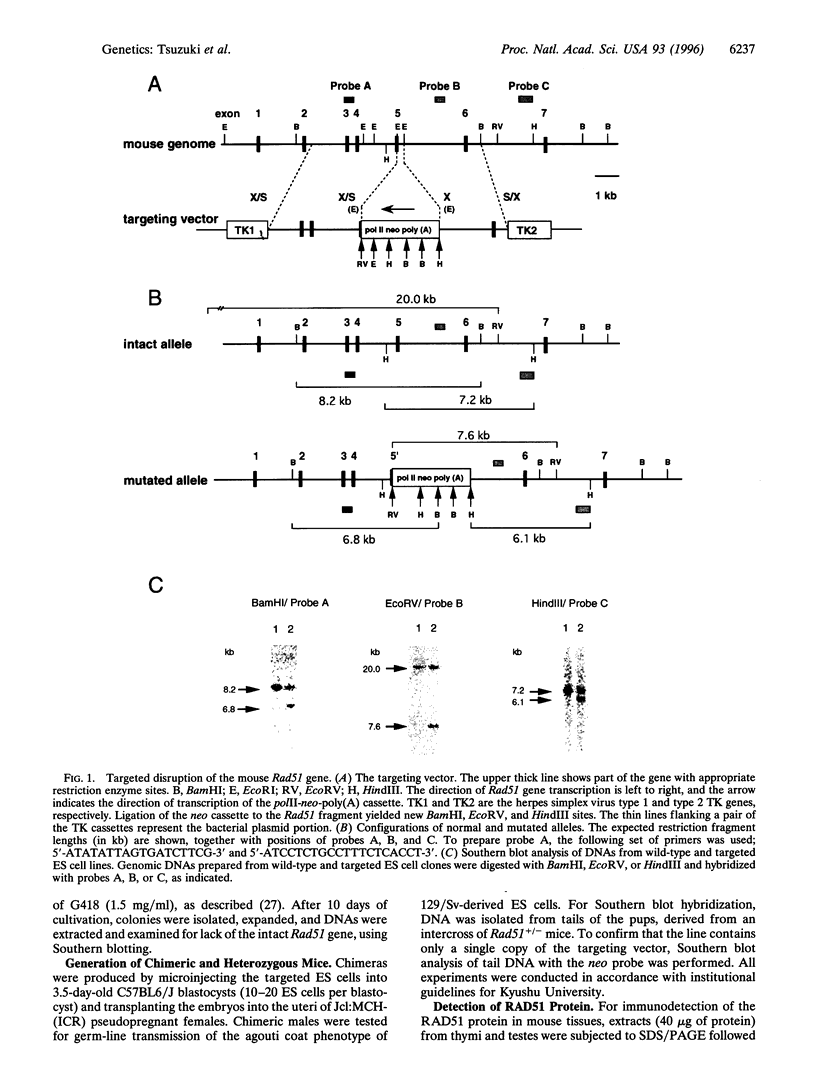
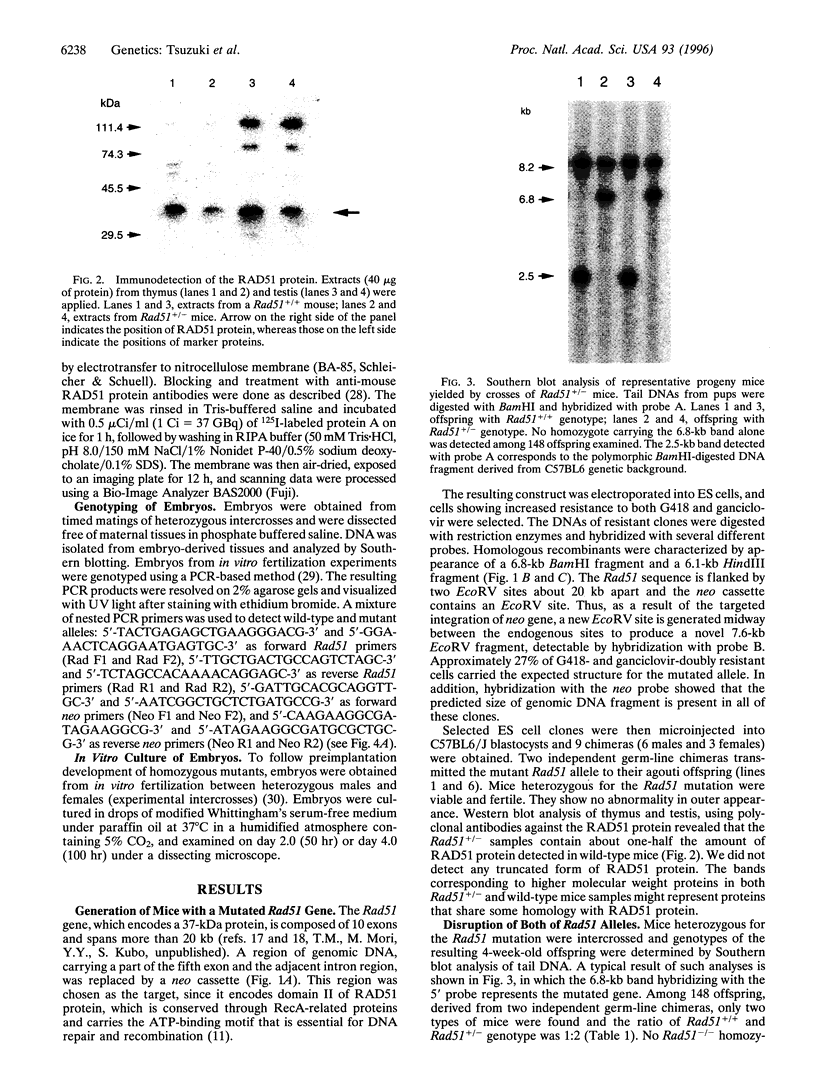
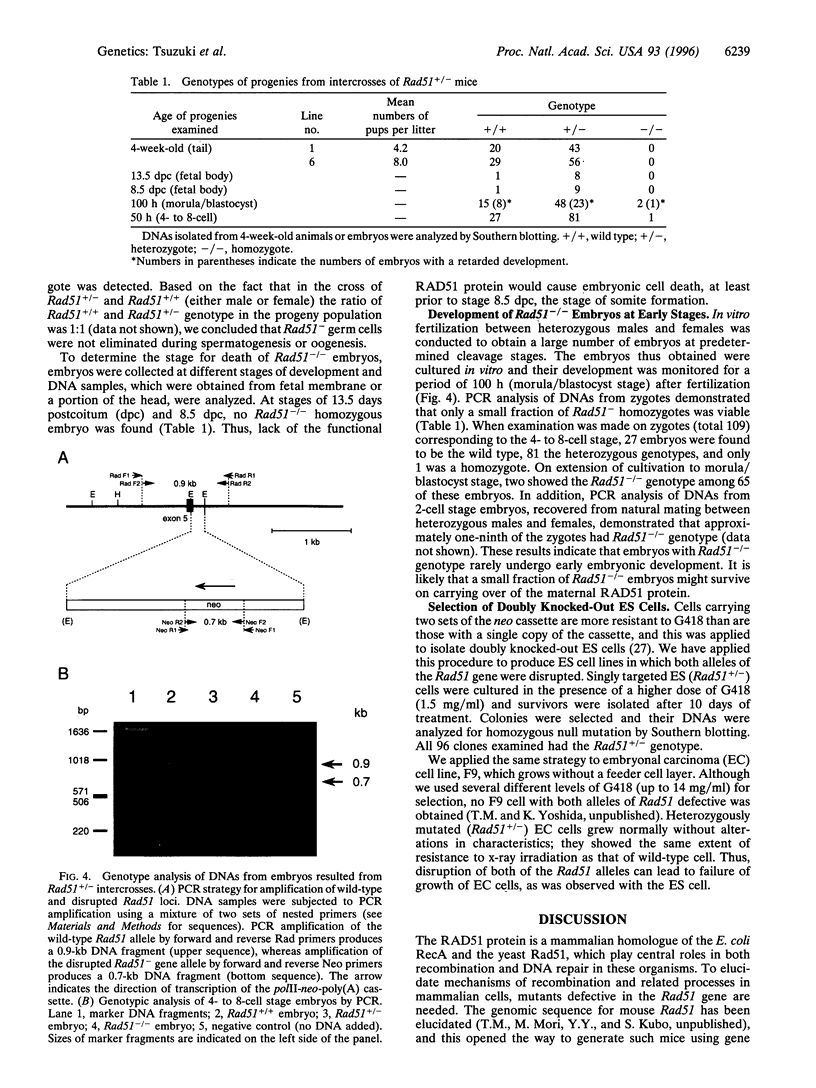
Abstract
The mouse Rad51 gene is a mammalian homologue of the Escherichia coli recA and yeast RAD51 genes, both of which are involved in homologous recombination and DNA repair. To elucidate the physiological role of RAD51 protein, the gene was targeted in embryonic stem (ES) cells. Mice heterozygous for the Rad51 null mutation were intercrossed and their offspring were genotyped. There were no homozygous (Rad51-/-) pups among 148 neonates examined but a few Rad51-/- embryos were identified when examined during the early stages of embryonic development. Doubly knocked-out ES cells were not detected under conditions of selective growth. These results are interpreted to mean that RAD51 protein plays an essential role in the proliferation of cell. The homozygous Rad51 null mutation can be categorized in cell-autonomous defects. Pre-implantational lethal mutations that disrupt basic molecular functions will thus interfere with cell viability.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adzuma K., Ogawa T., Ogawa H. Primary structure of the RAD52 gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2735–2744. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basile G., Aker M., Mortimer R. K. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional regulation of the yeast recombinational repair gene RAD51. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3235–3246. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezzubova O., Shinohara A., Mueller R. G., Ogawa H., Buerstedde J. M. A chicken RAD51 homologue is expressed at high levels in lymphoid and reproductive organs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 11;21(7):1577–1580. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.7.1577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK A. J., MARGULIES A. D. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF RECOMBINATION-DEFICIENT MUTANTS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Feb;53:451–459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. R. Altering the genome by homologous recombination. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1288–1292. doi: 10.1126/science.2660260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copp A. J. Death before birth: clues from gene knockouts and mutations. Trends Genet. 1995 Mar;11(3):87–93. