Abstract
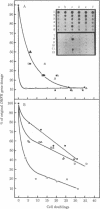
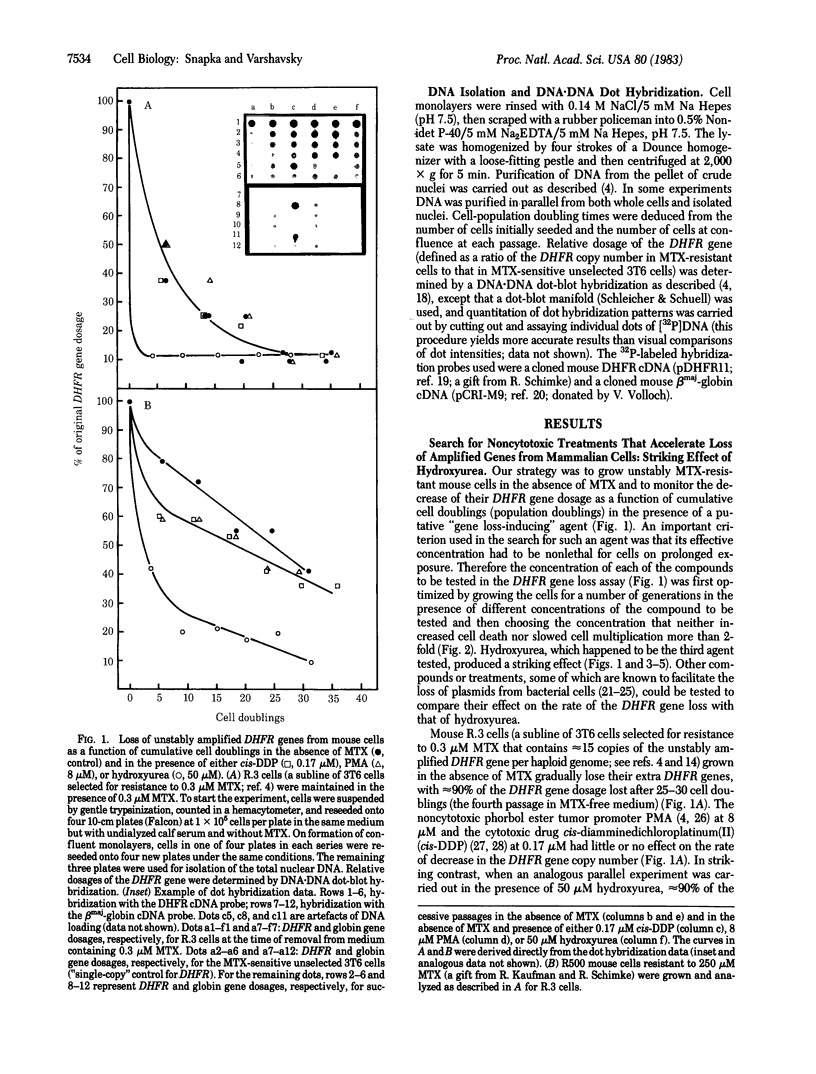
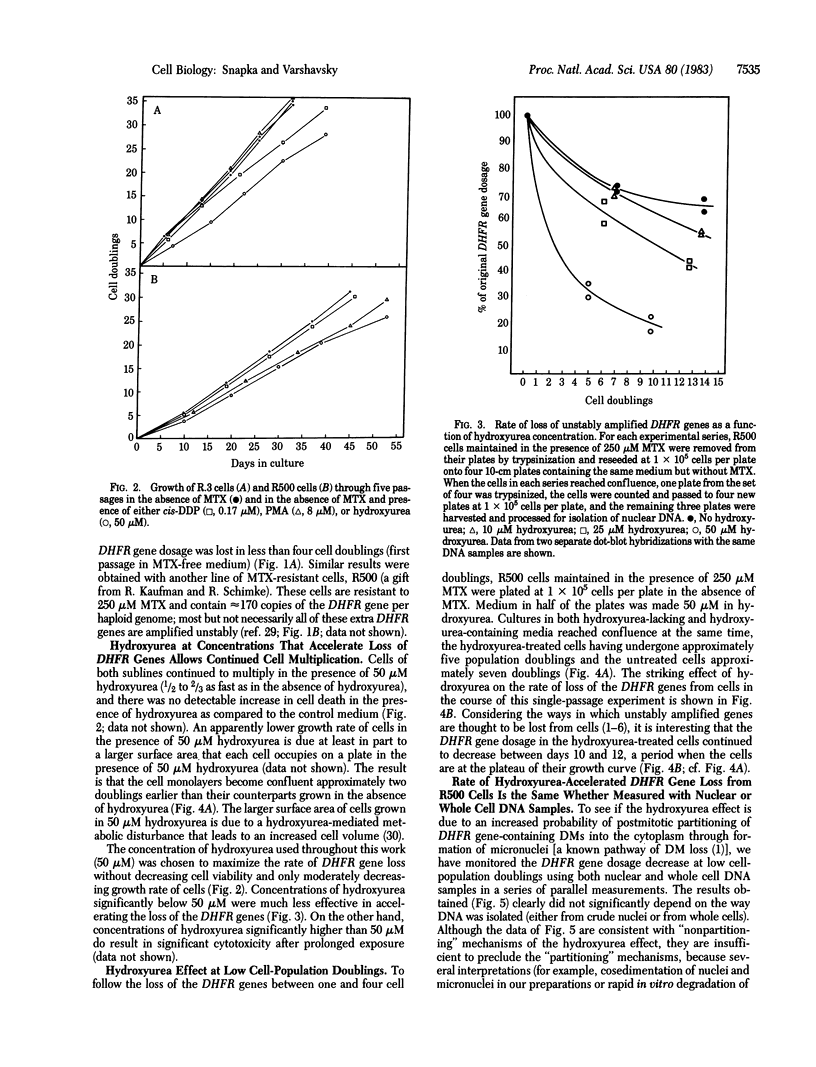
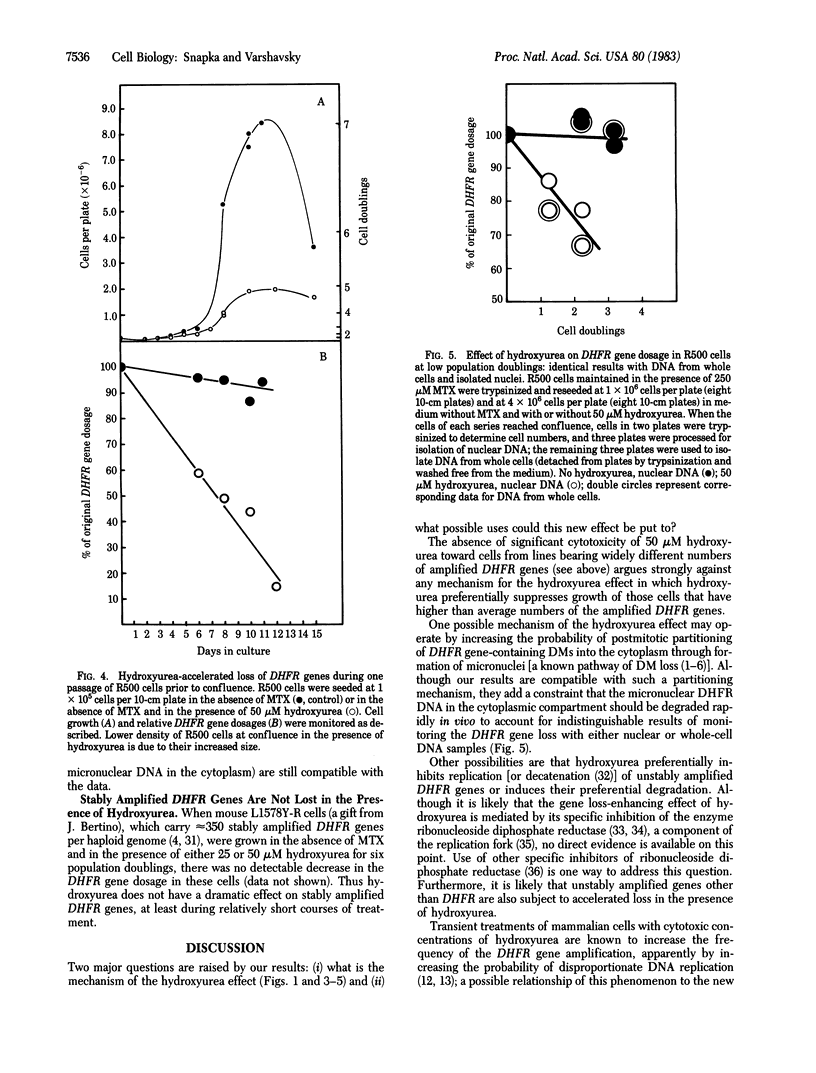
Previous work has shown that mammalian cells that carry unstably amplified genes for dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) gradually lose the amplified DHFR genes when grown in the absence of the DHFR inhibitor methotrexate (MTX). Unstably amplified genes occur on small acentric chromosomes called double minutes (DMs) or even smaller chromatin fragments, in contrast to stably amplified genes, which reside in centromere-containing chromosomes. We have found that the rate of loss of the unstably amplified DHFR genes can be greatly oncreased by growing the cells in the presence of a nonlethal concentration of hydroxyurea. For example, in one MTX-resistant subline studied, approximately equal to 90% of the original DHFR gene dosage is lost in 25-30 cell doublings in the absence of MTX. The same degree of loss is achieved, however, in less than 4 doublings if cells are grown in the presence of 50 microM hydroxyurea. This new effect of hydroxyurea does not appear to be due to changes in plating efficiency or selective cytotoxicity. In particular, no increase in cell death occurs at 50 microM hydroxyurea, and cells continue to multiply, albeit 1/2 to 2/3 as fast as in the absence of hydroxyurea. The ability to selectively accelerate the loss of amplified genes from mammalian cells as shown in the present work may have important implications both for the problem of drug resistance in cancer chemotherapy and for curing mammalian cells of extrachromosomally maintained DNA genomes of pathogenic viruses.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker P. E. Double minutes in human tumor cells. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1982 Feb;5(1):81–94. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(82)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsoum J., Varshavsky A. Mitogenic hormones and tumor promoters greatly increase the incidence of colony-forming cells bearing amplified dihydrofolate reductase genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5330–5334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouanchaud D. H., Scavizzi M. R., Chabbert Y. A. Elimination by ethidium bromide of antibiotic resistance in enterobacteria and staphylococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Dec;54(3):417–425. doi: 10.1099/00221287-54-3-417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. C., Beverley S. M., Schimke R. T. Relationship of amplified dihydrofolate reductase genes to double minute chromosomes in unstably resistant mouse fibroblast cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;1(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.12.