Abstract
Animals have co-evolved with mutualistic microbial communities, known as the microbiota, which are essential for organ development and function. We hypothesize that modern animal husbandry practices exert an impact on the intestinal microbiota. In this study, we compared the structure of the fecal microbiota between feral and domestic goats using the G2 PhyloChip and assessed the presence of five tetracycline resistance genes [tet(M), tet(S), tet(O), tet(Q) and tet(W)] by PCR. Feces were collected from 10 goats: 5 domestic from a farm in the main island of Puerto Rico and 5 feral from the remote dry island of Mona. There were 42 bacterial phyla from 153 families detected in the goats’ feces. A total of 84 PhyloChip-OTUs were different in the fecal microbiota of feral and domestic goat. Both feral and domestic goats carried antibiotic resistance genes tet(O) and tet(W), but domestic goats additionally carried tet(Q). Diet, host genetics and antibiotic exposure are likely determinant factors in shaping the intestinal microbiota and may explain the differences observed between feral and domestic goats fecal microbiota.
Keywords: feral, domestic, microbiome, antibiotic, resistance
1. Introduction
Animals have co-evolved with a microbial component that outnumbers the cells in the body of the host [1]. The microbiota is known to provide genes that contribute to important functions in the colonized organs, ranging from digestion [2], to protection against pathogens [3], development of the immune system [4], and endocrine functions [5,6].
Numerous selective forces have influenced microbial-host co-evolution shaping gut microbial diversity. Several factors may explain variations of the gut microbiota between individuals, including genotype [7], immune system [8], diet [9] and the initial colonizing microbial—founder-communities [10]. Domestication of animals during the last 10,000 years [11] has likely had an important effect in shaping the genomes of both hosts [12,13] and their microbes. Antibiotics—including tetracyclines, bacitracin, erythromycin, lincomycin, neomycin, penicillin, streptomycin, tylosin and virginiamycin—have been used in intensive agricultural systems [14] for prophylaxis and growth promotion [15]. Tetracycline is one of the most commonly used antibiotic, because of its low price and broad-spectrum activity. In 1997, the United States used a total of 2,294 tons of Tetracycline in the veterinary sector alone.
We hypothesize that domestication has had an impact on the microbiome of animals. The Spaniards introduced goats and pigs to the Americas nearly five centuries ago [16,17], and feral animals remain in several Caribbean islands without domestication pressures. We predict that, in relation to domestic goats, feral goats have different fecal bacterial communities and fewer antibiotic resistance genes. We also expect that community distances within each group are lower than between the two groups. Artificial diets [18], herd artificial selection, and most importantly, antibiotic use [19] might have impacted the microbiota of domestic animals. To test our hypothesis, we determined the structure of the fecal microbiota and assessed the presence of some tetracycline resistance genes in feral and domestic goats.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Fecal Bacterial Community Structures Differ Between Domestic and Feral Goats
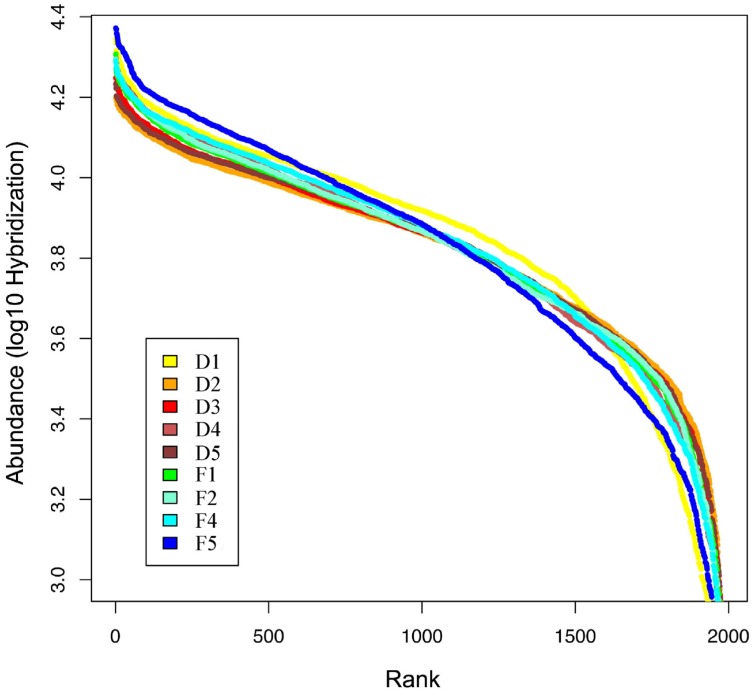
We used a high-density 16S rDNA microarray, the PhyloChip, to study the intestinal bacterial community structure of domestic and feral goats and despite the low number of animals one (goat D1) appears to be an outlier. The PhyloChip identified bacteria belonging to 42 phyla from 153 families (Table 1 and Table S1), with many OTUs detected in the Firmicutes (35%), Proteobacteria (33%), and Actinobacteria (9%) (Figure 1). Globally, at the phylum level, the composition of the bacterial community in goat feces appeared similar among all goats, regardless lifestyle (Figure 1), and to the fecal bacterial composition in other mammals [1]. Similarities at the phylum level are consistent with those at the OTU-level, also showing no differences in bacterial rank abundance between goat groups (Figure S1).
Table 1.
Number of bacterial taxonomic groups (OTUs ± s.e.) in feces from feral and domestic goats.
| Taxonomic level | Feral goats (n = 4) | Domestic goats (n = 5) | Total N |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phylum | 38 ± 1 | 40 ± 1 | 42 |
| Class | 45 ± 1 | 48 ± 1 | 52 |
| Order | 73 ± 2 | 76 ± 3 | 92 |
| Family | 157 ± 1 | 132 ± 4 | 153 |
| Subfamily | 290 ± 28 | 335 ± 46 | 548 |
| OTUs | 1,121 ± 47 | 1,268 ± 74 | 1,982 |
Figure 1.
Richness distribution of the 1,982 OTUs in 42 bacterial phyla among the feces of five domestic (D) and four feral (F) goats. (A) Abundant phyla. (B) Phyla less represented (i.e., ‘other’).
