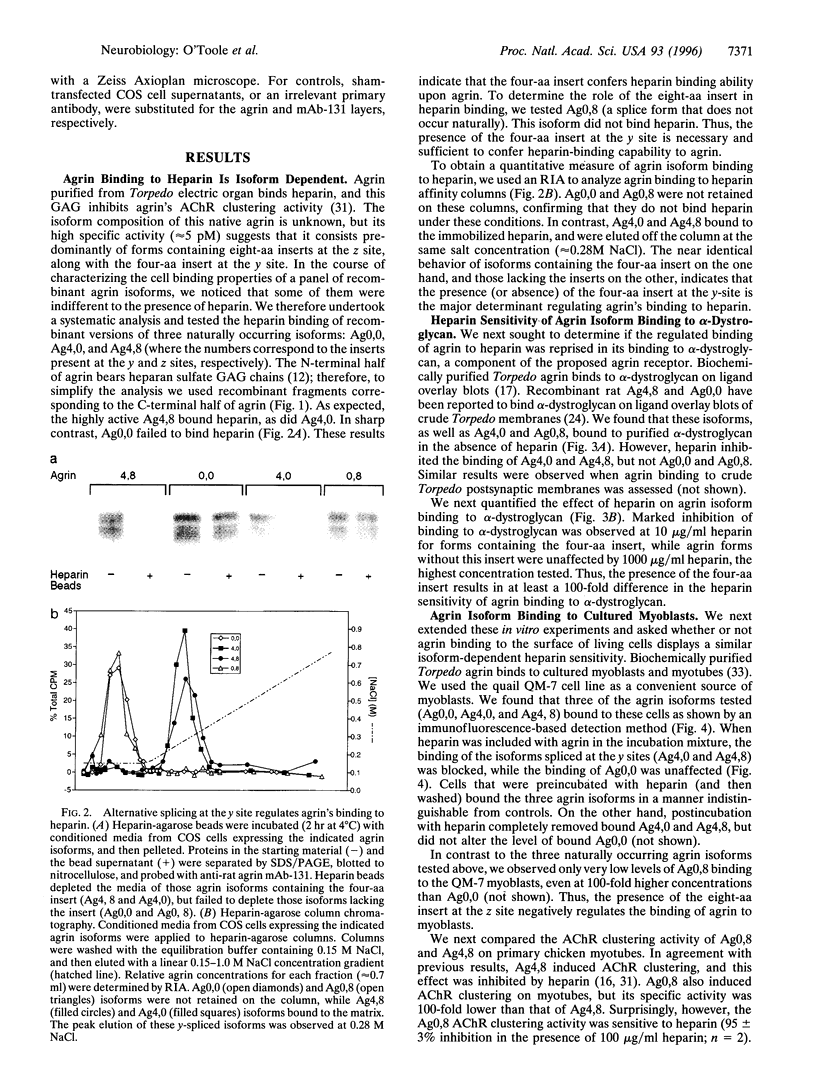
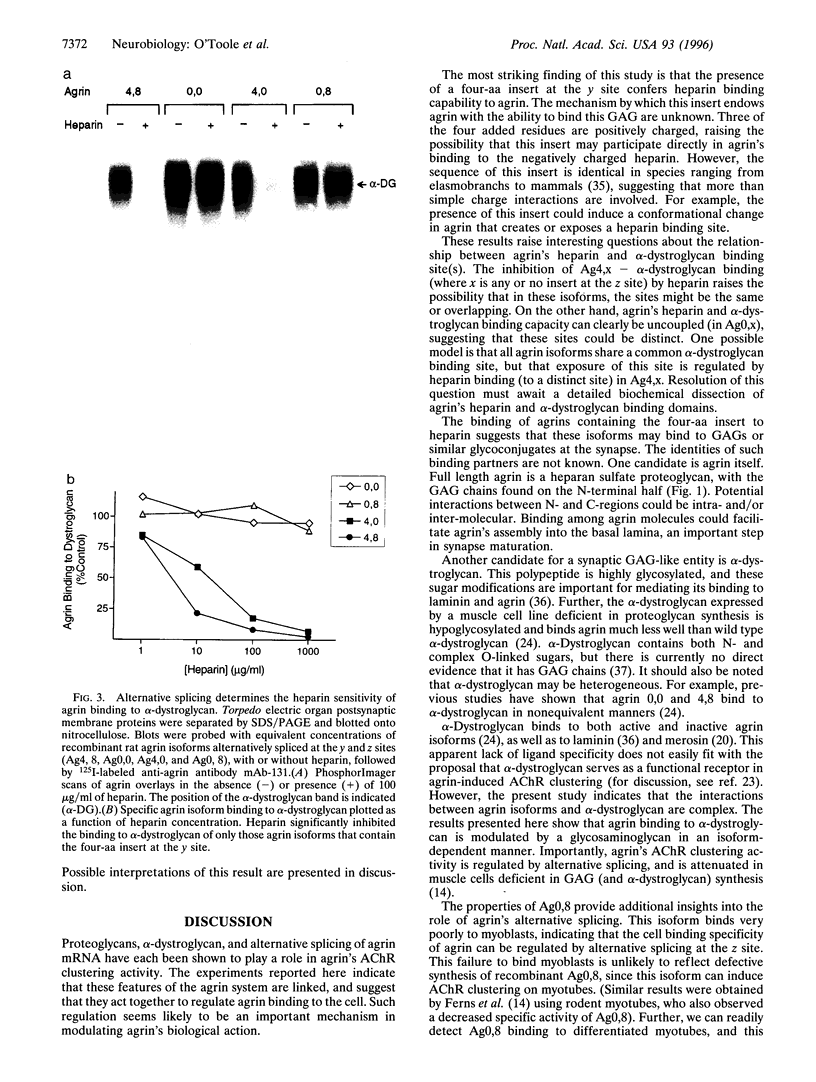
Agrin is a basal lamina molecule that directs key events in postsynaptic differentiation, most notably the aggregation of acetylcholine receptors (AChRs) on the muscle cell surface. Agrin's AChR clustering activity is regulated by alternative mRNA splicing. Agrin splice forms having inserts at two sites (y and z) in the C-terminal region are highly active, but isoforms lacking these inserts are weakly active. The biochemical consequences of this alternative splicing are unknown. Here, the binding of four recombinant agrin isoforms to heparin, to alpha-dystroglycan (a component of an agrin receptor), and to myoblasts was tested. The presence of a four-amino acid insert at the y site is necessary and sufficient to confer heparin binding ability to agrin. Moreover, the binding of agrin to alpha-dystroglycan is inhibited by heparin when this insert is present. Agrin binding to the cell surface showed analogous properties: heparin inhibits the binding of only those agrin isoforms containing this four-amino acid insert. The results show that alternative splicing of agrin regulates its binding to heparin and suggest that agrin's interaction with alpha-dystroglycan may be modulated by cell surface glycosaminoglycans in an isoform-dependent manner.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn A. H., Kunkel L. M. The structural and functional diversity of dystrophin. Nat Genet. 1993 Apr;3(4):283–291. doi: 10.1038/ng0493-283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antin P. B., Ordahl C. P. Isolation and characterization of an avian myogenic cell line. Dev Biol. 1991 Jan;143(1):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90058-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowe M. A., Deyst K. A., Leszyk J. D., Fallon J. R. Identification and purification of an agrin receptor from Torpedo postsynaptic membranes: a heteromeric complex related to the dystroglycans. Neuron. 1994 May;12(5):1173–1180. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90324-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowe M. A., Fallon J. R. The role of agrin in synapse formation. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1995;18:443–462. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.18.030195.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bönnemann C. G., Modi R., Noguchi S., Mizuno Y., Yoshida M., Gussoni E., McNally E. M., Duggan D. J., Angelini C., Hoffman E. P. Beta-sarcoglycan (A3b) mutations cause autosomal recessive muscular dystrophy with loss of the sarcoglycan complex. Nat Genet. 1995 Nov;11(3):266–273. doi: 10.1038/ng1195-266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campanelli J. T., Roberds S. L., Campbell K. P., Scheller R. H. A role for dystrophin-associated glycoproteins and utrophin in agrin-induced AChR clustering. Cell. 1994 Jun 3;77(5):663–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. W., Moody-Corbett F., Godfrey E. W. Neuritic deposition of agrin on culture substrate: implications for nerve-muscle synaptogenesis. J Neurosci. 1994 May;14(5 Pt 2):3293–3303. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-05-03293.