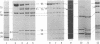Abstract
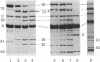
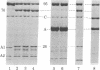
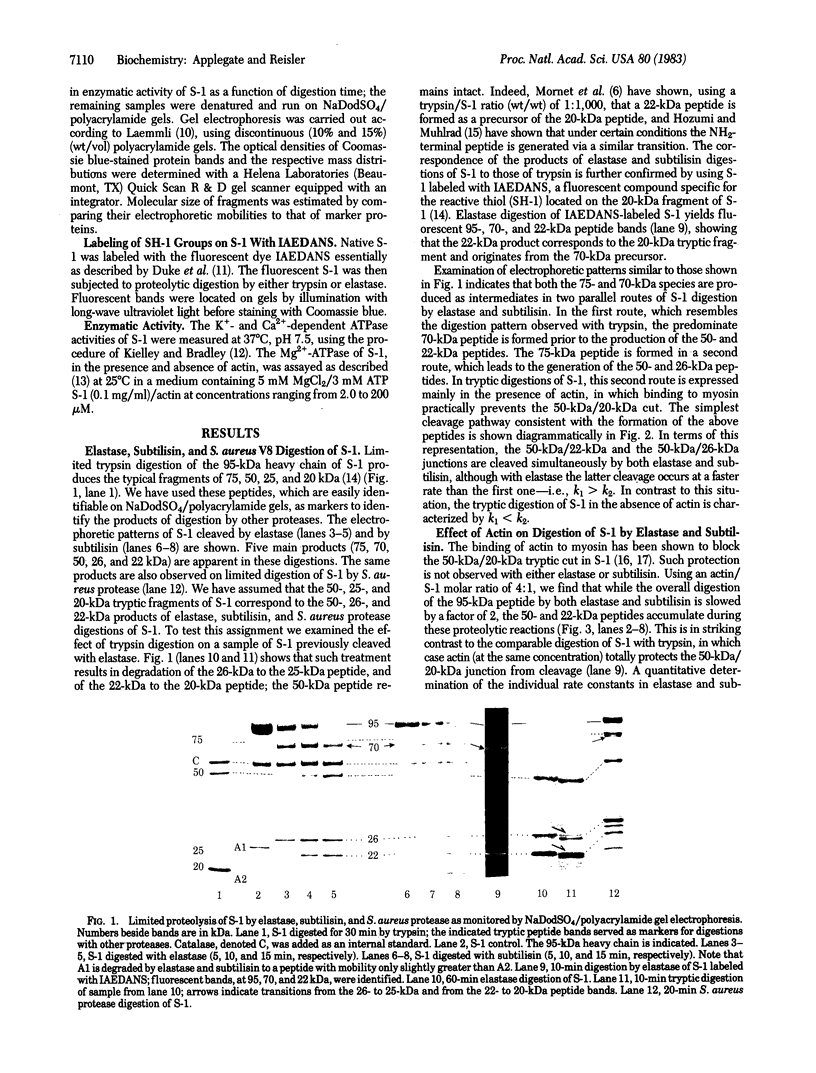
Proteolytic digestions of myosin subfragment 1 (S-1) with elastase, subtilisin, papain, thermolysin, and Staphylococcus aureus protease reveal that the two trypsin-sensitive regions in S-1 have broad protease susceptibility. The cleavage of S-1 by these enzymes yields products that correspond within 1-2 kilodaltons (kDa) to the 25-, 50-, and 20-kDa fragments produced by trypsin. Papain and thermolysin cut preferentially at the 26-kDa/70-kDa junction, whereas elastase, subtilisin, and S. aureus protease cleave both the 26-kDa/70-kDa and 75-kDa/22-kDa junctions in S-1. Binding of actin to S-1 decreases the rate of all proteolytic reactions in the 95-kDa heavy chain. The protection of the 26-kDa/70-kDa junction by actin is greatest against papain and thermolysin attack. The reaction times of elastase, subtilisin, and S. aureus protease with S-1 increase 2-fold in the presence of actin. However, in contrast to similar reactions with trypsin, they proceed at both junctions and lead to formation of the 50- and 22-kDa fragments. The cleavage of the 22-kDa/50-kDa junction by elastase increases the Km value for the actin-activated ATPase. The presence of the two protease-sensitive regions in S-1 is consistent with a three-domain structure of the myosin head and may have important implications to the mode of intersite communication in this protein.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Botts J., Muhlrad A., Takashi R., Morales M. F. Effects of tryptic digestion on myosin subfragment 1 and its actin-activated adenosinetriphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6903–6905. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bálint M., Wolf I., Tarcsafalvi A., Gergely J., Sréter F. A. Location of SH-1 and SH-2 in the heavy chain segment of heavy meromyosin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Oct;190(2):793–799. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke J., Takashi R., Ue K., Morales M. F. Reciprocal reactivities of specific thiols when actin binds to myosin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):302–306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey J. E., Harrington W. F. Self-association in the myosin system at high ionic strength. I. Sensitivity of the interaction to pH and ionic environment. Biochemistry. 1970 Feb 17;9(4):886–893. doi: 10.1021/bi00806a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hozumi T., Muhlrad A. Reactive lysyl of myosin subfragment 1: location on the 27K fragment and labeling properties. Biochemistry. 1981 May 12;20(10):2945–2950. doi: 10.1021/bi00513a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIELLEY W. W., BRADLEY L. B. The relationship between sulfhydryl groups and the activation of myosin adenosinetriphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1956 Feb;218(2):653–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Bertrand R. U., Pantel P., Audemard E., Kassab R. Proteolytic approach to structure and function of actin recognition site in myosin heads. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 14;20(8):2110–2120. doi: 10.1021/bi00511a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Bertrand R., Pantel P., Audemard E., Kassab R. Structure of the actin-myosin interface. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):301–306. doi: 10.1038/292301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mornet D., Pantel P., Audemard E., Kassab R. The limited tryptic cleavage of chymotryptic S-1: an approach to the characterization of the actin site in myosin heads. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Aug 13;89(3):925–932. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91867-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisler E. On the question of co-operative interaction of myosin heads with F-actin in the presence of ATP. J Mol Biol. 1980 Mar 25;138(1):93–107. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(80)80006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutoh K. Mapping of actin-binding sites on the heavy chain of myosin subfragment 1. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 29;22(7):1579–1585. doi: 10.1021/bi00276a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szilagyi L., Balint M., Sreter F. A., Gergely J. Photoaffinity labelling with an ATP analog of the N-terminal peptide of myosin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Apr 13;87(3):936–945. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G., Pope B. Studies on the chymotryptic digestion of myosin. Effects of divalent cations on proteolytic susceptibility. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr;111(2):129–157. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Sekine T. Interaction of myosin subfragment-1 with actin. I. Effect of actin binding on the susceptibility of subfragment-1 to trypsin. J Biochem. 1979 Dec;86(6):1855–1862. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Sekine T. Interaction of myosin subfragment-1 with actin. II. Location of the actin binding site in a fragment of subfragment-1 heavy chain. J Biochem. 1979 Dec;86(6):1863–1868. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Sekine T. Interaction of myosin subfragment-1 with actin. III. Effect of cleavage of the subfragment-1 heavy chain on its interaction with actin. J Biochem. 1979 Dec;86(6):1869–1881. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]