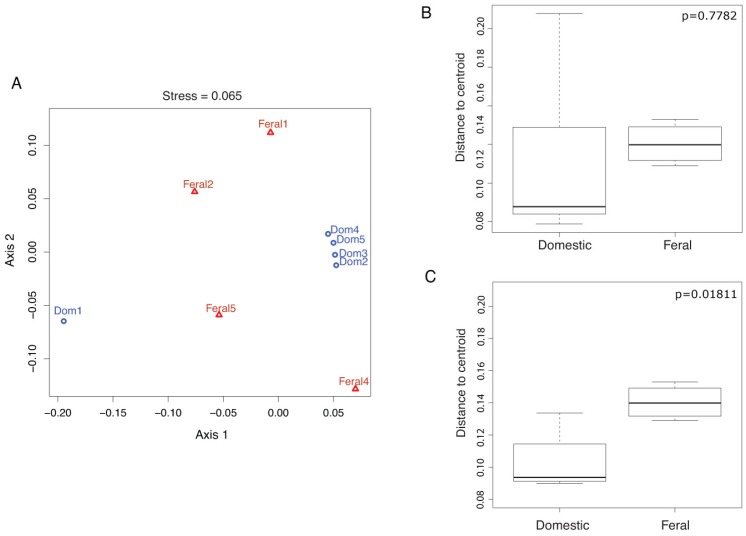
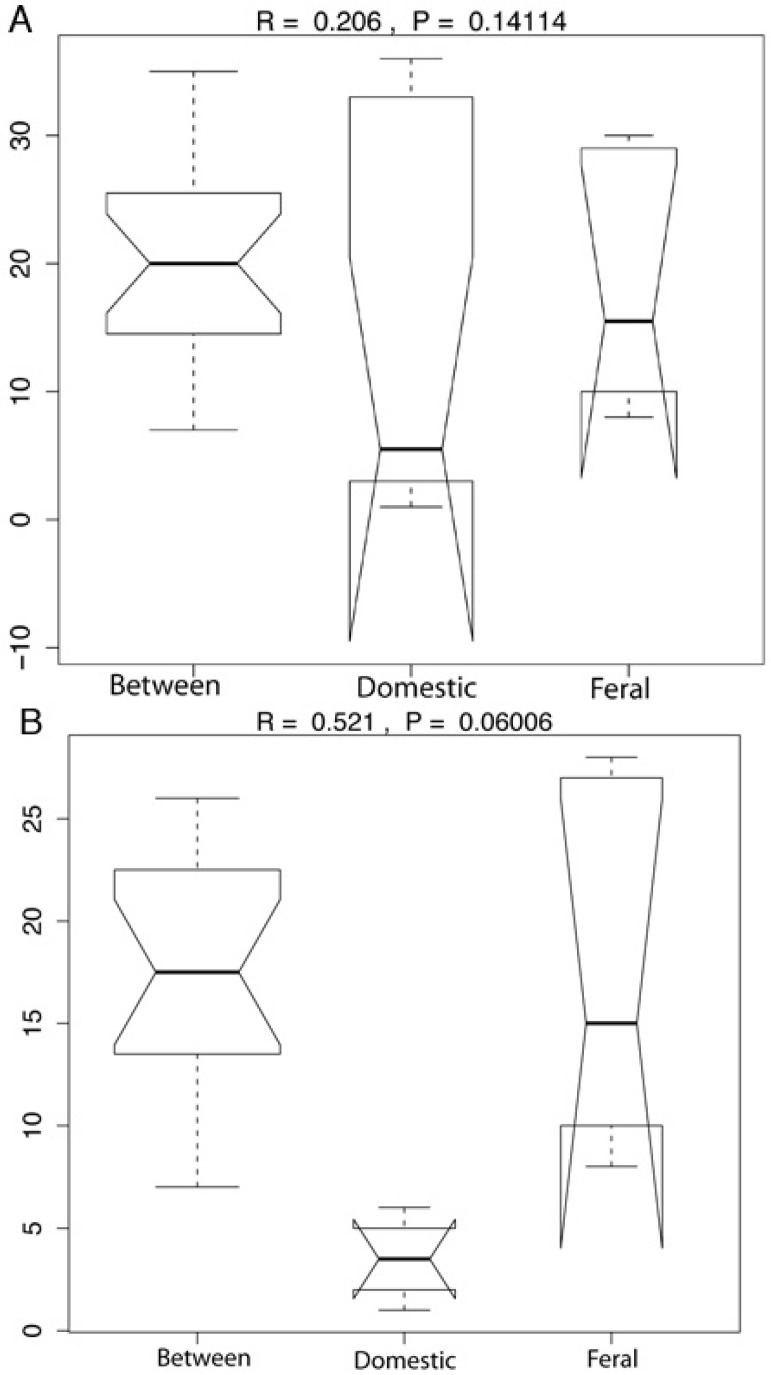
Beta diversity analyses at the PhyloChip-OTU-level using non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS, Figure 2(A)), UniFrac clustering (Figure S2) and PCoA (Figure S3) show that there was a clustering by goat group. However, the UniFrac significance test comparing pairwise distances showed no significant differences (p = 0.36) and the analysis of similarity using dissimilarity ranks, ANOSIM, showed only borderline significance (p = 0.141; R = 0.206), suggesting the lack of substantial dissimilarities between the fecal microbial communities of domestic and feral goats (Figure S4 (A)). Excluding D1 as an outlier (Figure S4 (B)) increases the significance of the inter-group differences (p = 0.06; R = 0.521), suggesting that inter-individual distances between goat groups are higher than those within each group.
Figure 2.
Bacterial Community Structure. (A) Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) of community structure in feral and domesticated goats at the PhyloChip-OTU-level; blue circles represent the domestic animals, while red triangles represent feral goats. The stress value is presented as a metaMDS stress. (B) Analyses of dispersion for the communities within each animal group. (C) Analyses of dispersion for each goat group without the domestic outlier Dom1.
The results of analysis of dispersion (Figure 2(B, C)) showed higher variance in the domestic goats group (Figure 2(B)). However, when excluding the outlier domestic goat (Figure 2(C)) the group differences appear largely due to the communities of domestic goats being less variable than those of feral goats. Clostridiaceae, Bacillaceae, Lachnospiraceae and Enterobacteriaceae OTUs were the most variable families detected among feral goats that contribute to a higher variance in feral, than domestic goats.