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deyst K. A., Bowe M. A., Leszyk J. D., Fallon J. R. The alpha-dystroglycan-beta-dystroglycan complex. Membrane organization and relationship to an agrin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 27;270(43):25956–25959. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.43.25956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ervasti J. M., Campbell K. P. A role for the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex as a transmembrane linker between laminin and actin. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(4):809–823. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.4.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallon J. R., Hall Z. W. Building synapses: agrin and dystroglycan stick together. Trends Neurosci. 1994 Nov;17(11):469–473. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90135-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallon J. R., Nitkin R. M., Reist N. E., Wallace B. G., McMahan U. J. Acetylcholine receptor-aggregating factor is similar to molecules concentrated at neuromuscular junctions. Nature. 1985 Jun 13;315(6020):571–574. doi: 10.1038/315571a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferns M. J., Campanelli J. T., Hoch W., Scheller R. H., Hall Z. The ability of agrin to cluster AChRs depends on alternative splicing and on cell surface proteoglycans. Neuron. 1993 Sep;11(3):491–502. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90153-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferns M., Hoch W., Campanelli J. T., Rupp F., Hall Z. W., Scheller R. H. RNA splicing regulates agrin-mediated acetylcholine receptor clustering activity on cultured myotubes. Neuron. 1992 Jun;8(6):1079–1086. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90129-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fertuck H. C., Salpeter M. M. Quantitation of junctional and extrajunctional acetylcholine receptors by electron microscope autoradiography after 125I-alpha-bungarotoxin binding at mouse neuromuscular junctions. J Cell Biol. 1976 Apr;69(1):144–158. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee S. H., Montanaro F., Lindenbaum M. H., Carbonetto S. Dystroglycan-alpha, a dystrophin-associated glycoprotein, is a functional agrin receptor. Cell. 1994 Jun 3;77(5):675–686. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesemann M., Denzer A. J., Ruegg M. A. Acetylcholine receptor-aggregating activity of agrin isoforms and mapping of the active site. J Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;128(4):625–636. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.4.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch W., Campanelli J. T., Harrison S., Scheller R. H. Structural domains of agrin required for clustering of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 15;13(12):2814–2821. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06575.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch W., Ferns M., Campanelli J. T., Hall Z. W., Scheller R. H. Developmental regulation of highly active alternatively spliced forms of agrin. Neuron. 1993 Sep;11(3):479–490. