Abstract
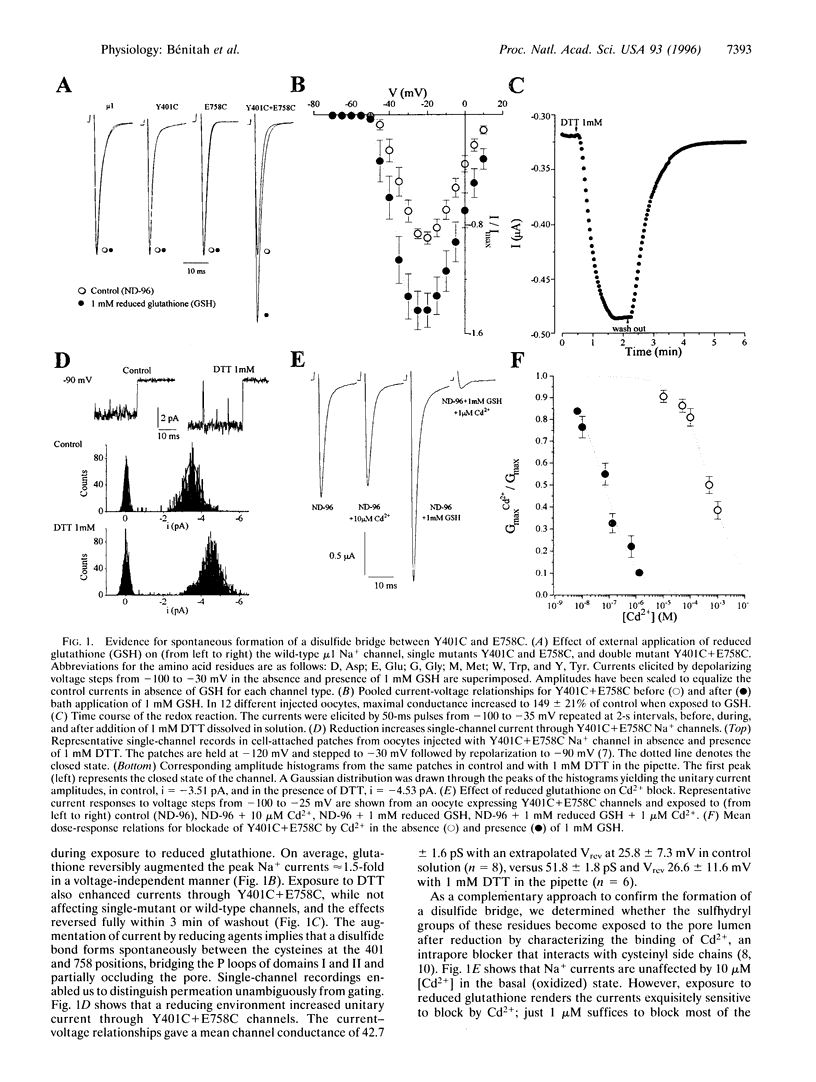
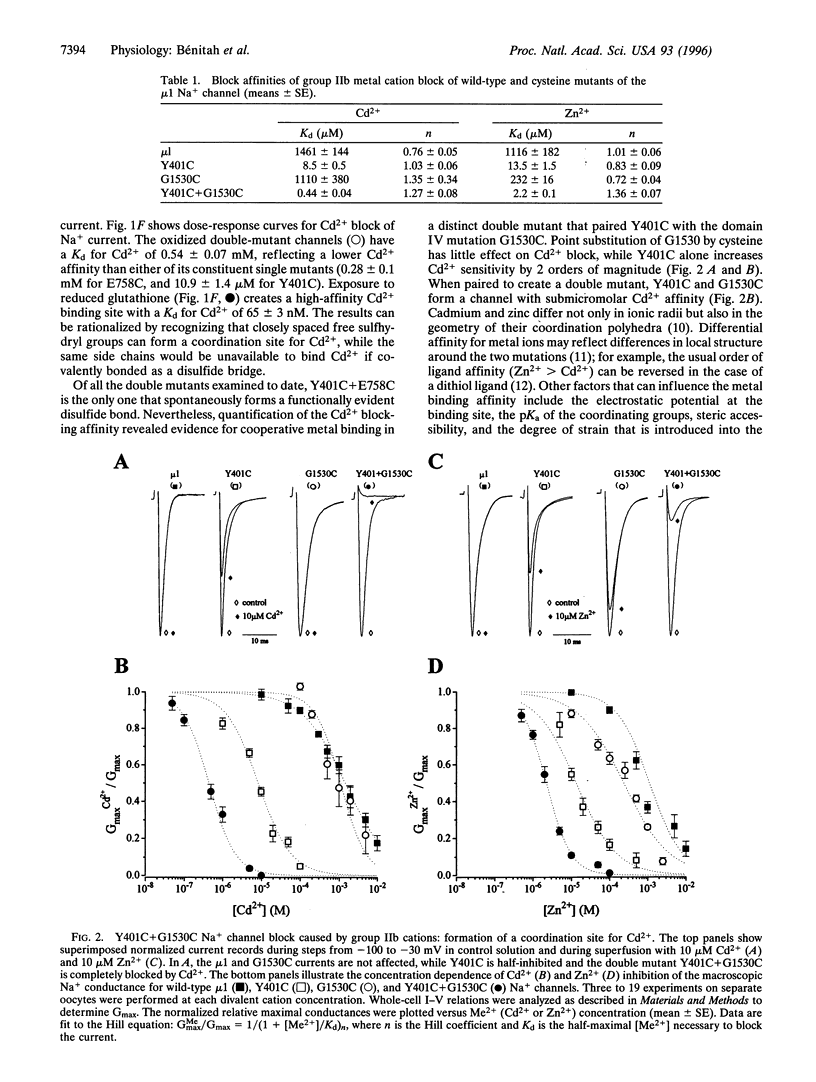
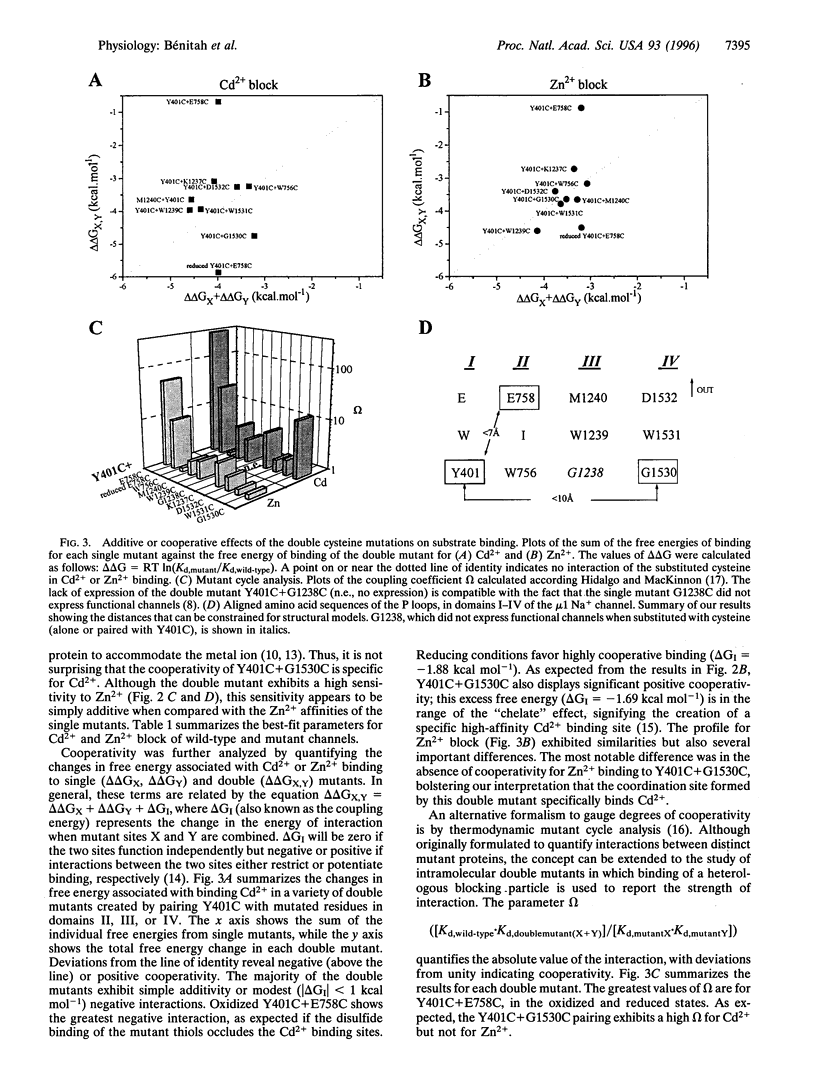
The pores of voltage-gated ion channels are lined by protein loops that determine selectivity and conductance. The relative orientations of these "P" loops remain uncertain, as do the distances between them. Using site-directed mutagenesis, we introduced pairs of cysteines into the P loops of micro1 rat skeletal muscle sodium channels and sought functional evidence of proximity between the substituted residues. Only cysteinyl residues that are in close proximity can form disulfide bonds or metal-chelating sites. The mutant Y401C (domain I) spontaneously formed a disulfide bond when paired with E758C in the P loop of domain II; the same residue, when coupled with G1530C in domain IV, created a high-affinity binding site for Cd2+ ions. The results provide the first specific constraints for intramolecular dimensions of the sodium channel pore.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold F. H., Haymore B. L. Engineered metal-binding proteins: purification to protein folding. Science. 1991 Jun 28;252(5014):1796–1797. doi: 10.1126/science.1648261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backx P. H., Yue D. T., Lawrence J. H., Marban E., Tomaselli G. F. Molecular localization of an ion-binding site within the pore of mammalian sodium channels. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):248–251. doi: 10.1126/science.1321496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Careaga C. L., Falke J. J. Thermal motions of surface alpha-helices in the D-galactose chemosensory receptor. Detection by disulfide trapping. J Mol Biol. 1992 Aug 20;226(4):1219–1235. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)91063-u. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti P. Geometry of interaction of metal ions with sulfur-containing ligands in protein structures. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 11;28(14):6081–6085. doi: 10.1021/bi00440a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falke J. J., Dernburg A. F., Sternberg D. A., Zalkin N., Milligan D. L., Koshland D. E., Jr Structure of a bacterial sensory receptor. A site-directed sulfhydryl study. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14850–14858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falke J. J., Koshland D. E., Jr Global flexibility in a sensory receptor: a site-directed cross-linking approach. Science. 1987 Sep 25;237(4822):1596–1600. doi: 10.1126/science.2820061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glusker J. P. Structural aspects of metal liganding to functional groups in proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1991;42:1–76. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60534-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy H. R., Seetharamulu P. Molecular model of the action potential sodium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):508–512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann S. H., Terlau H., Stühmer W., Imoto K., Numa S. Calcium channel characteristics conferred on the sodium channel by single mutations. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):441–443. doi: 10.1038/356441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo P., MacKinnon R. Revealing the architecture of a K+ channel pore through mutant cycles with a peptide inhibitor. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):307–310. doi: 10.1126/science.7716527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkind G. M., Fozzard H. A. A structural model of the tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin binding site of the Na+ channel. Biophys J. 1994 Jan;66(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80746-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lü Q., Miller C. Silver as a probe of pore-forming residues in a potassium channel. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):304–307. doi: 10.1126/science.7716526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura M., Matthews B. W. Control of enzyme activity by an engineered disulfide bond. Science. 1989 Feb 10;243(4892):792–794. doi: 10.1126/science.2916125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Suzuki H., Numa S., Stühmer W. A single point mutation confers tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin insensitivity on the sodium channel II. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 18;259(1):213–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81531-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pakula A. A., Simon M. I. Determination of transmembrane protein structure by disulfide cross-linking: the Escherichia coli Tar receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):4144–4148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.4144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantoliano M. W., Ladner R. C., Bryan P. N., Rollence M. L., Wood J. F., Poulos T. L. Protein engineering of subtilisin BPN': enhanced stabilization through the introduction of two cysteines to form a disulfide bond. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 21;26(8):2077–2082. doi: 10.1021/bi00382a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. J., Wetzel R. Unpaired cysteine-54 interferes with the ability of an engineered disulfide to stabilize T4 lysozyme. Biochemistry. 