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9525(00)89008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng C., Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Location of crossovers during gene targeting with insertion and replacement vectors. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2134–2140. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan J. W., Milne G. T., Weaver D. T. Homotypic and heterotypic protein associations control Rad51 function in double-strand break repair. Genes Dev. 1994 Nov 1;8(21):2552–2562. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.21.2552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery H. S., Schild D., Kellogg D. E., Mortimer R. K. Sequence of RAD54, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene involved in recombination and repair. Gene. 1991 Jul 31;104(1):103–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90473-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Game J. C., Mortimer R. K. A genetic study of x-ray sensitive mutants in yeast. Mutat Res. 1974 Sep;24(3):281–292. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(74)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hays S. L., Firmenich A. A., Berg P. Complex formation in yeast double-strand break repair: participation of Rad51, Rad52, Rad55, and Rad57 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jul 18;92(15):6925–6929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.15.6925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. D., Symington L. S. Functional differences and interactions among the putative RecA homologs Rad51, Rad55, and Rad57. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Sep;15(9):4843–4850. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.9.4843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawate H., Ihara K., Kohda K., Sakumi K., Sekiguchi M. Mouse methyltransferase for repair of O6-methylguanine and O4-methylthymine in DNA. Carcinogenesis. 1995 Jul;16(7):1595–1602. doi: 10.1093/carcin/16.7.1595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczykowski S. C., Dixon D. A., Eggleston A. K., Lauder S. D., Rehrauer W. M. Biochemistry of homologous recombination in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1994 Sep;58(3):401–465. doi: 10.1128/mr.58.3.401-465.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczykowski S. C., Eggleston A. K. Homologous pairing and DNA strand-exchange proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:991–1043. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.005015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küppers R., Zhao M., Hansmann M. L., Rajewsky K. Tracing B cell development in human germinal centres by molecular analysis of single cells picked from histological sections. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):4955–4967. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06189.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larue L., Ohsugi M., Hirchenhain J., Kemler R. E-cadherin null mutant embryos fail to form a trophectoderm epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 16;91(17):8263–8267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.17.8263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnuson T., Epstein C. J. Oligosyndactyly: a lethal mutation in the mouse that results in mitotic arrest very early in development. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):823–833. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90277-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Disruption of the proto-oncogene int-2 in mouse embryo-derived stem cells: a general strategy for targeting mutations to non-selectable genes. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):348–352. doi: 10.1038/336348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita T., Yoshimura Y., Yamamoto A., Murata K., Mori M., Yamamoto H., Matsushiro A. A mouse homolog of the Escherichia coli recA and Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD51 genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6577–6580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen R. M., Conner D. A., Chao S., Geisterfer-Lowrance A. A., Seidman J. G. Production of homozygous mutant ES cells with a single targeting construct. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2391–2395. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M. Helical interactions in homologous pairing and strand exchange driven by RecA protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5355–5358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rancourt D. E., Tsuzuki T., Capecchi M. R. Genetic interaction between hoxb-5 and hoxb-6 is revealed by nonallelic noncomplementation. Genes Dev. 1995 Jan 1;9(1):108–122. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.1.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riethmacher D., Brinkmann V., Birchmeier C. A targeted mutation in the mouse E-cadherin gene results in defective preimplantation development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 31;92(3):855–859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.3.