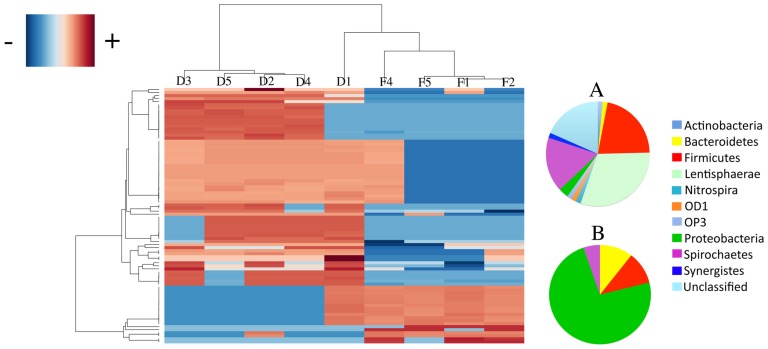
To detect specific taxa responsible for suggested group differences we performed an ANOVA test (based on the quality of the means of richness and relative OTU abundance), which indicated 84 (4.2%) PhyloChip-OTUs accounting for group differences (Figure 3; Table S2). The differing OTUs belonged to 34 families and 11 phyla (Table S3). Domestic goats had higher representation of 28 of the 34 families that differed between feral and domestic goats. Bacterial families overrepresented in domestic goats belonged to Actinobacteria (7 of 7 families), Bacteroidetes (2 of 3 families), Firmicutes (4 of 4 families) and Proteobacteria (9 of 13 families), among others (Table S3). Feral goats were enriched in Proteobacteria (5 of 13 families), Bacteroidetes (1 of 3 families) and Nitrospira [(1 of 1 family); (Table S3)].
Figure 3.
Hierarchical clustering and heatmap of the 84 OTUs that significantly differ between feral and domesticated goats. On the right, the pie charts depict phylum level distributions between bacterial taxa that were highly abundant in domestic (A) and in feral (B) goats.
2.2. Diet and Selective Breeding Might Affect Gut Bacterial Community Structure
Environmental factors such as diet [9] and genetic factors [7] might underlie the microbiome differences in the gut communities of feral and domestic goats. Diet is an important determinant of the structure of intestinal communities [20]. Feral ungulates are browsers that consume 86 plant species in Mona island, mostly leguminous vines, canopy species or tree species from the intermediate forest stratum [21], while domestic goats, however, are fed hay and animal feedstuff. The exclusive presence of Prevotellaceae OTUs in feral goats (Table S3), which include fiber-degrading bacteria, may be related to the natural plant-based diet with a content of hemicellulose higher than the artificial feedstuff consumed by the domestic goats. The greater abundance of Bradyrhizobiaceae (nitrogen fixing soil bacteria) and Nitrospiraceae (nitrifying bacteria) OTUs in feral goats (Table S3) is consistent with the grazing of these animals (in Mona island), with possible ingestion of legume plants and soil, which may contain these bacterial groups. Other factors affecting the animal microbiome might include climate and animal ranges. Animals in Mona Island exercise freely, and are exposed directly to the harsh climate conditions of a desert island, which might lead to dehydration. In contrast, domestic animals are confined, and provided with shelter, food and water.
In addition, geographical isolation of feral goats in Mona Island might have led to inbreeding and the consequent decrease in genetic diversity of their gut microbial communities, in relation to domestic goats. Host genetics has been altered in domestic goats, since breeders select individuals with improved production performance [12]. The evolutionary development and domestication processes determine the genetic diversity of animal species [13].
2.3. Goat’s Gut Bacteria as a Reservoir of Antibiotic Resistance Genes
In our study, all animals harbored fecal tet(O) and tet(W) genes (both in the digestive tract of swine and cows [22]; Table 2). The exclusive presence of tet(Q) in domestic goats is consistent with higher antibiotic exposure in farm animals. Interestingly, tet(M), found in human gut bifidobacteria [23], pig gut streptococci [22] and cow rumen bacteria [22], was absent in all goats in this study. They also lacked tet(S), a gene typical of human oral bacteria [24].
Table 2.
Detection of Tetracycline resistance genes in feces from feral and domestic goats.
| Goats | tet(M) | tet(S) | tet(O) | tet(Q) | tet(W) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feral (n = 5) | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 5 |
| Domestic (n = 5) | 0 | 0 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
The results of this study are consistent with those in other studies comparing captive and feral [25] or wild animals [26,27], showing that domestic or urban animals have higher antibiotic resistance. The presence of antibiotic resistant bacteria in wild and feral animals [25,26,28,29] suggests that either the natural baseline of antibiotic resistance in pristine environments is not zero or that the wild environments are not completely pristine. However, antibiotics are not the only compounds that select for antibiotic resistance genes in bacteria. Bioactive compounds like Cu [30] have been found to co-select for tetracycline resistant bacteria isolated from soil.
Antibiotics can alter the intestinal environment, not only through their direct effect on bacteria, but also by affecting gut physiology. Depletion of bacteria and their microbial products that feed the colonocytes, can lead to thinning of the intestinal wall and to abnormal development of the intestine [31]. Antibiotic administration has been shown to result in a decrease in overall richness of the bacterial gastrointestinal communities in mice [19].
The increase in antibiotic resistance genes in the past couple of decades has been attributed to the use of antibiotics, since bacteria develop resistance when exposed to low antibiotic doses [32]. This and many other studies confirm that antibiotic resistance genes (and resistant populations) persist in the mammalian intestinal tracts even in the absence of antibiotics. The mechanisms for the persistence of these reservoirs are not clear, but it appears that the benefits for the survival of bacterial species are worth the costs.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Animals and Samples
A total of 10 goats (Capra hircus) were included in the study. Five goats were from Mona Island, which is located in the Mona Passage between Hispaniola and Puerto Rico in the northeastern Caribbean (46 miles west of Puerto Rico; 18°5′12″N 67°53′22″W). It is a remote dry island with low human impact, inhabited by feral goats and pigs [21]. Five other goats were domestic goats, from a farm in Dajao, Bayamón, in the main island of Puerto Rico. Domestic animals were reported to receive Penicillin when they were sick and Daivonex as an anti-parasitic.
Fresh fecal samples were obtained from ten goats. Animals were observed to defecate and the feces were collected with a sterile spatula, carefully sampling the top part of the pellet that was not in contact with the soil. Samples were placed in microvials and immediately placed in dry ice, transported to the laboratory and stored at −70 °C for 1 month before extracting the DNA. Fecal samples were collected with permission from the Department of Natural and Environmental Resources of Puerto Rico (number 08-IC-025).