1986 Feb 11;25(3):733–739. doi: 10.1021/bi00351a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-García M. T., Chiamvimonvat N., Marban E., Tomaselli G. F. Structure of the sodium channel pore revealed by serial cysteine mutagenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jan 9;93(1):300–304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.1.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satin J., Kyle J. W., Chen M., Bell P., Cribbs L. L., Fozzard H. A., Rogart R. B. A mutant of TTX-resistant cardiac sodium channels with TTX-sensitive properties. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1202–1205. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan N., Sowdhamini R., Ramakrishnan C., Balaram P. Conformations of disulfide bridges in proteins. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1990 Aug;36(2):147–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1990.tb00958.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terlau H., Heinemann S. H., Stühmer W., Pusch M., Conti F., Imoto K., Numa S. Mapping the site of block by tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin of sodium channel II. FEBS Lett. 1991 Nov 18;293(1-2):93–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81159-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimmer J. S., Cooperman S. S., Tomiko S. A., Zhou J. Y., Crean S. M., Boyle M. B., Kallen R. G., Sheng Z. H., Barchi R. L., Sigworth F. J. Primary structure and functional expression of a mammalian skeletal muscle sodium channel. Neuron. 1989 Jul;3(1):33–49. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90113-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. A. Additivity of mutational effects in proteins. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 18;29(37):8509–8517. doi: 10.1021/bi00489a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel R., Perry L. J., Baase W. A., Becktel W. J. Disulfide bonds and thermal stability in T4 lysozyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):401–405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G., Sodickson D., Chen T. Y., Jurman M. E. An engineered cysteine in the external mouth of a K+ channel allows inactivation to be modulated by metal binding. Biophys J. 1994 Apr;66(4):1068–1075. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80888-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Z., DeRose E. F., Mullen G. P., Petering D. H., Shaw C. F., 3rd Sequential proton resonance assignments and metal cluster topology of lobster metallothionein-1. Biochemistry. 1994 Aug 2;33(30):8858–8865. doi: 10.1021/bi00196a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]