Abstract
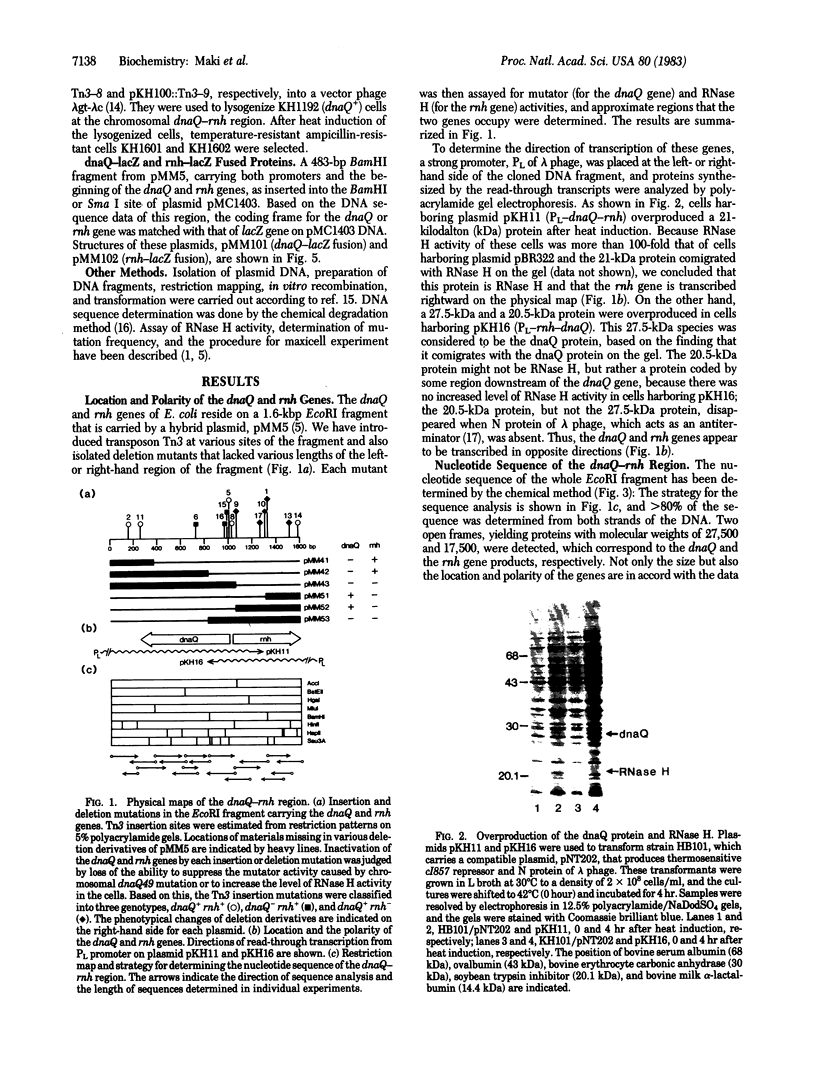
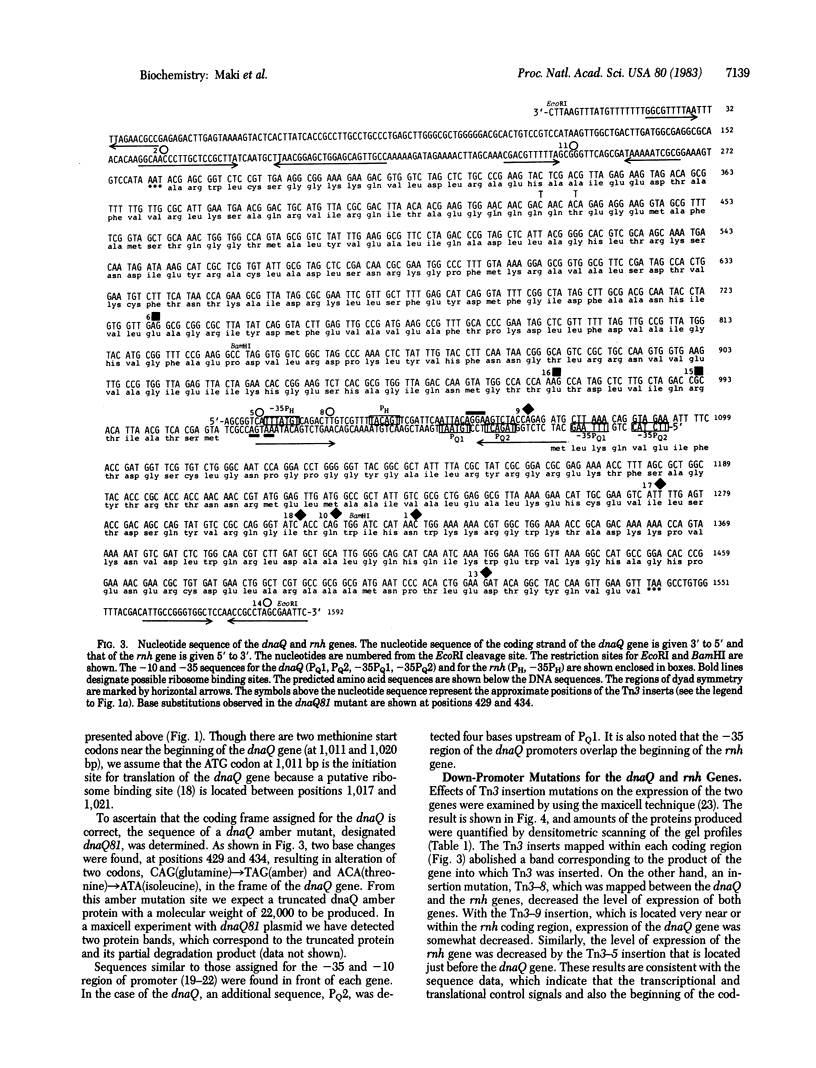
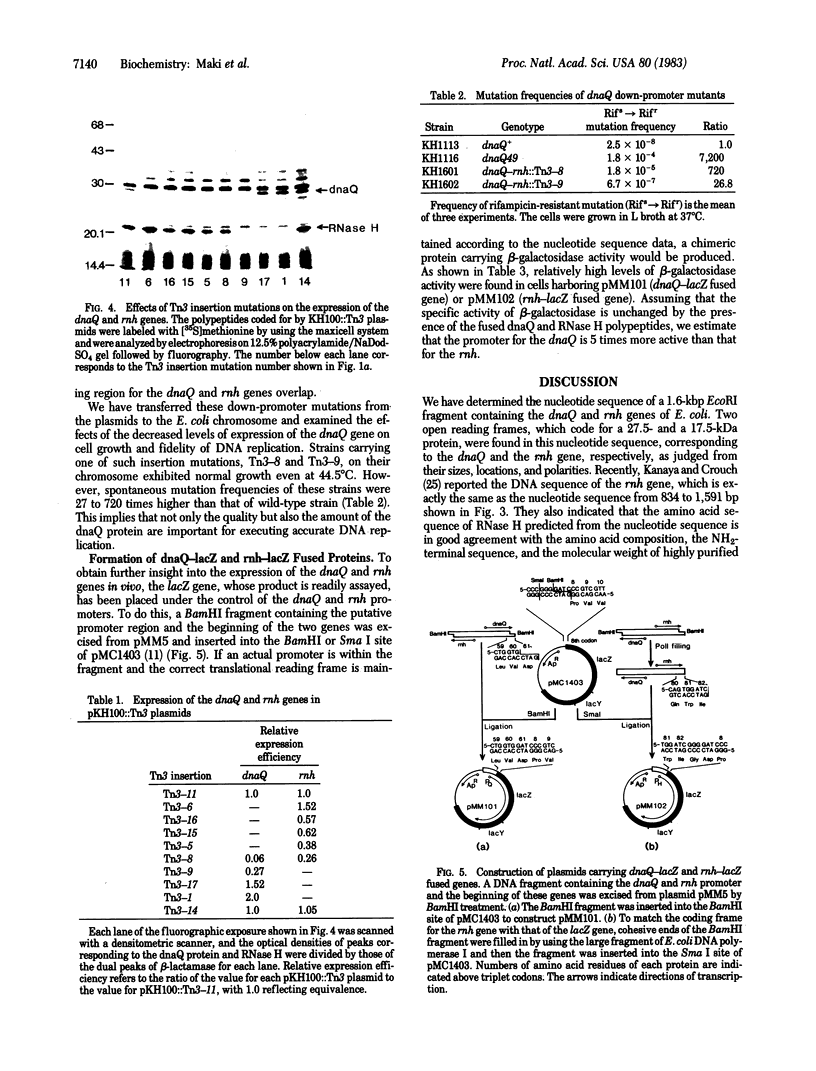
A 1.6-kilobase-pair DNA fragment derived from the Escherichia coli chromosome was analyzed by Tn3 transposon insertion and deletion mapping to locate a mutator gene, dnaQ (mutD), and the rnh gene that codes for RNase H. When a strong promoter, PL of lambda phage, was placed at the right- and left-side of the cloned DNA fragment, the dnaQ protein and RNase H, respectively were overproduced. These results suggested that the two genes are transcribed in opposite directions and that their promoters are located in a narrow region between the genes. Nucleotide sequence analysis confirmed this and further revealed that transcriptional and translational initiation signals for the two genes overlap. From the sequence data it was deduced that the dnaQ protein and RNase H consist of 243 and 155 triplets and have molecular weights of 27,500 and 17,500, respectively. dnaQ81 amber mutant showed two codon alterations, CAG(glutamine-195) leads to TAG(amber) and ACA(threonine-193) leads to ATA(isoleucine). The dnaQ-lacZ and the rnh-lacZ fused genes were constructed and hybrid proteins with beta-galactosidase activity were produced. From beta-galactosidase levels it was estimated that the promoter for dnaQ is 5 times more active than that for rnh.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Casadaban M. J., Chou J., Cohen S. N. In vitro gene fusions that join an enzymatically active beta-galactosidase segment to amino-terminal fragments of exogenous proteins: Escherichia coli plasmid vectors for the detection and cloning of translational initiation signals. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):971–980. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.971-980.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Boyer H. W., Helling R. B. Construction of biologically functional bacterial plasmids in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3240–3244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox E. C., Horner D. L. Structure and coding properties of a dominant Escherichia coli mutator gene, mutD. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2295–2299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degnen G. E., Cox E. C. Conditional mutator gene in Escherichia coli: isolation, mapping, and effector studies. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):477–487. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.477-487.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H., Lu C., Burgers P. M. Mutator strains of Escherichia coli, mutD and dnaQ, with defective exonucleolytic editing by DNA polymerase III holoenzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2189–2192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. S., Ames B. N. Localized mutagenesis of any specific small region of the bacterial chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3158–3162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi T., Maki H., Maruyama M., Sekiguchi M. Identification of the dnaQ gene product and location of the structural gene for RNase H of Escherichia coli by cloning of the genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3770–3774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi T., Maki H., Sekiguchi M. A new conditional lethal mutator (dnaQ49) in Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Jul 25;163(3):277–283. doi: 10.1007/BF00271956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi T., Maki H., Sekiguchi M. Conditional lethality of Escherichia coli strains carrying dnaE and dnaQ mutations. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;181(1):24–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00339000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Tomizawa J. Formation of an RNA primer for initiation of replication of ColE1 DNA by ribonuclease H. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2450–2454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanaya S., Crouch R. J. DNA sequence of the gene coding for Escherichia coli ribonuclease H. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1276–1281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretschmer P. J., Cohen S. N. Selected translocation of plasmid genes: frequency and regional specificity of translocation of the Tn3 element. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):888–899. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.888-899.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Tiemeier D., Enquist L. EK2 derivatives of bacteriophage lambda useful in the cloning of DNA from higher organisms: the lambdagtWES system. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):175–177. doi: 10.1126/science.322278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama M., Horiuchi T., Maki H., Sekiguchi M. A dominant (mutD5) and a recessive (dnaQ49) mutator of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jul 15;167(4):757–771. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80109-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHenry C. S., Crow W. DNA polymerase III of Escherichia coli. Purification and identification of subunits. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 10;254(5):1748–1753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E., Falke D., Zahn R. K., Arendes J. Ribonuclease H levels in herpes simplex virus-infected cells. Arch Virol. 1980;64(3):269–275. doi: 10.1007/BF01322706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E., Geurtsen W., Zahn R. K., Arendes J. Cell cycle-dependent alterations of the two types of ribonucleases H in L5178y cells. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jan 28;110(1):119–122. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata T., Horiuchi T. Isolation and characterization of a temperature-sensitive amber suppressor mutant of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1973;123(1):77–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00282991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribnow D. Nucleotide sequence of an RNA polymerase binding site at an early T7 promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):784–788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. Determinant of cistron specificity in bacterial ribosomes. Nature. 1975 Mar 6;254(5495):34–38. doi: 10.1038/254034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stüber D., Bujard H. Organization of transcriptional signals in plasmids pBR322 and pACYC184. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):167–171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takanami M., Sugimoto K., Sugisaki H., Okamoto T. Sequence of promoter for coat protein gene of bacteriophage fd. Nature. 1976 Mar 25;260(5549):297–302. doi: 10.1038/260297a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