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90152-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibraghimov-Beskrovnaya O., Ervasti J. M., Leveille C. J., Slaughter C. A., Sernett S. W., Campbell K. P. Primary structure of dystrophin-associated glycoproteins linking dystrophin to the extracellular matrix. Nature. 1992 Feb 20;355(6362):696–702. doi: 10.1038/355696a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung D., Yang B., Meyer J., Chamberlain J. S., Campbell K. P. Identification and characterization of the dystrophin anchoring site on beta-dystroglycan. J Biol Chem. 1995 Nov 10;270(45):27305–27310. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.45.27305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieth E., Fallon J. R. Muscle agrin: neural regulation and localization at nerve-induced acetylcholine receptor clusters. J Neurosci. 1993 Jun;13(6):2509–2514. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-06-02509.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahan U. J., Horton S. E., Werle M. J., Honig L. S., Kröger S., Ruegg M. A., Escher G. Agrin isoforms and their role in synaptogenesis. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;4(5):869–874. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90113-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mook-Jung I., Gordon H. Acetylcholine receptor clustering in C2 muscle cells requires chondroitin sulfate. J Neurobiol. 1995 Dec;28(4):482–492. doi: 10.1002/neu.480280408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nastuk M. A., Lieth E., Ma J. Y., Cardasis C. A., Moynihan E. B., McKechnie B. A., Fallon J. R. The putative agrin receptor binds ligand in a calcium-dependent manner and aggregates during agrin-induced acetylcholine receptor clustering. Neuron. 1991 Nov;7(5):807–818. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90283-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi S., McNally E. M., Ben Othmane K., Hagiwara Y., Mizuno Y., Yoshida M., Yamamoto H., Bönnemann C. G., Gussoni E., Denton P. H. Mutations in the dystrophin-associated protein gamma-sarcoglycan in chromosome 13 muscular dystrophy. Science. 1995 Nov 3;270(5237):819–822. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5237.819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reist N. E., Magill C., McMahan U. J. Agrin-like molecules at synaptic sites in normal, denervated, and damaged skeletal muscles. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2457–2469. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reist N. E., Werle M. J., McMahan U. J. Agrin released by motor neurons induces the aggregation of acetylcholine receptors at neuromuscular junctions. Neuron. 1992 May;8(5):865–868. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90200-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruegg M. A., Tsim K. W., Horton S. E., Kröger S., Escher G., Gensch E. M., McMahan U. J. The agrin gene codes for a family of basal lamina proteins that differ in function and distribution. Neuron. 1992 Apr;8(4):691–699. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90090-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp F., Ozçelik T., Linial M., Peterson K., Francke U., Scheller R. Structure and chromosomal localization of the mammalian agrin gene. J Neurosci. 