Abstract
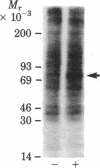
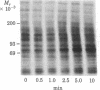
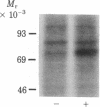
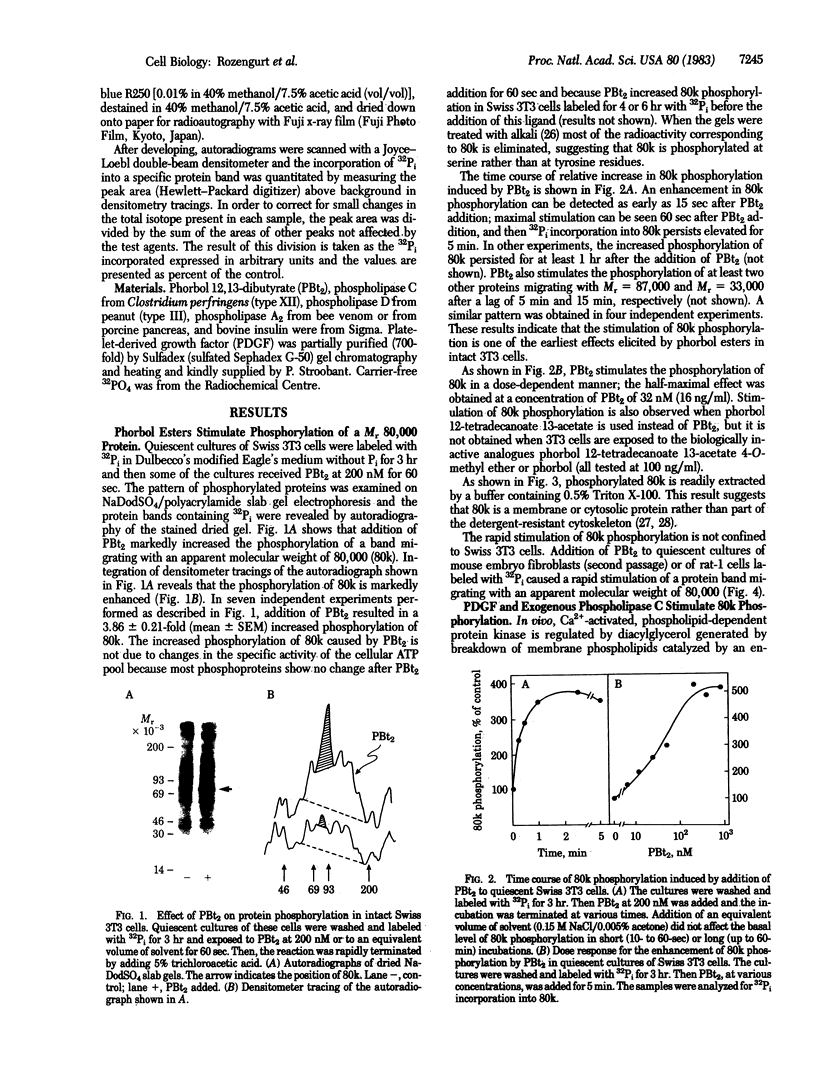
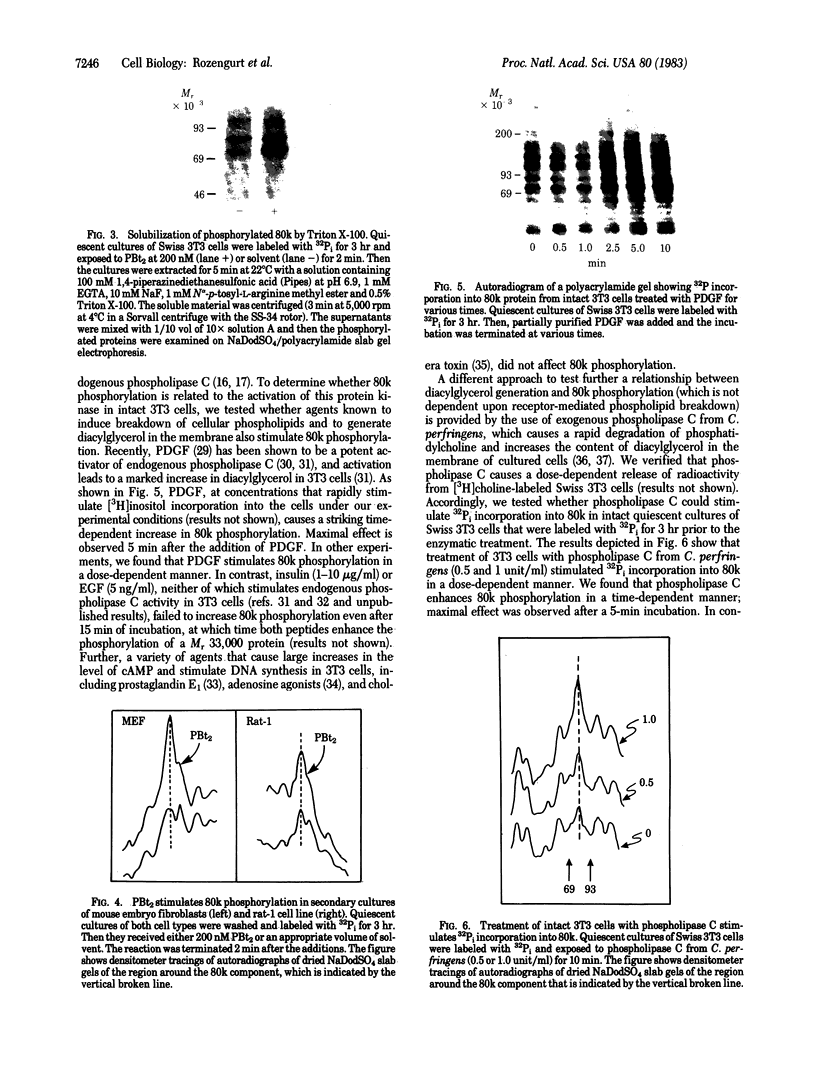
Addition of biologically active phorbol esters to intact quiescent 3T3 mouse cells stimulates an extremely rapid (detectable within seconds) phosphorylation of a Mr 80,000 cellular protein (termed "80k"). Phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate enhances 80k phosphorylation in a dose-dependent manner; half-maximal effect is obtained at 32 nM. The possibility that this phosphorylation is related to the activation of Ca2+-activated phospholipid-dependent protein kinase is suggested by the fact that phospholipid breakdown induced by exogenous treatment of the cells with phospholipase C from Clostridium perfringens or with platelet-derived growth factor, which is a potent activator of endogenous phospholipase C activity, also causes a rapid enhancement of 80k phosphorylation. Moreover, prolonged pretreatment of the cells with phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate, which leads to a marked decrease in the number of specific phorbol ester binding sites, prevents the phosphorylation of 80k stimulated by phorbol esters, phospholipase C, and platelet-derived growth factor. These findings provide evidence obtained with intact cells that implicate the stimulation of Ca2+-activated phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in the action of phorbol esters and other growth factors.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashendel C. L., Staller J. M., Boutwell R. K. Identification of a calcium- and phospholipid- dependent phorbol ester binding activity in the soluble fraction of mouse tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Feb 28;111(1):340–345. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker M. A., Dicker P., Rozengurt E. Mitogenic enhancement of purine base phosphoribosylation in Swiss mouse 3T3 cells. Am J Physiol. 1983 Mar;244(3):C288–C296. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.244.3.C288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ze'ev A., Duerr A., Solomon F., Penman S. The outer boundary of the cytoskeleton: a lamina derived from plasma membrane proteins. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):859–865. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90326-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom G. S., Lockwood A. H. Specific protein phosphorylation during cyclic AMP-mediated morphological reversion of transformed cells. J Supramol Struct. 1980;14(2):241–254. doi: 10.1002/jss.400140213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen-Pope D. F., Ross R. Platelet-derived growth factor. II. Specific binding to cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5161–5171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D., Dicker P., Rozengurt E. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding to surface receptors by tumor promotors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Feb 28;86(4):1037–1043. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90221-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. K., Rozengurt E. Binding of phorbol esters to high-affinity sites on murine fibroblastic cells elicits a mitogenic response. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Jul;112(1):42–50. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041120108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M., Rozengurt E. Stimulation of DNA synthesis in murine fibroblasts by the tumour promoter teleocidin: relationship to phorbol esters and vasopressin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Feb 26;104(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91372-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Changes in protein phosphorylation in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed chicken embryo cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):165–178. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dicker P., Rozengurt E. Phorbol ester stimulation of Na influx and Na-K pump activity in Swiss 3T3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 May 15;100(1):433–441. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(81)80115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dicker P., Rozengurt E. Phorbol esters and vasopressin stimulate DNA synthesis by a common mechanism. Nature. 1980 Oct 16;287(5783):607–612. doi: 10.1038/287607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dicker P., Rozengurt E. Stimulation of DNA synthesis by tumour promoter and pure mitogenic factors. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):723–726. doi: 10.1038/276723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dicker P., Rozengurt E. Synergistic stimulation of early events and DNA synthesis by phorbol esters, polypeptide growth factors, and retinoids in cultured fibroblasts. J Supramol Struct. 1979;11(1):79–93. doi: 10.1002/jss.400110109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelehrter T. D., Rozengurt E. Stimulation of monovalent ion fluxes and DNA synthesis in 3T3 cells by melittin and vasopressin is not mediated by phospholipid deacylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Nov 28;97(2):716–724. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90323-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habenicht A. J., Glomset J. A., King W. C., Nist C., Mitchell C. D., Ross R. Early changes in phosphatidylinositol and arachidonic acid metabolism in quiescent swiss 3T3 cells stimulated to divide by platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12329–12335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Westermark B., Wasteson A. Specific receptors for platelet-derived growth factor on cells derived from connective tissue and glia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3664–3668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. S., Huang S. S., Kennedy B., Deuel T. F. Platelet-derived growth factor. Specific binding to target cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8130–8136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juskevich J. C., Kuhn D. M., Lovenberg W. Phosphorylation of brain cytosol proteins. Effects of phospholipids and calmodulin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1950–1953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent C. Stimulation of phospholipid metabolism in embryonic muscle cells treated with phospholipase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4474–4478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Inohara S., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase from rat brain. Subcellular distribution, purification, and properties. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13341–13348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto A., Takai Y., Mori T., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Activation of calcium and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by diacylglycerol, its possible relation to phosphatidylinositol turnover. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2273–2276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft A. S., Anderson W. B. Phorbol esters increase the amount of Ca2+, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase associated with plasma membrane. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):621–623. doi: 10.1038/301621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Andersson R. G., Wise B. C., Mackerlova L., Salomonsson I., Brackett N. L., Katoh N., Shoji M., Wrenn R. W. Calcium-dependent protein kinase: widespread occurrence in various tissues and phyla of the animal kingdom and comparison of effects of phospholipid, calmodulin, and trifluoperazine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7039–7043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach K. L., James M. L., Blumberg P. M. Characterization of a specific phorbol ester aporeceptor in mouse brain cytosol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4208–4212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. S., Weinstein I. B. Mechanism of tumor promoter inhibition of cellular binding of epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5168–5172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori T., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Yu B., Nishizuka Y. Inhibitory action of chlorpromazine, dibucaine, and other phospholipid-interacting drugs on calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8378–8380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J. E., Kuhn L. J., Vandenbark G. R. Phorbol diester receptor copurifies with protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):36–40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Vogel A. The platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E. Adenosine receptor activation in quiescent Swiss 3T3 cells. Enhancement of cAMP levels, DNA synthesis and cell division. Exp Cell Res. 1982 May;139(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90319-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Collins M. K., Keehan M. Mitogenic effect of prostaglandin E1 in Swiss 3T3 cells: role of cyclic AMP. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Sep;116(3):379–384. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041160316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Heppel L. A. Serum rapidly stimulates ouabain-sensitive 86-RB+ influx in quiescent 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4492–4495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Legg A., Pettican P. Vasopressin stimulation of mouse 3T3 cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1284–1287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Legg A., Strang G., Courtenay-Luck N. Cyclic AMP: a mitogenic signal for Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4392–4396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Sinnett-Smith J. Bombesin stimulation of DNA synthesis and cell division in cultures of Swiss 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2936–2940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shier W. T., Durkin J. P. Role of stimulation of arachidonic acid release in the proliferative response of 3T3 mouse fibroblasts to platelet-derived growth factor. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Aug;112(2):171–181. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041120204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoyab M., De Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Biologically active phorbol esters specifically alter affinity of epidermal growth factor membrane receptors. Nature. 1979 May 31;279(5712):387–391. doi: 10.1038/279387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleight R., Kent C. Regulation of phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis in mammalian cells. I. Effects of phospholipase C treatment on phosphatidylcholine metabolism in Chinese hamster ovary cells and LM mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):824–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODARO G. J., GREEN H. Quantitative studies of the growth of mouse embryo cells in culture and their development into established lines. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:299–313. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kishimoto A., Iwasa Y., Kawahara Y., Mori T., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-dependent activation of a multifunctional protein kinase by membrane phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3692–3695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]