Abstract
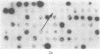
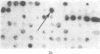
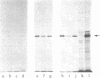
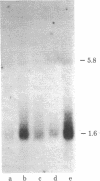
Cloned cDNA sequences of human adenosine deaminase (ADA; adenosine aminohydrolase, EC 3.5.4.4) have been isolated from a cDNA library constructed in bacteriophage lambda gt10. The cDNA for the library was prepared from poly(A)+ RNA isolated from a human T-lymphoblast cell line, CCRF-CEM. The library was initially screened by differential plaque hybridization to labeled cDNA prepared from human T- and B-lymphoblast cell lines with a 21-fold difference in levels of translatable ADA mRNA. Two recombinants containing cloned cDNA sequences for ADA were identified by hybridization-selected translation. Both recombinants contained approximately 1,600 base pairs of inserted human DNA. Restriction maps of the two inserts were not identical. One contained approximately 40 base pairs of additional DNA toward the center of the cDNA. The cloned cDNA specifically hybridized to five fragments generated by HindIII digestion of human genomic DNA. It also hybridized to human lymphoblast RNA species 1.6 and 5.8 kilobases in length. The cDNA was used as a probe to estimate ADA mRNA levels in human lymphoblast cell lines. ADA mRNA levels correlate closely with levels of ADA catalytic activity and ADA protein in cell lines containing structurally normal ADA. A leukemic T-lymphoblast line produced 6 to 9 times as much ADA protein and ADA mRNA as transformed B-lymphoblast lines. Two mutant B-lymphoblast lines from patients with hereditary ADA deficiency contained unstable ADA protein but had 3 to 4 times the normal level of ADA mRNA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian G. S., Hutton J. J. Adenosine deaminase messenger RNAs in lymphoblast cell lines derived from leukemic patients and patients with hereditary adenosine deaminase deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1649–1660. doi: 10.1172/JCI110920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt F. W., Kellems R. E., Bertino J. R., Schimke R. T. Selective multiplication of dihydrofolate reductase genes in methotrexate-resistant variants of cultured murine cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1357–1370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnie G. D., Burns J. H., Wiedemann L. M., Warnock A. M., Tindle R. W., Burnett A. K., Tansey P., Lucie N. P., Robertson M. R. A new approach to the classification of human leukaemias: measurement of the relative abundance of a specific RNA sequence by means of molecular hybridisation. Lancet. 1983 Jan 29;1(8318):197–200. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92584-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennand J., Chinault A. C., Konecki D. S., Melton D. W., Caskey C. T. Cloned cDNA sequences of the hypoxanthine/guanine phosphoribosyltransferase gene from a mouse neuroblastoma cell line found to have amplified genomic sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1950–1954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daddona P. E., Frohman M. A., Kelley W. N. Human adenosine deaminase and its binding protein in normal and adenosine deaminase-deficient fibroblast cell strains. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5681–5687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daddona P. E. Human adenosine deaminase. Properties and turnover in cultured T and B lymphoblasts. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12496–12501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giblett E. R., Anderson J. E., Cohen F., Pollara B., Meuwissen H. J. Adenosine-deaminase deficiency in two patients with severely impaired cellular immunity. Lancet. 1972 Nov 18;2(7786):1067–1069. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92345-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn R., Martiniuk F., Roegner-Maniscalco V., Ellenbogen A., Perignon J. L., Jenkins T. Genetic heterogeneity in partial adenosine deaminase deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1887–1892. doi: 10.1172/JCI110944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn R., Roegner V., Jenkins T., Seaman C., Piomelli S., Borkowsky W. Erythrocyte adenosine deaminase deficiency without immunodeficiency. Evidence for an unstable mutant enzyme. J Clin Invest. 1979 Oct;64(4):1130–1139. doi: 10.1172/JCI109552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyt M. A., Knight D. M., Das A., Miller H. I., Echols H. Control of phage lambda development by stability and synthesis of cII protein: role of the viral cIII and host hflA, himA and himD genes. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):565–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90312-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locker J. Analytical and preparative electrophoresis of RNA in agarose-urea. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 1;98(2):358–367. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90154-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott R. P., Tritsch G. L., Formeister J. F. Adenosine deaminase and nucleoside phosphorylase activities in normal human blood mononuclear cell subpopulations. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Nov;42(2):303–307. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., van deSande H. Chain length determination of small double- and single-stranded DNA molecules by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 26;14(17):3787–3794. doi: 10.1021/bi00688a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. W., Jr, Gelfand E. W. Biochemistry of diseases of immunodevelopment. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:845–877. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. W., Konecki D. S., Ledbetter D. H., Hejtmancik J. F., Caskey C. T. In vitro translation of hypoxanthine/guanine phosphoribosyltransferase mRNA: characterization of a mouse neuroblastoma cell line that has elevated levels of hypoxanthine/guanine phosphoribosyltransferase protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6977–6980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parnes J. R., Velan B., Felsenfeld A., Ramanathan L., Ferrini U., Appella E., Seidman J. G. Mouse beta 2-microglobulin cDNA clones: a screening procedure for cDNA clones corresponding to rare mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2253–2257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. F., Seegmiller J. E. Adenosine deaminase deficiency and severe combined immunodeficiency disease. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1980;51:167–210. doi: 10.1002/9780470122969.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung R., Silber R., Quagliata F., Conklyn M., Gottesman J., Hirschhorn R. Adenosine deaminase activity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Relationship to B- and T-cell subpopulations. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):756–761. doi: 10.1172/JCI108334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Padgett R. A., Stark G. R. Gene amplification causes overproduction of the first three enzymes of UMP synthesis in N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate-resistant hamster cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8679–8689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiginton D. A., Coleman M. S., Hutton J. J. Purification, characterization and radioimmunoassay of adenosine deaminase from human leukaemic granulocytes. Biochem J. 1981 May 1;195(2):389–397. doi: 10.1042/bj1950389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiginton D. A., Hutton J. J. Immunoreactive protein in adenosine deaminase deficient human lymphoblast cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3211–3217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida A. Amino acid substitution (histidine to tyrosine) in a glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase variant (G6PD Hektoen) associated with over-production. J Mol Biol. 1970 Sep 28;52(3):483–490. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90414-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]