3.2. DNA Extraction and Amplification
Fecal DNA was extracted using the MoBio Powersoil kit®, after homogenizing 250 mg feces from individual pellets in 200 µl of saline solution (0.9% NaCl), mixing in 1.5 mL tubes at high speed for 20s in a bead-beater, instead of the recommended ten minutes vortex step. The 16S rDNA was amplified using universal primers 27F (5'-AGA GTT TGA TCC TGG CTC AG-3') and 1492R (5'-GGT TAC CTT GTT ACG ACTT-3'). Each PCR mix contained 50 units/mL Taq DNA polymerase, 400 μM of each dNTP, 3 mM MgCl2, and 5 pmol of each primer. The PCR amplification was performed with a gradient of annealing temperatures from 48 to 58 °C. One of the feral samples failed to amplify the 16S rRNA gene. Pooled amplicons from eight different annealing temperatures were purified using the QIAquick PCR Purification Kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA) for each of the nine goats.
3.3. DNA Array Hybridization
We used the G2 PhyloChip 16S rDNA microarray, previously validated using qPCR and clone libraries [33,34], to characterize bacterial communities. The G2 PhyloChip microarray has 506,944 probes representing ~8,700 bacterial and archaeal taxa [33]. Although there are no sp-level taxa obtained, as with sequencing, each operational taxonomic unit (OTU) is based on an average of 25 probe pairs, each consisting of a perfectly matched and a mismatched probe, and represents 16S rDNA sequences with 0–3% sequence divergence [33].
The purified PCR products (200 ng) were fragmented using DNase I (0.02 Umg−1 DNA; Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), biotin-labeled, and hybridized onto the PhyloChip as described by Brodie et al [34]. The PhyloChips were scanned using Gene Array Scanning (Affimetrix), and intensity was recorded using the standard Affymetrix software GeneChip microarray analysis suite, version 5.1. A bacterial taxon was considered present in a sample when ≥90% of the probe set designed for it was positive (positive fraction ≥ 0.9) [33].
3.4. Data and Statistical Analysis
UniFrac analyses [35] were used to compare fecal bacterial communities from feral and domestic goats, based on the phylogenetic tree, with the positive OTUs and an environment file describing the metadata for each sample, as provided by PhyloTrac [36,37]. UniFrac significance test was performed for pairwise comparisons of fecal bacterial communities using the Bonferroni correction. Jackknife environment clusters and principal coordinates analyses (PCoA) [35] were performed taking into account the relative abundances of organisms (weighted), as well as the shared branch lengths between samples. We also performed analysis of similarities (ANOSIM) using the Bray-Curtis dissimilarity, and dissimilarity ranks between and within classes were calculated and plotted. A distance matrix was calculated from the normalized log transformed intensity values of the PhyloChip-OTUs using a Bray-Curtis distance metric within the function ‘vegdist’ in the R package ‘vegan’ [38]. The distance matrix was represented as a nonmetric multidimensional scaling plot (NMDS) and the stress value (goodness of fit) was calculated, both using the function ‘metaMDS’. The relative group variance homogeneity was verified with the function ‘betadisper’ also in the “vegan” package. The boxplot function was run setting the parameter as NULL to make sure that the box was the same each time. We used additional ANOVA test to compare beta-dispersion between domestic and feral goats.
We used the statistical program “R” [39] to draw rank abundance curves from the data to visualize PhyloChip-OTU richness, overall diversity (with the “Adonis” function) and to build the heatmap with OTUs that significantly differed between feral and domestic goats as determined by ANOVA with p-values corrected for multiple observations, using the Holm procedure [40].
3.5. Detection of Tetracycline Resistance Genes
Five tetracycline ribosomal protection genes [tet(M), tet(O), tet(Q), tet(S) and tet(W)], were detected by PCR using specific primers [41,42] with an annealing temperature of 55 °C, except for tet(W) amplification which used 64 °C [43]. We used tetracycline resistance plasmids, for each of the resistance genes tested, as PCR positive controls. Each PCR mix contained 50 units/mL of Taq DNA polymerase, 400 μM of each dNTP, and 3 mM MgCl2. Amplicons were observed in 1% agarose gels stained with ethidium bromide (0.5 µg/mL; Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA).
4. Conclusions
Feral and domestic goats of Puerto Rico differed in the structure of their fecal bacterial communities, and, despite the absence of antibiotic pressures, feral goats carried fecal antibiotic resistance genes, although fewer than domestic goats. Diet, host genetic differences and antibiotic exposure might account for the differences in the microbiota between feral and domestic goats.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NSF CREST HRD0206200. A portion of this work was performed at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory under Department of Energy contract number DE-AC02-05CH11231. We thank Miguel Gueimonde and Rod Mackie for providing plasmids containing tetracycline resistance genes. We acknowledge undergraduate students Maite Ferrer, María del Mar Rodríguez Berríos, Ivonne Reyes, Lidia Ocasio and Anamaría Noriega for their help in sample processing.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1.
Phylum ranking, number of families and average number of bacterial OTUs (± s.e.) in domestic and feral goats.