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. C., Tlsty T. D., Schimke R. T. Enhancement of methotrexate resistance and dihydrofolate reductase gene amplification by treatment of mouse 3T6 cells with hydroxyurea. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1097–1107. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaube S., Murphy M. L. The effects of hydroxyurea and related compounds on the rat fetus. Cancer Res. 1966 Jul;26(7):1448–1457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S., Groudine M. Amplification of endogenous myc-related DNA sequences in a human myeloid leukaemia cell line. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):679–681. doi: 10.1038/298679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell J. K. Double minutes and homogeneously staining regions: gene amplification in mammalian cells. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:21–59. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.000321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danilevskaya O. N., Gragerov A. I. Curing of Escherichia coli K12 plasmids by coumermycin. Mol Gen Genet. 1980 Apr;178(1):233–235. doi: 10.1007/BF00267235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L., O'Brien T. G., Baird W. M. Tumor promoters and the mechanism of tumor promotion. Adv Cancer Res. 1980;32:1–74. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60360-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolnick B. J., Berenson R. J., Bertino J. R., Kaufman R. J., Nunberg J. H., Schimke R. T. Correlation of dihydrofolate reductase elevation with gene amplification in a homogeneously staining chromosomal region in L5178Y cells. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):394–402. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducore J. M., Erickson L. C., Zwelling L. A., Laurent G., Kohn K. W. Comparative studies of DNA cross-linking and cytotoxicity in Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines treated with cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) and L-phenylalanine mustard. Cancer Res. 1982 Mar;42(3):897–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engström Y., Eriksson S., Thelander L., Akerman M. Ribonucleotide reductase from calf thymus. Purification and properties. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 10;18(14):2941–2948. doi: 10.1021/bi00581a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn F. E., Ciak J. Elimination of resistance determinants from R-factor R1 by intercalative compounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jan;9(1):77–80. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlin J. L., Biedler J. L. Replication pattern of a large homogenously staining chromosome region in antifolate-resistant Chinese hamster cell lines. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Apr;107(1):101–114. