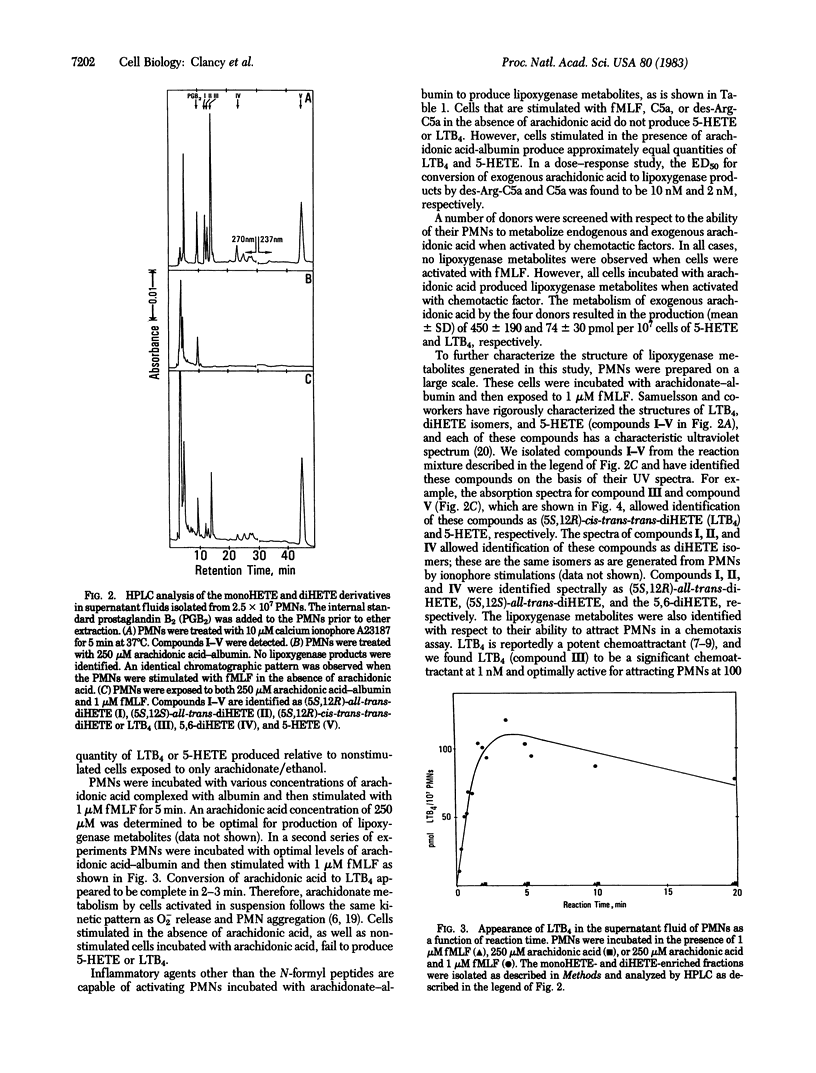
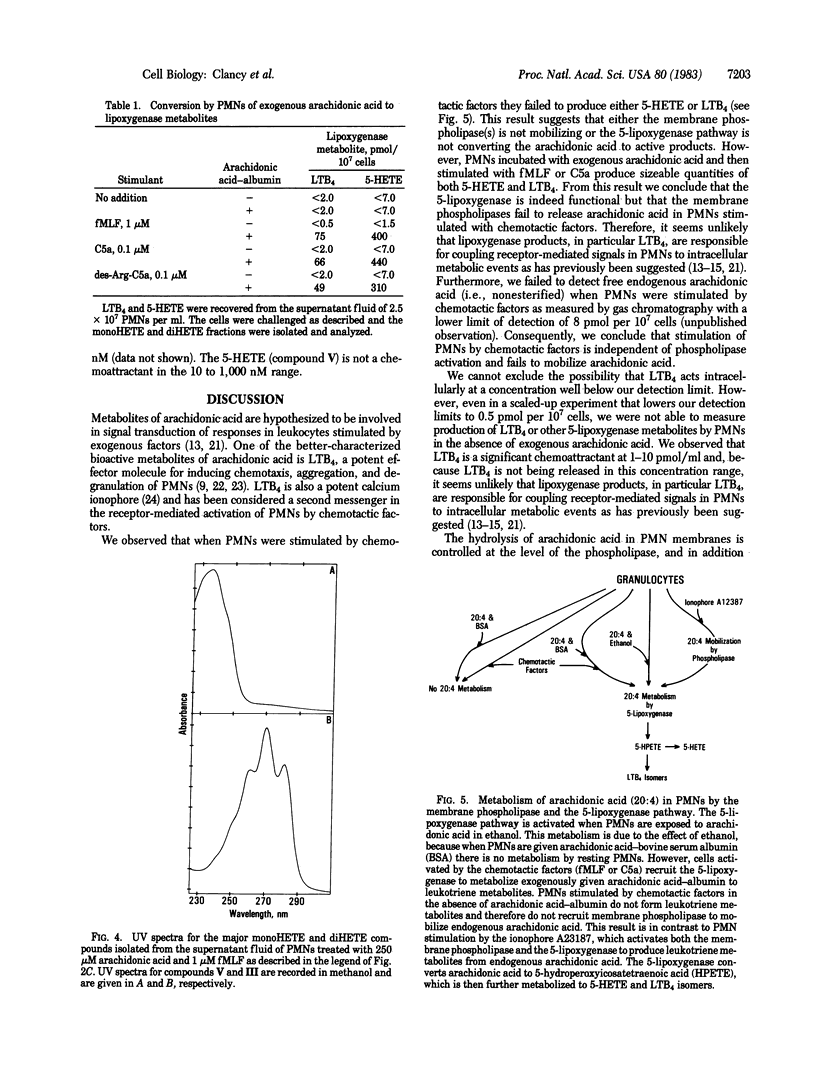
Abstract
Release of arachidonic acid by the membrane phospholipase and metabolism by the 5-lipoxygenase pathway was examined in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs). The 5-lipoxygenase pathway is activated when PMNs are given arachidonic acid in ethanol and there is extensive metabolism to 5-hydroxyicosatetraenoic acid (5-HETE) and leukotriene B4 (LTB4). This activation event was shown to be altered by the ethanol because resting PMNs given arachidonic acid with bovine serum albumin fail to metabolize arachidonic acid. However, cells activated by the inflammatory agents N-formyl-Met-Leu-Phe (fMLF) or complement component C5a recruit the 5-lipoxygenase to metabolize exogenous arachidonic acid to 5-HETE and LTB4. When PMNs were incubated with arachidonic acid-bovine serum albumin and challenged with fMLF or C5a (des-Arg-C5a) they produced 49-75 pmol of LTB4 and 310-440 pmol of 5-HETE per 10(7) cells. PMNs stimulated by fMLF or C5a (des-Arg-C5a) do not induce membrane phospholipases to mobilize endogenous arachidonic acid and neither 5-HETE nor LTB4 is formed. In contrast, PMN stimulation by the ionophore A23187 activates both the membrane phospholipase and the 5-lipoxygenase to produce 5-HETE and LTB4 from endogenous arachidonic acid. Our results indicate that the lipoxygenase pathway is inoperative in resting PMNs but can be recruited by chemotactic factors to act on arachidonate from extracellular sources. It was previously believed that formation of 5-HETE and LTB4 by the PMN depends solely on phospholipase to mobilize endogenous arachidonic acid. The results reported here refute this concept and indicate that the role of phospholipase activation in PMN may be overestimated. Therefore, subsequent involvement of lipoxygenase products in mediating stimulation of PMN by inflammatory factors (e.g., as in aggregation and chemotaxis) remains in question unless an exogenous source of arachidonate can be identified.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson J. P., Simchowitz L., Mehta J., Stenson W. F. 5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraynoic acid (ETYA) inhibits binding of N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (FLMP) to its receptor on human granulocytes. A note of caution. Immunopharmacology. 1982 Feb;4(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(82)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badwey J. A., Curnutte J. T., Karnovsky M. L. cis-Polyunsaturated fatty acids induce high levels of superoxide production by human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12640–12643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker E. L., Showell H. J., Henson P. M., Hsu L. S. The ability of chemotactic factors to induce lysosomal enzyme release. I. The characteristics of the release, the importance of surfaces and the relation of enzyme release to chemotactic responsiveness. J Immunol. 1974 Jun;112(6):2047–2054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker E. L., Stossel T. P. Chemotaxis. Fed Proc. 1980 Oct;39(12):2949–2952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Hamberg M., Samuelsson B. Transformation of arachidonic acid and homo-gamma-linolenic acid by rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Monohydroxy acids from novel lipoxygenases. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 25;251(24):7816–7820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Samuelsson B. Arachidonic acid metabolism in polymorphonuclear leukocytes: effects of ionophore A23187. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2148–2152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgeat P., Samuelsson B. Metabolism of arachidonic acid in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Structural analysis of novel hydroxylated compounds. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7865–7869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenoweth D. E., Hugli T. E. Demonstration of specific C5a receptor on intact human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3943–3947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahinden C. A., Fehr J., Hugli T. E. Role of cell surface contact in the kinetics of superoxide production by granulocytes. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):113–121. doi: 10.1172/JCI110948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahinden C., Fehr J. Receptor-directed inhibition of chemotactic factor-induced neutrophil hyperactivity by pyrazolon derivatives. Definition of a chemotactic peptide antagonist. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):884–891. doi: 10.1172/JCI109955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahinden C., Galanos C., Fehr J. Granulocyte activation by endotoxin. I. Correlation between adherence and other granulocyte functions, and role of endotoxin structure on biologic activity. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):857–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez H. N., Henson P. M., Otani A., Hugli T. E. Chemotactic response to human C3a and C5a anaphylatoxins. I. Evaluation of C3a and C5a leukotaxis in vitro and under stimulated in vivo conditions. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):109–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford-Hutchinson A. W., Bray M. A., Doig M. V., Shipley M. E., Smith M. J. Leukotriene B, a potent chemokinetic and aggregating substance released from polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):264–265. doi: 10.1038/286264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridovich S. E., Porter N. A. Oxidation of arachidonic acid in micelles by superoxide and hydrogen peroxide. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):260–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Pickett W. C. Novel structural determinants of the human neutrophil chemotactic activity of leukotriene B. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):482–487. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafstrom I., Palmblad J., Malmsten C. L., Rådmark O., Samuelsson B. Leukotriene B4--a stereospecific stimulator for release of lysosomal enzymes from neutrophils. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jul 20;130(1):146–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80684-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Corcoran B. A., Venkatasubramanian K., Schiffmann E., Axelrod J. Chemoattractants stimulate degradation of methylated phospholipids and release of arachidonic acid in rabbit leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2640–2643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humes J. L., Sadowski S., Galavage M., Goldenberg M., Subers E., Bonney R. J., Kuehl F. A., Jr Evidence for two sources of arachidonic acid for oxidative metabolism by mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1591–1594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmeyer J. E., Snyderman R., Johnston R. B., Jr Stimulation of neutrophil oxidative metabolism by chemotactic peptides: influence of calcium ion concentration and cytochalasin B and comparison with stimulation by phorbol myristate acetate. Blood. 1979 Jul;54(1):35–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. C., Hammarström S., Samuelsson B. Leukotriene C: a slow-reacting substance from murine mastocytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4275–4279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccache P. H., Molski T. F., Becker E. L., Borgeat P., Picard S., Vallerand P., Sha'afi R. I. Specificity of the effect of lipoxygenase metabolites of arachidonic acid on calcium homeostasis in neutrophils. Correlation with functional activity. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8608–8611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J., Wilkinson S., Cuatrecasas P. Receptor-mediated uptake and degradation of 125I-chemotactic peptide by human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):10700–10706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Showell H. J., Becker E. L., Ward P. A. Neutrophil aggregation and degranulation. Effect of arachidonic acid. Am J Pathol. 1979 May;95(2):433–444. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmblad J., Malmsten C. L., Udén A. M., Rådmark O., Engstedt L., Samuelsson B. Leukotriene B4 is a potent and stereospecific stimulator of neutrophil chemotaxis and adherence. Blood. 1981 Sep;58(3):658–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett W. C., Jesse R. L., Cohen P. Initiation of phospholipase A2 activity in human platelets by the calcium ion ionophore A23187. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 18;486(1):209–213. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Corcoran B. A., Wahl S. M. N-formylmethionyl peptides as chemoattractants for leucocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1059–1062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serhan C. N., Fridovich J., Goetzl E. J., Dunham P. B., Weissmann G. Leukotriene B4 and phosphatidic acid are calcium ionophores. Studies employing arsenazo III in liposomes. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):4746–4752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showell H. J., Naccache P. H., Sha'afi R. I., Becker E. L. Inhibition of rabbit neutrophil lysosomal enzyme secretion, non-stimulated and chemotactic factor stimulated locomotion by nordihydroguaiaretic acid. Life Sci. 1980 Aug 4;27(5):421–426. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90191-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen J. E., Weissmann G. Effects of indomethacin, 5,8,11,14-eicosatetraynoic acid, and p-bromophenacyl bromide on lysosomal enzyme release and superoxide anion generation by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Feb 15;29(4):533–538. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90373-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