| Phylum | Phylum Ranking | N Families | Average N OTUs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Domestic | Feral | Domestic | Feral | Domestic (N = 5) | Feral (N = 4) | |
| Firmicutes | 1 | 1 | 25 | 25 | 485 ± 23.9 | 421 ± 21.9 |
| Proteobacteria | 2 | 2 | 70 | 59 | 340 ± 47.5 | 326 ± 31.0 |
| Actinobacteria | 3 | 3 | 31 | 29 | 115 ± 10.5 | 93 ± 2.1 |
| Bacteroidetes | 4 | 4 | 11 | 11 | 88 ± 4.8 | 82 ± 6.9 |
| Acidobacteria | 5 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 40 ± 1.7 | 37 ± 3.7 |
| Spirochaetes | 6 | 11 | 2 | 2 | 28 ± 2.1 | 9 ± 4.1 |
| Chloroflexi | 7 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 25 ± 1.4 | 22 ± 1.8 |
| Unclassified | 8 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 23 ± 1.3 | 20 ± 1.0 |
| Verrucomicrobia | 9 | 8 | 5 | 5 | 21 ± 0.6 | 19 ± 1.0 |
| Cyanobacteria | 10 | 9 | 1 | 1 | 14 ± 2.0 | 16 ± 4.6 |
| Planctomycetes | 11 | 10 | 4 | 4 | 12 ± 0.7 | 13 ± 0.6 |
| Gemmatimonadetes | 12 | 12 | 1 | 1 | 7 ± 0.7 | 6 ± 1.1 |
| Chlorobi | 13 | 15 | 2 | 2 | 6 ± 0.8 | 4 ± 0.7 |
| OP10 | 14 | 14 | 1 | 1 | 5 ± 0.6 | 4 ± 0.3 |
| TM7 | 15 | 16 | 1 | 1 | 5 ± 0.4 | 4 ± 0.9 |
| Synergistes | 16 | 19 | 1 | 1 | 5 ± 0.4 | 3 ± 0.3 |
| Natronoanaerobium | 17 | 13 | 1 | 1 | 4 ± 0.7 | 5 ± 0.5 |
| Deinococcus-Thermus | 18 | 17 | 1 | 1 | 4 ± 0.0 | 4 ± 0.0 |
| OP9/JS1 | 19 | 22 | 1 | 1 | 4 ± 0.6 | 3 ± 0.5 |
| NC10 | 20 | 18 | 1 | 1 | 4 ± 0.2 | 4 ± 0.3 |
| Nitrospira | 21 | 24 | 1 | 1 | 3 ± 0.6 | 3 ± 0.6 |
| Lentisphaerae | 22 | 20 | 1 | 1 | 3 ± 0.0 | 3 ± 0.0 |
| OP3 | 23 | 21 | 1 | 1 | 3 ± 0.0 | 3 ± 0.0 |
| BRC1 | 24 | 25 | 1 | 1 | 3 ± 0.0 | 3 ± 0.5 |
| Chlamydiae | 25 | 23 | 3 | 3 | 2 ± 0.2 | 3 ± 0.3 |
| Aquificae | 26 | 27 | 2 | 2 | 2 ± 0.4 | 2 ± 0.5 |
| marine group A | 27 | 29 | 1 | 1 | 2 ± 0.5 | 1 ± 0.3 |
| Caldithrix | 28 | 26 | 1 | 1 | 2 ± 0.0 | 2 ± 0.0 |
| WS3 | 29 | 28 | 1 | 1 | 2 ± 0.2 | 2 ± 0.3 |
| SPAM | 30 | 30 | 1 | 1 | 1 ± 0.2 | 1 ± 0.0 |
| DSS1 | 31 | 31 | 1 | 1 | 1 ± 0.2 | 1 ± 0.0 |
| TM6 | 32 | 35 | 1 | 1 | 1 ± 0.2 | 1 ± 0.3 |
| LD1PA group | 33 | 32 | 1 | 1 | 1 ± 0.0 | 1 ± 0.0 |
| OP8 | 34 | 33 | 1 | 1 | 1 ± 0.0 | 1 ± 0.0 |
| Thermodesulfobacteria | 35 | 34 | 1 | 1 | 1 ± 0.0 | 1 ± 0.0 |
| AD3 | 36 | 36 | 1 | 1 | 1 ± 0.0 | 1 ± 0.3 |
| Thermotogae | 37 | 37 | 1 | 1 | 1 ± 0.2 | 1 ± 0.3 |
| WS5 | 38 | 38 | 1 | 1 | 1 ± 0.2 | 1 ± 0.3 |
| Coprothermobacteria | 39 | 39 | 1 | 1 | 1 ± 0.2 | 1 ± 0.3 |
| OD1 | 40 | 41 | 1 | 0 | 1 ± 0.2 | 0 ± 0.0 |
| Deferribacteres | 41 | 40 | 1 | 1 | 1 ± 0.2 | 0 ± 0.3 |
| Termite group 1 | 42 | 42 | 1 | 0 | 0 ± 0.4 | 0 ± 0.0 |
Figure S1.
Bacterial Rank-abundance curves for fecal bacteria in domestic (D1-5) and feral (F1-5) goats.
Figure S2.
UniFrac clustering of fecal bacterial communities in domestic and feral goats. (Jackknifing node support represented by black circles) Excluding D1, an outlier, the fecal bacterial communities of domestic and feral goats largely cluster separately.
Figure S3.
Principal coordinates analysis (PCoA): depicting the fecal bacterial communities of five domestic (D) and four feral (F) goats using weighted UniFrac distances. Each point corresponds to a community coded according to the goat group. The percentage of variation explained by the plotted principal coordinates is indicated on the axes. Emphasis of domestic and feral goat-associated community clustering indicated by the lines around each group.
Figure S4.
Analyses of similarities (ANOSIM) with dissimilarity ranks between and within domestic and feral goats. A) Boxplots of analyses of dissimilarity ranks. B) Boxplots of analyses of dissimilarity ranks without one domestic group outlier.
Table S2.
PhyloChip-OTUs statistical significance of ANOVA results, indicating differences between domestic and feral goats (p < 0.05).
| Taxa | p-value Holm correction |
|---|---|
| Bacteria;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetales;Spirochaetaceae;sf_1;6562 | 3.51E-11 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Deltaproteobacteria;Unclassified;Unclassified;sf_9;9890 | 8.45E-05 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Epsilonproteobacteria;Campylobacterales;Helicobacteraceae;sf_3;10467 | 0.0006201 |
| Bacteria;Actinobacteria;Actinobacteria;Actinomycetales;Thermomonosporaceae;sf_1;1546 | 0.00126733 |
| Bacteria;Firmicutes;gut clone group;Unclassified;Unclassified;sf_1;4400 | 0.00747837 |
| Bacteria;OP3;Unclassified;Unclassified;Unclassified;sf_2;349 | 0.00775145 |
| Bacteria;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetales;Spirochaetaceae;sf_1;6506 | 0.00825169 |
| Bacteria;Bacteroidetes;Bacteroidetes;Bacteroidales;Unclassified;sf_15;6233 | 0.00850866 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Alphaproteobacteria;Rhodobacterales;Rhodobacteraceae;sf_1;7508 | 0.00853058 |
| Bacteria;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetales;Spirochaetaceae;sf_1;6571 | 0.0087866 |
| Bacteria;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetales;Spirochaetaceae;sf_1;6476 | 0.00905065 |
| Bacteria;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetales;Spirochaetaceae;sf_1;6568 | 0.00914326 |
| Bacteria;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetales;Spirochaetaceae;sf_1;6490 | 0.00938643 |
| Bacteria;Actinobacteria;Actinobacteria;Actinomycetales;Micromonosporaceae;sf_1;1910 | 0.00962793 |
| Bacteria;Actinobacteria;Actinobacteria;Actinomycetales;Micromonosporaceae;sf_1;1488 | 0.00962793 |
| Bacteria;Actinobacteria;Actinobacteria;Actinomycetales;Micromonosporaceae;sf_1;1633 | 0.00962793 |
| Bacteria;Actinobacteria;Actinobacteria;Actinomycetales;Micromonosporaceae;sf_1;1760 | 0.00962793 |
| Bacteria;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetales;Spirochaetaceae;sf_1;6507 | 0.00962793 |
| Bacteria;Synergistes;Unclassified;Unclassified;Unclassified;sf_3;117 | 0.00962793 |
| Bacteria;Firmicutes;Catabacter;Unclassified;Unclassified;sf_4;4517 | 0.00962793 |
| Bacteria;OD1;OP11-5;Unclassified;Unclassified;sf_1;515 | 0.00962793 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Gammaproteobacteria;Alteromonadales;Alteromonadaceae;sf_1;8222 | 0.00962883 |
| Bacteria;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetales;Spirochaetaceae;sf_1;6489 | 0.00963896 |
| Bacteria;Actinobacteria;Actinobacteria;Actinomycetales;Kineosporiaceae;sf_1;1581 | 0.00966581 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Gammaproteobacteria;Unclassified;Unclassified;sf_3;8606 | 0.00966755 |
| Bacteria;Firmicutes;Clostridia;Clostridiales;Lachnospiraceae;sf_5;4324 | 0.00967552 |