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041070112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Schimke R. T. Amplification and loss of dihydrofolate reductase genes in a Chinese hamster ovary cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;1(12):1069–1076. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.12.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakoff I. H., Brown N. C., Reichard P. Inhibition of ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase by hydroxyurea. Cancer Res. 1968 Aug;28(8):1559–1565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levan G., Mandahl N., Bengtsson B. O., Levan A. Experimental elimination and recovery of double minute chromosomes in malignant cell populations. Hereditas. 1977;86(1):75–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1977.tb01214.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters J., Keeley B., Gay H., Attardi G. Variable content of double minute chromosomes is not correlated with degree of phenotype instability in methotrexate-resistant human cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 May;2(5):498–507. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.5.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowell P. C. The clonal evolution of tumor cell populations. Science. 1976 Oct 1;194(4260):23–28. doi: 10.1126/science.959840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunberg J. H., Kaufman R. J., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N., Schimke R. T. Structure and genomic organization of the mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90510-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poste G., Fidler I. J. The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):139–146. doi: 10.1038/283139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. M., Buck L. B., Axel R. A structure for amplified DNA. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):53–63. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90334-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochaix J. D., Rougeon F., Mach B. Electron microscope analysis of mouse and rabbit globin and immunoglobulin gene sequences. Gene. 1978 Feb;3(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato A., Cory J. G. Evaluation of combinations of drugs that inhibit Ehrlich tumor cell ribonucleotide reductase. Cancer Res. 1981 May;41(5):1637–1641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T., Brown P. C., Kaufman R. J., McGrogan M., Slate D. L. Chromosomal and extrachromosomal localization of amplified dihydrofolate reductase genes in cultured mammalian cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):785–797. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Alitalo K., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., George D. A cellular oncogene (c-Ki-ras) is amplified, overexpressed, and located within karyotypic abnormalities in mouse adrenocortical tumour cells. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):497–501. doi: 10.1038/303497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair W. K. Hydroxyurea: effects on Chinese hamster cells grown in culture. Cancer Res. 1967 Feb;27(2):297–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Mahowald A. P. Amplification of genes for chorion proteins during oogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1096–1100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundin O., Varshavsky A. Arrest of segregation leads to accumulation of highly intertwined catenated dimers: dissection of the final stages of SV40 DNA replication. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):659–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90173-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomoeda M., Inuzuka M., Kubo N., Nakamura S. Effective elimination of drug resistance and sex factors in Escherichia coli by sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):1078–1089. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.1078-1089.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turek L. P., Byrne J. C., Lowy D. R., Dvoretzky I., Friedman R. M., Howley P. M. Interferon induces morphologic reversion with elimination of extrachromosomal viral genomes in bovine papillomavirus-transformed mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7914–7918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. On the possibility of metabolic control of replicon "misfiring": relationship to emergence of malignant phenotypes in mammalian cell lineages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3673–3677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. Phorbol ester dramatically increases incidence of methotrexate-resistant mouse cells: possible mechanisms and relevance to tumor promotion. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90074-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C., Swartz M. N., McHugh G. L. Antagonism of the B subunit of DNA gyrase eliminates plasmids pBR322 and pMG110 from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):338–344. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.338-344.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachow K. R., Ostrow R. S., Bender M., Watts S., Okagaki T., Pass F., Faras A. J. Detection of human papillomavirus DNA in anogenital neoplasias. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):771–773. doi: 10.1038/300771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- veer Reddy G. P., Pardee A. B. Coupled ribonucleoside diphosphate reduction, channeling, and incorporation into DNA of mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12526–12531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]