Abstract
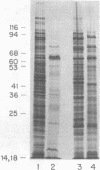
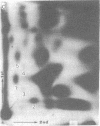
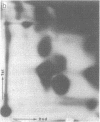
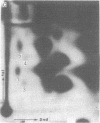
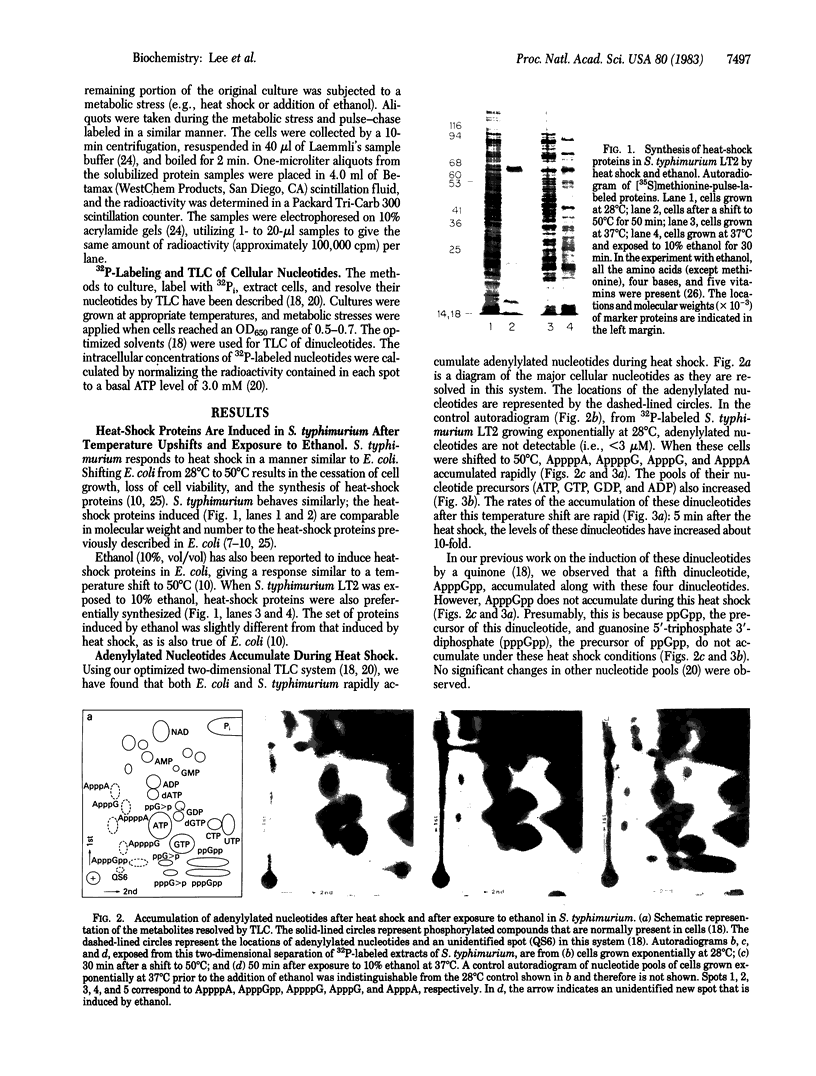
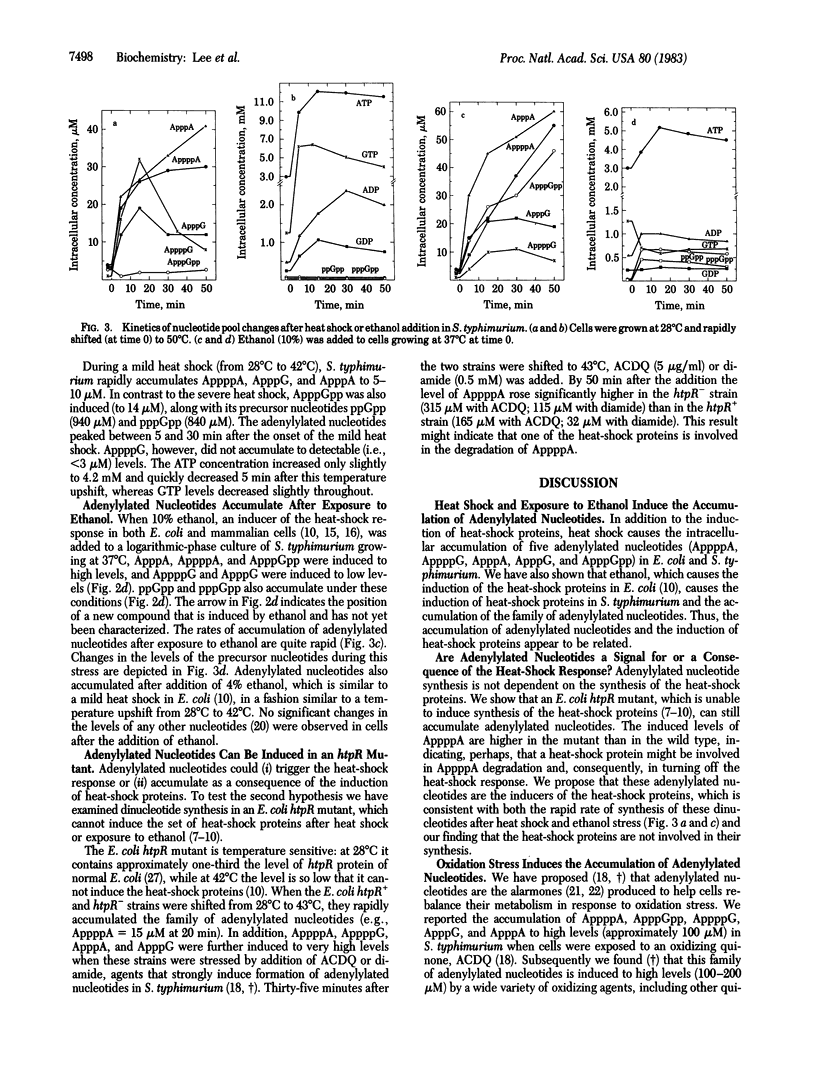
Salmonella typhimurium LT2 induces a set of heat-shock proteins analogous to those found previously in Escherichia coli. These are virtually the only proteins synthesized after a temperature shift from 28 degrees C to 50 degrees C. Using a two-dimensional thin-layer chromatographic system developed to resolve adenylylated nucleotides, we have found that S. typhimurium and E. coli accumulate P1,P4-diadenosine-5'-tetraphosphate (AppppA), P1-(adenosine-5')-P3-(guanosine-3'-diphosphate-5')-triphosphate (ApppGpp), P1-(adenosine-5')-P4-(guanosine-5')-tetraphosphate (AppppG), P1-(adenosine-5')-P3-(guanosine-5')-triphosphate (ApppG), and P1,P3-diadenosine-5'-triphosphate (ApppA) after heat shock. These same adenylylated nucleotides accumulate after exposure to ethanol, an agent also known to induce the heat-shock response in a variety of cells. AppppA, ApppGpp, AppppG, ApppG, and ApppA were previously shown to accumulate under conditions of oxidation stress. We proposed that these adenylylated nucleotides may be alarmones--i.e., regulatory molecules, alerting cells to the onset of oxidation stress. The finding that these dinucleotides accumulate in response to heat shock suggests that oxidation and heat shock have a common physiological effect on cells. We hypothesize that these dinucleotides signal the onset of these stresses and trigger the "heat-shock response."