| Bacteria;Firmicutes;Clostridia;Clostridiales;Lachnospiraceae;sf_5;2810 | 0.00967554 |
| Bacteria;Firmicutes;Clostridia;Clostridiales;Lachnospiraceae;sf_5;3223 | 0.00967787 |
| Bacteria;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetales;Spirochaetaceae;sf_1;6487 | 0.00968213 |
| Bacteria;Actinobacteria;Actinobacteria;Acidimicrobiales;Acidimicrobiaceae;sf_1;2014 | 0.00970127 |
| Bacteria;Firmicutes;gut clone group;Unclassified;Unclassified;sf_1;4579 | 0.00970475 |
| Bacteria;Actinobacteria;Actinobacteria;Actinomycetales;Gordoniaceae;sf_1;1654 | 0.00971853 |
| Bacteria;Firmicutes;Clostridia;Clostridiales;Unclassified;sf_17;3099 | 0.00977429 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Unclassified;Unclassified;Unclassified;sf_8;8247 | 0.00978004 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Alphaproteobacteria;Bradyrhizobiales;Bradyrhizobiaceae;sf_1;7477 | 0.00979143 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Betaproteobacteria;Nitrosomonadales;Nitrosomonadaceae;sf_1;7770 | 0.00979751 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Deltaproteobacteria;Myxococcales;Polyangiaceae;sf_3;9671 | 0.00980123 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Epsilonproteobacteria;Campylobacterales;Helicobacteraceae;sf_3;10417 | 0.00981157 |
| Bacteria;Actinobacteria;Actinobacteria;Acidimicrobiales;Microthrixineae;sf_12;1721 | 0.00987931 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Deltaproteobacteria;EB1021 group;Unclassified;sf_4;9741 | 0.00990536 |
| Bacteria;Actinobacteria;Actinobacteria;Actinomycetales;Gordoniaceae;sf_1;1184 | 0.01015274 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Gammaproteobacteria;Aeromonadales;Succinivibrionaceae;sf_1;8822 | 0.01020072 |
| Bacteria;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetales;Spirochaetaceae;sf_1;6508 | 0.01036306 |
| Bacteria;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetales;Spirochaetaceae;sf_1;6488 | 0.0104335 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Alphaproteobacteria;Bradyrhizobiales;Bradyrhizobiaceae;sf_1;7044 | 0.01047121 |
| Bacteria;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetales;Spirochaetaceae;sf_1;6523 | 0.01062729 |
| Bacteria;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetales;Spirochaetaceae;sf_1;6494 | 0.01082364 |
| Bacteria;Actinobacteria;Actinobacteria;Actinomycetales;Promicromonosporaceae;sf_1;1711 | 0.01086604 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Alphaproteobacteria;Bradyrhizobiales;Bradyrhizobiaceae;sf_1;6799 | 0.01118413 |
| Bacteria;Firmicutes;Mollicutes;Mycoplasmatales;Mycoplasmataceae;sf_1;3929 | 0.01120143 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Gammaproteobacteria;Enterobacteriales;Enterobacteriaceae;sf_1;8607 | 0.01120143 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Gammaproteobacteria;Thiotrichales;Thiotrichaceae;sf_3;8477 | 0.01120143 |
| Bacteria;Lentisphaerae;Unclassified;Unclassified;Unclassified;sf_5;10330 | 0.01120143 |
| Bacteria;Lentisphaerae;Unclassified;Unclassified;Unclassified;sf_5;9704 | 0.01120143 |
| Bacteria;Unclassified;Unclassified;Unclassified;Unclassified;sf_160;2385 | 0.01120143 |
| Bacteria;Firmicutes;Catabacter;Unclassified;Unclassified;sf_4;4325 | 0.01120143 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Alphaproteobacteria;Rhodobacterales;Rhodobacteraceae;sf_1;7511 | 0.01120154 |
| Bacteria;Nitrospira;Nitrospira;Nitrospirales;Nitrospiraceae;sf_3;833 | 0.01126881 |
| Bacteria;Firmicutes;Clostridia;Clostridiales;Lachnospiraceae;sf_5;4489 | 0.01129829 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Alphaproteobacteria;Rhizobiales;Bradyrhizobiaceae;sf_1;7029 | 0.01138694 |
| Bacteria;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetales;Spirochaetaceae;sf_1;6479 | 0.01144975 |
| Bacteria;Firmicutes;Clostridia;Clostridiales;Lachnospiraceae;sf_5;3075 | 0.01145728 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Alphaproteobacteria;Bradyrhizobiales;Bradyrhizobiaceae;sf_1;6636 | 0.01173191 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Alphaproteobacteria;Bradyrhizobiales;Bradyrhizobiaceae;sf_1;7522 | 0.01173191 |
| Bacteria;Actinobacteria;Actinobacteria;Actinomycetales;Micromonosporaceae;sf_1;1931 | 0.01174823 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Gammaproteobacteria;Enterobacteriales;Enterobacteriaceae;sf_1;8362 | 0.01178839 |
| Bacteria;Bacteroidetes;Flavobacteria;Flavobacteriales;Flavobacteriaceae;sf_1;6274 | 0.01184388 |
| Bacteria;Bacteroidetes;Bacteroidetes;Bacteroidales;Prevotellaceae;sf_1;5398 | 0.01200674 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Alphaproteobacteria;Bradyrhizobiales;Beijerinck/Rhodoplan/Methylocyst; sf_3;7219 | 0.01219961 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Alphaproteobacteria;Bradyrhizobiales;Bradyrhizobiaceae;sf_1;6768 | 0.01267711 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Alphaproteobacteria;Bradyrhizobiales;Bradyrhizobiaceae;sf_1;6867 | 0.01287698 |
| Bacteria;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetes;Spirochaetales;Spirochaetaceae;sf_1;6580 | 0.01365949 |
| Bacteria;Firmicutes;Mollicutes;Unclassified;Unclassified;sf_1;4000 | 0.01386526 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Alphaproteobacteria;Rhizobiales;Rhizobiaceae;sf_1;6770 | 0.0145046 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Alphaproteobacteria;Bradyrhizobiales;Bradyrhizobiaceae;sf_1;7316 | 0.01458135 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Alphaproteobacteria;Bradyrhizobiales;Bradyrhizobiaceae;sf_1;7333 | 0.01458135 |
| Bacteria;Firmicutes;Clostridia;Clostridiales;Clostridiaceae;sf_12;4384 | 0.0149426 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Alphaproteobacteria;Rhodobacterales;Rhodobacteraceae;sf_1;6652 | 0.01867578 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Epsilonproteobacteria;Campylobacterales;Helicobacteraceae;sf_23;10443 | 0.02022574 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Epsilonproteobacteria;Campylobacterales;Helicobacteraceae;sf_3;10576 | 0.02022574 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Deltaproteobacteria;Myxococcales;Polyangiaceae;sf_4;9733 | 0.02218193 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Alphaproteobacteria;Sphingomonadales;Sphingomonadaceae;sf_1;7215 | 0.0467565 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Alphaproteobacteria;Sphingomonadales;Sphingomonadaceae;sf_1;7100 | 0.04689578 |
| Bacteria;Proteobacteria;Gammaproteobacteria;Alteromonadales;Alteromonadaceae;sf_1;8978 | 0.04825366 |
Table S3.