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara A., Ogawa H., Matsuda Y., Ushio N., Ikeo K., Ogawa T. Cloning of human, mouse and fission yeast recombination genes homologous to RAD51 and recA. Nat Genet. 1993 Jul;4(3):239–243. doi: 10.1038/ng0793-239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara A., Ogawa H., Ogawa T. Rad51 protein involved in repair and recombination in S. cerevisiae is a RecA-like protein. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):457–470. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90447-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spyropoulos D. D., Capecchi M. R. Targeted disruption of the even-skipped gene, evx1, causes early postimplantation lethality of the mouse conceptus. Genes Dev. 1994 Aug 15;8(16):1949–1961. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.16.1949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Story R. M., Weber I. T., Steitz T. A. The structure of the E. coli recA protein monomer and polymer. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):318–325. doi: 10.1038/355318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi E., Matsuda Y., Hori T., Yasuda N., Tsuji S., Mori M., Yoshimura Y., Yamamoto A., Morita T., Matsushiro A. Chromosome mapping of the human (RECA) and mouse (Reca) homologs of the yeast RAD51 and Escherichia coli recA genes to human (15q15.1) and mouse (2F1) chromosomes by direct R-banding fluorescence in situ hybridization. Genomics. 1994 Jan 15;19(2):376–378. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. C. The processing of recombination intermediates: mechanistic insights from studies of bacterial proteins. Cell. 1994 Jan 14;76(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90168-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto A., Taki T., Yagi H., Habu T., Yoshida K., Yoshimura Y., Yamamoto K., Matsushiro A., Nishimune Y., Morita T. Cell cycle-dependent expression of the mouse Rad51 gene in proliferating cells. Mol Gen Genet. 1996 Apr 24;251(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF02174338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura Y., Morita T., Yamamoto A., Matsushiro A. Cloning and sequence of the human RecA-like gene cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 11;21(7):1665–1665. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.7.1665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







