Abstract
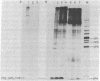
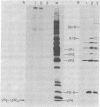
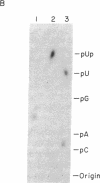
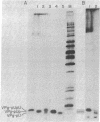
A small nucleotidyl-protein has been synthesized in vitro in a membrane fraction of poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Analyses of the nucleotides and polypeptide have shown that the nucleotidyl-protein is VPg-pUpU: the genome-linked protein of poliovirion RNA covalently bound to the first two 5'-terminal nucleotides of poliovirus RNA. Synthesis of VPg-pUpU in vitro was sensitive to nonionic detergent. We suggest that VPg-pUpU is part of the initiation complex in poliovirus RNA replication in a membranous environment.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler C. J., Elzinga M., Wimmer E. The genome-linked protein of picornaviruses. VIII. Complete amino acid sequence of poliovirus VPg and carboxy-terminal analysis of its precursor, P3-9. J Gen Virol. 1983 Feb;64(Pt 2):349–355. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-2-349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambros V., Baltimore D. Purification and properties of a HeLa cell enzyme able to remove the 5'-terminal protein from poliovirus RNA. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6739–6744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambros V., Pettersson R. F., Baltimore D. An enzymatic activity in uninfected cells that cleaves the linkage between poliovirion RNA and the 5' terminal protein. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1439–1446. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Anti-VPg antibody inhibition of the poliovirus replicase reaction and production of covalent complexes of VPg-related proteins and RNA. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):745–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90279-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Antibodies against the chemically synthesized genome-linked protein of poliovirus react with native virus-specific proteins. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):395–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90357-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Baltimore D. In vitro copying of viral positive strand RNA by poliovirus replicase. Characterization of the reaction and its products. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12359–12366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Tamm I. The role of cytoplasmic membranes in poliovirus biosynthesis. Virology. 1970 Sep;42(1):100–111. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90242-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J. Eukaryotic DNA replication: viral and plasmid model systems. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:901–934. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.004345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Ostrove J. M., Kelly T. J., Jr Initiation of adenovirus DNA replication: detection of covalent complexes between nucleotide and the 80-kilodalton terminal protein. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):265–270. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.265-270.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowie A., Jat P., Kamen R. Determination of sequences at the capped 5' ends of polyoma virus early region transcripts synthesized in vivo and in vitro demonstrates an unusual microheterogeneity. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 5;159(2):225–255. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90494-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford N. M., Baltimore D. Genome-linked protein VPg of poliovirus is present as free VPg and VPg-pUpU in poliovirus-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7452–7455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A., Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Poliovirus replicase: a soluble enzyme able to initiate copying of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A., Zabel P., Baltimore D. Dependence of the activity of the poliovirus replicase on the host cell protein. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):423–429. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90516-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Rothberg P. G., Wimmer E. The fate of VPg during in vitro translation of poliovirus RNA. FEBS Lett. 1981 Sep 28;132(2):219–223. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81164-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsch-Häsler K., Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Replication of picornaviruses. I. Evidence from in vitro RNA synthesis that poly(A) of the poliovirus genome is genetically coded. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1512–1517. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1512-1517.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Ehrenfeld E. Comparison of replication complexes synthesizing poliovirus RNA. Virology. 1981 May;111(1):33–46. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90651-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Baltimore D. Poliovirus polyuridylic acid polymerase and RNA replicase have the same viral polypeptide. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.352-360.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanecak R., Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Proteolytic processing of poliovirus polypeptides: antibodies to polypeptide P3-7c inhibit cleavage at glutamine-glycine pairs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3973–3977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Adler C. J., Rothberg P. G., Martinko J., Nathenson S. G., Wimmer E. The genome-linked protein of picornaviruses. VII. Genetic mapping of poliovirus VPg by protein and RNA sequence studies. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):295–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90137-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Semler B. L., Rothberg P. G., Larsen G. R., Adler C. J., Dorner A. J., Emini E. A., Hanecak R., Lee J. J., van der Werf S. Primary structure, gene organization and polypeptide expression of poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):547–553. doi: 10.1038/291547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. F., Nomoto A., Detjen B. M., Wimmer E. A protein covalently linked to poliovirus genome RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):59–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Detjen B., Pozzatti R., Wimmer E. The location of the polio genome protein in viral RNAs and its implication for RNA synthesis. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):208–213. doi: 10.1038/268208a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg P. G., Harris T. J., Nomoto A., Wimmer E. O4-(5'-uridylyl)tyrosine is the bond between the genome-linked protein and the RNA of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4868–4872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Hanecak R., Dorner L. F., Wimmer E. A membrane-associated precursor to poliovirus VPg identified by immunoprecipitation with antibodies directed against a synthetic heptapeptide. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):405–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90358-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Kitamura N., Rothberg P. G., Wishart W. L., Wimmer E. Poliovirus replication proteins: RNA sequence encoding P3-1b and the sites of proteolytic processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3464–3468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Hanecak R., Dorner L. F., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Poliovirus RNA synthesis in vitro: structural elements and antibody inhibition. Virology. 1983 Apr 30;126(2):624–635. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(83)80018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takegami T., Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Membrane fractions active in poliovirus RNA replication contain VPg precursor polypeptides. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):33–47. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90316-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke T. A., Flanegan J. B. Identification of poliovirus polypeptide P63 as a soluble RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):732–740. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.732-740.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke T. A., Rickles R. J., Flanegan J. B. Genome-length copies of poliovirion RNA are synthesized in vitro by the poliovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4610–4617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vartapetian A. B., Kunin E. V., Chumakov K. M., Bogdanov A. A., Agol V. I. Initsiatsiia sinteza RNK virusa éntsefalomiokardita v beskletochnoi sisteme i vozmozhnoe uchastie v étom protsesse belka VPg. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1982;267(4):963–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer E. Genome-linked proteins of viruses. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):199–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90335-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]