Taxonomic distribution of 84 OTUs overrepresented in one of the goat groups.
| Phylum | Family | Domestic | Feral |
|---|---|---|---|
| Actinobacteria | Acidimicrobiaceae | 1 | 0 |
| Gordoniaceae | 2 | 0 | |
| Kineosporiaceae | 1 | 0 | |
| Micromonosporaceae | 5 | 0 | |
| Microthrixineae | 1 | 0 | |
| Promicromonosporaceae | 1 | 0 | |
| Thermomonosporaceae | 1 | 0 | |
| Bacteroidetes | Flavobacteriaceae | 1 | 0 |
| Prevotellaceae | 0 | 1 | |
| Unclassified | 1 | 0 | |
| Firmicutes | Clostridiaceae | 1 | 0 |
| Lachnospiraceae | 4 | 1 | |
| Mycoplasmataceae | 1 | 0 | |
| Unclassified | 5 | 1 | |
| Lentisphaerae | Unclassified | 2 | 0 |
| Nitrospira | Nitrospiraceae | 0 | 1 |
| OD1 | Unclassified | 1 | 0 |
| OP3 | Unclassified | 1 | 0 |
| Proteobacteria | Alteromonadaceae | 2 | 0 |
| Beijerinck/Rhodoplan/Methylocyst | 0 | 1 | |
| Bradyrhizobiaceae | 0 | 10 | |
| Enterobacteriaceae | 1 | 1 | |
| Helicobacteraceae | 4 | 0 | |
| Nitrosomonadaceae | 1 | 0 | |
| Polyangiaceae | 2 | 0 | |
| Rhizobiaceae | 0 | 1 | |
| Rhodobacteraceae | 2 | 1 | |
| Sphingomonadaceae | 2 | 0 | |
| Succinivibrionaceae | 1 | 0 | |
| Thiotrichaceae | 0 | 1 | |
| Unclassified | 4 | 0 | |
| Spirochaetes | Spirochaetaceae | 15 | 0 |
| Synergistes | Unclassified | 1 | 0 |
| Unclassified | Unclassified | 1 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 65 | 19 | |
References
- 1.Ley R.E., Hamady M., Lozupone C., Turnbaugh P.J., Ramey R.R., Bircher J.S., Schlegel M.L., Tucker T.A., Schrenzel M.D., Knight R., Gordon J.I. Evolution of mammals and their gut microbes. Science. 2008;320:1647–1651. doi: 10.1126/science.1155725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Backhed F., Ding H., Wang T., Hooper L.V., Koh G.Y., Nagy A., Semenkovich C.F., Gordon J.I. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2004;101:15718–15723. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407076101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dillon R.J., Vennard C.T., Buckling A., Charnley A.K. Diversity of locust gut bacteria protects against pathogen invasion. Ecol. Lett. 2005;8:1291–1298. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2005.00828.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cebra J.J. Influences of microbiota on intestinal immune system development. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999;69:1046–1051. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/69.5.1046s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Konturek J.W., Konturek S.J., Kwiecien N., Bielanski W., Pawlik T., Rembiasz K., Domschke W. Leptin in the control of gastric secretion and gut hormones in humans infected with Helicobacter pylori. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2001;36:1148–1154. doi: 10.1080/00365520152584761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Nwokolo C.U., Freshwater D.A., O’Hare P., Randeva H.S. Plasma ghrelin following cure of Helicobacter pylori. Gut. 2003;52:637–640. doi: 10.1136/gut.52.5.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zoetendal E.G., Akkermans A.D.L., Akkermans-van Vliet W.M., de Visser J.A.G.M., de Vos W.M. The host genotype affects the bacterial community in the human gastrointestinal tract. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2001;13:129–134. doi: 10.3402/mehd.v13i3.8013. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Macdonald T.T., Monteleone G. Immunity, inflammation, and allergy in the gut. Science. 2005;307:1920–1925. doi: 10.1126/science.1106442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ley R.E., Turnbaugh P.J., Klein S., Gordon J.I. Microbial ecology: Human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature. 2006;444:1022–1023. doi: 10.1038/4441022a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rawls J.F., Samuel B.S., Gordon J.I. Gnotobiotic zebrafish reveal evolutionarily conserved responses to the gut microbiota. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2004;101:4596–4601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400706101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zeder M.A., Hesse B. The initial domestication of goats (Capra hircus) in the zagros mountains 10,000 years ago. Science. 2000;287:2254–2257. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5461.2254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Shrestha J.N.B., Fahmy M.H. Breeding goats for meat production: A review: 1. Genetic resources, management and breed evaluation. Small Rumin. Res. 2005;58:93–106. doi: 10.1016/S0921-4488(03)00183-4. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Glazko V. An attempt at understanding the genetic basis of domestication. Anim. Sci. Papers Rep. 2003;21:109–120. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Khachatourians G. Agricultural use of antibiotics and the evolution and transfer of antibiotic resistant bacteria. Can. Med. Assoc. 1998;159:1129–1136. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Butaye P., Devriese L.A., Haesebrouck F. Antimicrobial growth promoters used in animal feed: A review of the less well known antibiotics and their effects on Gram-positive bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003;16:175–188. doi: 10.1128/CMR.16.2.175-188.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Heatwoke H., Levins R., Byer M. Biogeography of the puerto rican bank. Atoll Res. Bull. 1981;251:1042–1055. doi: 10.2307/1935570. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sponenberg D.P. Colonial spanish sheep, goats, hogs, and asses in the United States. Zootecnia. 1992;41:415–419. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Yang G., Bao B., Peatman E., Li H., Huang L., Ren D. Analysis of the composition of the bacterial community in puffer fish Takifugu obscurus. Aquaculture. 2007;262:183–191. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2006.11.031. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Croswell A., Amir E., Teggatz P., Barman M., Salzman N. Prolonged impact of antibiotics on intestinal microbial ecology and susceptibility to enteric salmonella infection. Infect. Immun. 2009;77:2741–2753. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00006-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Leser T.D., Lindecrona R.H., Jensen T.K., Jensen B.B., Moller K. Changes in bacterial community structure in the colon of pigs fed different experimental diets and after infection with Brachyspira hyodysenteriae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000;66:3290–3296. doi: 10.1128/AEM.66.8.3290-3296.