1992 Sep;12(9):3535–3544. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-09-03535.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smalheiser N. R., Kim E. Purification of cranin, a laminin binding membrane protein. Identity with dystroglycan and reassessment of its carbohydrate moieties. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 23;270(25):15425–15433. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.25.15425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. A., O'Dowd D. K. Cell-specific regulation of agrin RNA splicing in the chick ciliary ganglion. Neuron. 1994 Apr;12(4):795–804. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90332-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama J., Bowen D. C., Hall Z. W. Dystroglycan binds nerve and muscle agrin. Neuron. 1994 Jul;13(1):103–115. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90462-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki A., Yoshida M., Hayashi K., Mizuno Y., Hagiwara Y., Ozawa E. Molecular organization at the glycoprotein-complex-binding site of dystrophin. Three dystrophin-associated proteins bind directly to the carboxy-terminal portion of dystrophin. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Mar 1;220(2):283–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18624.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsen G., Halfter W., Kröger S., Cole G. J. Agrin is a heparan sulfate proteoglycan. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 17;270(7):3392–3399. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.7.3392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. G. Agrin-induced specializations contain cytoplasmic, membrane, and extracellular matrix-associated components of the postsynaptic apparatus. J Neurosci. 1989 Apr;9(4):1294–1302. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-04-01294.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. G. Inhibition of agrin-induced acetylcholine-receptor aggregation by heparin, heparan sulfate, and other polyanions. J Neurosci. 1990 Nov;10(11):3576–3582. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-11-03576.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worton R. Muscular dystrophies: diseases of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex. Science. 1995 Nov 3;270(5237):755–756. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5237.755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada H., Shimizu T., Tanaka T., Campbell K. P., Matsumura K. Dystroglycan is a binding protein of laminin and merosin in peripheral nerve. FEBS Lett. 1994 Sep 19;352(1):49–53. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00917-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Suzuki A., Yamamoto H., Noguchi S., Mizuno Y., Ozawa E. Dissociation of the complex of dystrophin and its associated proteins into several unique groups by n-octyl beta-D-glucoside. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Jun 15;222(3):1055–1061. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18958.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]