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames B. N. Dietary carcinogens and anticarcinogens. Oxygen radicals and degenerative diseases. Science. 1983 Sep 23;221(4617):1256–1264. doi: 10.1126/science.6351251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames B. N., Tsang T. H., Buck M., Christman M. F. The leader mRNA of the histidine attenuator region resembles tRNAHis: possible general regulatory implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5240–5242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M., Bonner J. J. The induction of gene activity in drosophilia by heat shock. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckman D., Cooper S. Temperature-sensitive nonsense mutations in essential genes of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1336–1342. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1336-1342.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanquet S., Plateau P., Brevet A. The role of zinc in 5',5'-diadenosine tetraphosphate production by aminoacyl-transfer RNA synthetases. Mol Cell Biochem. 1983;52(1):3–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00230583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. R., Ames B. N. Complete analysis of cellular nucleotides by two-dimensional thin layer chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9759–9769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. R., Ames B. N. ZTP (5-amino 4-imidazole carboxamide riboside 5'-triphosphate): a proposed alarmone for 10-formyl-tetrahydrofolate deficiency. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):929–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90455-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S., Ruettinger T. A temperature sensitive nonsense mutation affecting the synthesis of a major protein of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Aug 5;139(2):167–176. doi: 10.1007/BF00264696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Halbrook J. Inducible repair of oxidative DNA damage in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1983 Aug 4;304(5925):466–468. doi: 10.1038/304466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiDomenico B. J., Bugaisky G. E., Lindquist S. The heat shock response is self-regulated at both the transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):593–603. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90315-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drahos D. J., Hendrix R. W. Effect of bacteriophage lambda infection on synthesis of groE protein and other Escherichia coli proteins. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):1050–1063. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.1050-1063.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flodgaard H., Klenow H. Abundant amounts of diadenosine 5',5"'-P1,P4-tetraphosphate are present and releasable, but metabolically inactive, in human platelets. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 15;208(3):737–742. doi: 10.1042/bj2080737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridovich I. The biology of oxygen radicals. Science. 1978 Sep 8;201(4359):875–880. doi: 10.1126/science.210504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goerlich O., Foeckler R., Holler E. Mechanism of synthesis of adenosine(5')tetraphospho(5')adenosine (AppppA) by aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Aug;126(1):135–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06757.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt F. Diadenosine 5',5'''-P1,P4-tetraphosphate triggers initiation of in vitro DNA replication in baby hamster kidney cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):371–375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirshfield I. N., Zamecnik P. C. Thiosine-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 with growth-medium-dependent lysl-tRNA synthetase activity. I. Isolation and physiological characterization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 15;259(3):330–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khandjian E. W., Türler H. Simian virus 40 and polyoma virus induce synthesis of heat shock proteins in permissive cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;3(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochan J., Murialdo H. Stimulation of groE synthesis in Escherichia coli by bacteriophage lambda infection. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):1166–1170. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.1166-1170.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosower E. M., Kosower N. S. Lest I forget thee, glutathione. Nature. 1969 Oct 11;224(5215):117–120. doi: 10.1038/224117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. C., Bochner B. R., Ames B. N. Diadenosine 5',5"'-P1,P4-tetraphosphate and related adenylylated nucleotides in Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6827–6834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepock J. R. Involvement of membranes in cellular responses to hyperthermia. Radiat Res. 1982 Dec;92(3):433–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson W., Oppermann H., Jackson J. Transition series metals and sulfhydryl reagents induce the synthesis of four proteins in eukaryotic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980;606(1):170–180. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G. C., Hahn G. M. Ethanol-induced tolerance to heat and to adriamycin. Nature. 1978 Aug 17;274(5672):699–701. doi: 10.1038/274699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G. C. Induction of thermotolerance and enhanced heat shock protein synthesis in Chinese hamster fibroblasts by sodium arsenite and by ethanol. J Cell Physiol. 1983 May;115(2):116–122. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041150203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G. C., Werb Z. Correlation between synthesis of heat shock proteins and development of thermotolerance in Chinese hamster fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3218–3222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maness P. F., Perry M. E., Levy B. T. P1,P4-Di(adenosine-5')tetraphosphate inhibits phosphorylation of immunoglobulin G by Rous sarcoma virus pp60src. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4055–4058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A. Selective modification of glutathione metabolism. Science. 1983 Apr 29;220(4596):472–477. doi: 10.1126/science.6836290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchel R. E., Morrison D. P. Heat-shock induction of ionizing radiation resistance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and correlation with stationary growth phase. Radiat Res. 1982 May;90(2):284–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. B., Russo A., Kinsella T. J., Glatstein E. Glutathione elevation during thermotolerance induction and thermosensitization by glutathione depletion. Cancer Res. 1983 Mar;43(3):987–991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A., Lau E. T. Molecular cloning and expression of a gene that controls the high-temperature regulon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):597–603. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.597-603.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A. Positive regulatory gene for temperature-controlled proteins in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 May 29;100(2):894–900. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80257-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Induction of the synthesis of a 70,000 dalton mammalian heat shock protein by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):913–919. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90453-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie A. Determination of diadenosine tetraphosphate (Ap4A) levels in subpicomole quantities by a phosphodiesterase luciferin--luciferase coupled assay: application as a specific assay for diadenosine tetraphosphatase. Anal Biochem. 1981 Aug;115(2):302–307. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann H., Levinson W., Bishop J. M. A cellular protein that associates with the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus is also a heat-shock protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1067–1071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plesset J., Palm C., McLaughlin C. S. Induction of heat shock proteins and thermotolerance by ethanol in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Oct 15;108(3):1340–1345. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)92147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst H., Hamprecht K., Gekeler V. Replicon initiation frequency and intracellular levels of ATP, ADP, AMP and of diadenosine 5',5'''-P1,P4-tetraphosphate in ehrlich ascites cells cultured aerobically and anaerobically. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jan 27;110(2):688–693. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91204-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapaport E., Svihovec S. K., Zamecnik P. C. Relationship of the first step in protein synthesis to ppGpp: formation of A(5')ppp(5')Gpp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2653–2657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapaport E., Zamecnik P. C. Presence of diadenosine 5',5''' -P1, P4-tetraphosphate (Ap4A) in mamalian cells in levels varying widely with proliferative activity of the tissue: a possible positive "pleiotypic activator". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3984–3988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ropp M., Courgeon A. M., Calvayrac R., Best-Belpomme M. The possible role of the superoxide ion in the induction of heat-shock and specific proteins in aerobic Drosophila cells during return to normoxia after a period of anaerobiosis. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;61(6):456–461. doi: 10.1139/o83-061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydström J. Energy-linked nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Oct 5;463(2):155–184. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(77)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saavedra R. A., Anderson G. R. A cancer-associated lactate dehydrogenase is expressed in normal retina. Science. 1983 Jul 15;221(4607):291–292. doi: 10.1126/science.6857286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens J. C., Artz S. W., Ames B. N. Guanosine 5'-diphosphate 3'-diphosphate (ppGpp): positive effector for histidine operon transcription and general signal for amino-acid deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4389–4393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thor H., Smith M. T., Hartzell P., Bellomo G., Jewell S. A., Orrenius S. The metabolism of menadione (2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone) by isolated hepatocytes. A study of the implications of oxidative stress in intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12419–12425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly K., McKittrick N., Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C. The dnaK protein modulates the heat-shock response of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90396-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly K., VanBogelen R. A., Georgopoulos C., Neidhardt F. C. Identification of the heat-inducible protein C15.4 as the groES gene product in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1505–1507. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1505-1507.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanBogelen R. A., Vaughn V., Neidhardt F. C. Gene for heat-inducible lysyl-tRNA synthetase (lysU) maps near cadA in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):1066–1068. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.1066-1068.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L., Kodaira R., Neidhardt F. C. Physiological regulation of a decontrolled lac operon. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):212–222. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.212-222.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch W. J., Garrels J. I., Thomas G. P., Lin J. J., Feramisco J. R. Biochemical characterization of the mammalian stress proteins and identification of two stress proteins as glucose- and Ca2+-ionophore-regulated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7102–7111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westman G., Marklund S. L. Diethyldithiocarbamate, a superoxide dismutase inhibitor, decreases the radioresistance of Chinese hamster cells. Radiat Res. 1980 Aug;83(2):303–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebauer K., Ogilvie A., Kersten W. The molecular basis of leucine auxotrophy of quinone-treated Escherichia coli. Active site-directed modification of leucyl-tRNA synthetase by 6-amino-7-chloro-5,8-dioxoquinoline. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):327–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittwer A. J. Specific incorporation of selenium into lysine- and glutamate- accepting tRNAs from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8637–8641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamori T., Ito K., Nakamura Y., Yura T. Transient regulation of protein synthesis in Escherichia coli upon shift-up of growth temperature. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1133–1140. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1133-1140.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamori T., Yura T. Genetic control of heat-shock protein synthesis and its bearing on growth and thermal resistance in Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):860–864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamecnik P. C., Rapaport E., Baril E. F. Priming of DNA synthesis by diadenosine 5',5"'-P1,P4-tetraphosphate with a double-stranded octadecamer as a template and DNA polymerase alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1791–1794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]