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Meléndez-Ackerman E.J., Cortés C., Sustache J., Aragón S., Morales-Vargas M., García-Bermúdez M., Fernández D.S. Diet of feral goats in Mona Island Reserve, Puerto Rico. Caribb. J. Sci. 2008;44:199–205. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Aminov R.I., Garrigues-Jeanjean N., Mackie R.I. Molecular ecology of tetracycline resistance: Development and validation of primers for detection of tetracycline resistance genes encoding ribosomal protection proteins. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001;67:22–32. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.1.22-32.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Aires J., Doucet Populaire F., Butel M.J. Tetracycline resistance mediated by tet(W), tet(M), and tet(O) genes of Bifidobacterium isolates from humans. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007;73:2751–2754. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02459-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ready D., Pratten J., Roberts A.P., Bedi R., Mullany P., Wilson M. Potential role of Veillonella spp. as a reservoir of transferable tetracycline resistance in the oral cavity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006;50:2866–2868. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00217-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Stanton T.B., Humphrey S.B., Stoffregen W.C. Chlortetracycline-resistant intestinal bacteria in organically-raised and feral swine. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011;77 doi: 10.1128/AEM.00688-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Osterblad M., Norrdahl K., Korpimaki E., Huovinen P. Antibiotic resistance. How wild are wild mammals? Nature. 2001;409:37–38. doi: 10.1038/35051173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gardner P., Smith D.H., Beer H., Moellering R.C., Jr. Recovery of resistance (R) factors from a drug-free community. Lancet. 1969;2:774–776. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(69)90482-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Routman E., Miller R.D., Phillips-Conroy J., Hartl D.L. Antibiotic resistance and population structure in Escherichia coli from free-ranging African yellow baboons. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985;50:749–754. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.749-754.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gilliver M.A., Bennett M., Begon M., Hazel S.M., Hart C.A. Antibiotic resistance found in wild rodents. Nature. 1999;401:233–234. doi: 10.1038/45724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Berg J., Tom-Petersen A., Nybroe O. Copper amendment of agricultural soil selects for bacterial antibiotic resistance in the field. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2005;40:146–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2004.01650.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Coates M.D., MK., Kon S.K. The effect of antibiotics on the intestine of the chick. Br. J. Nutr. 1955;9:110–119. doi: 10.1079/BJN19550016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Guillemot D., Carbon C., Balkau B., Geslin P., Lecoeur H., Vauzelle-Kervroëdan F., Bouvenot G., Eschwége E. Low dosage and long treatment duration of beta-lactam: Risk factors for carriage of penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1998;279:365–370. doi: 10.1001/jama.279.5.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.DeSantis T.Z., Brodie E.L., Moberg J.P., Zubieta I.X., Piceno Y.M., Andersen G.L. High-density universal 16S rRNA microarray analysis reveals broader diversity than typical clone library when sampling the environment. Microb. Ecol. 2007;53:371–383. doi: 10.1007/s00248-006-9134-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Brodie E.L., Desantis T.Z., Joyner D.C., Baek S.M., Larsen J.T., Andersen G.L., Hazen T.C., Richardson P.M., Herman D.J., Tokunaga T.K., et al. Application of a high-density oligonucleotide microarray approach to study bacterial population dynamics during uranium reduction and reoxidation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006;72:6288–6298. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00246-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lozupone C., Hamady M., Knight R. UniFrac-An online tool for comparing microbial community diversity in a phylogenetic context. BMC Bioinforma. 2006;7 doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Schatz M.C., Phillippy A.M., Gajer P., DeSantis T.Z., Andersen G.L., Ravel J. Integrated microbial survey analysis of Prokaryotic communities for the PhyloChip microarray. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010;76:5636–5638. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00303-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.PhyloTrac: Environmental Sample Analysis. [(accessed on 28 November 2011)]. Available online: http://www.phylotrac.org/Home.html.
- 38.The R Project for Statistical Computing. [(accessed on 28 November 2011)]. Available online: http://www.R-project.org.
- 39.Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing; Vienna, Austria: 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dudoit S., Yang Y.H., Callow M.J., Speed T.P. Statistical methods for identifying differentially expressed genes in replicated cDNA microarray experiments. Tech. Rep. 2000;12:111–139. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Schnappinger D., Hillen W. Tetracyclines: Antibiotic action, uptake, and resistance mechanisms. Arch. Microbiol. 1996;165:359–369. doi: 10.1007/s002030050339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Roberts M.C. Update on acquired tetracycline resistance genes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005;245:195–203. doi: 10.1016/j.femsle.2005.02.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Villedieu A., Diaz-Torres M.L., Hunt N., McNab R., Spratt D.A., Wilson M., Mullany P. Prevalence of tetracycline resistance genes in oral bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003;47:878–882. doi: 10.1128/AAC.47.3.878-882.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]