Abstract
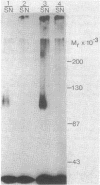
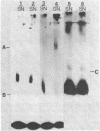
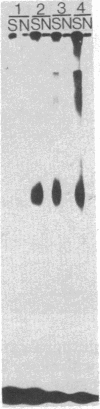
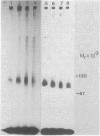
A cell surface glycoprotein receptor for nerve growth factor (NGF) has been identified by covalent crosslinking to 125I-labeled NGF (125I-NGF). Either ethyldimethylisopropyl-aminocarbodiimide or hydroxysuccinimidyl-p-azidobenzoate causes highly specific crosslinking of 125I-NGF to a similar receptor species on rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells and on human melanoma A875 cells. The NGF-receptor complex migrates as a broad band in NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis with an apparent Mr of approximately equal to 100,000. Because the NaDodSO4-denatured complex apparently contains a single Mr 13,000 NGF chain, the apparent molecular weight of the receptor itself is 87,000. Inhibition of protein glycosylation by tunicamycin generates smaller 125I-NGF-receptor complexes. The mobility of the smallest of these in NaDodSO4 gel electrophoresis corresponds to a Mr of 90,000 for the complex and, hence, 77,000 for the carbohydrate-deficient receptor. A second NGF-receptor complex with a Mr of 225,000 also is obtained from A875 cells but only occasionally from PC12 cells. Tunicamycin treatment decreases the molecular weight of these species by 10,000-15,000. Substantial purification of the Mr 100,000 NGF-receptor complex was achieved by lectin affinity chromatography on columns of wheat germ agglutinin linked to Affi-Gel 15. The specific absorption of NGF-receptor complexes to these columns indicates that the receptor is a glycoprotein that contains N-acetyl-D-glucosamine.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aloe L., Levi-Montalcini R. Nerve growth factor-induced transformation of immature chromaffin cells in vivo into sympathetic neurons: effect of antiserum to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1246–1250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee S. P., Cuatrecasas P., Snyder S. H. Nerve growth factor receptor binding. Influence of enzymes, ions, and protein reagents. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1427–1433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell M. A., Schechter A. L., Vaughn K. M. Clonal variants of PC12 pheochromocytoma cells with altered response to nerve growth factor. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):857–866. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90449-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell M. A., Shooter E. M. Dissociation equilibrium constant of beta nerve growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8532–8536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton L. E., Wilson W. H., Shooter E. M. Nerve growth factor in mouse saliva. Rapid isolation procedures for and characterization of 7 S nerve growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 10;253(21):7807–7812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costrini N. V., Kogan M., Kukreja K., Bradshaw R. A. Physical properties of the detergent-extracted nerve growth factor receptor of sympathetic ganglia. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11242–11246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. L., Grosse V. A., Kucherlapati R., Bothwell M. Genetic analysis of epidermal growth factor action: assignment of human epidermal growth factor receptor gene to chromosome 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4188–4192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabricant R. N., De Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Nerve growth factor receptors on human melanoma cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):565–569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazier W. A., Boyd L. F., Bradshaw R. A. Properties of the specific binding of 125I-nerve growth factor to responsive peripheral neurons. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 10;249(17):5513–5519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Tischler A. S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrup K., Shooter E. M. Properties of the beta nerve growth factor receptor of avian dorsal root ganglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3884–3888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrup K., Thoenen H. Properties of the nerve growth factor receptor of a clonal line of rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Jun;121(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90445-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. L., MacAndrew V. I., Jr, Pilch P. F. Identification of the glucagon receptor in rat liver membranes by photoaffinity crosslinking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):875–878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler J. A., Cochard P., Black I. B. Nerve growth factor alters the fate of embryonic neuroblasts. Nature. 1979 Jul 12;280(5718):141–142. doi: 10.1038/280141a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo R. T., Pigeon M. L. Expression of membrane IGM by a human B lymphoblastoid cell line in the presence of monensin. Mol Immunol. 1983 Mar;20(3):345–348. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90074-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landreth G. E., Shooter E. M. Nerve growth factor receptors on PC12 cells: ligand-induced conversion from low- to high-affinity states. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4751–4755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Angeletti P. U. Nerve growth factor. Physiol Rev. 1968 Jul;48(3):534–569. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.3.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R. The nerve growth factor: its mode of action on sensory and sympathetic nerve cells. Harvey Lect. 1966;60:217–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massague J., Buxser S., Johnson G. L., Czech M. P. Affinity labeling of a nerve growth factor receptor component on rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec 8;693(1):205–212. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90488-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massague J., Guillette B. J., Czech M. P., Morgan C. J., Bradshaw R. A. Identification of a nerve growth factor receptor protein in sympathetic ganglia membranes by affinity labeling. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9419–9424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olender E. J., Stach R. W. Sequestration of 125I-labeled beta nerve growth factor by sympathetic neurons. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9338–9343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puma P., Buxser S. E., Watson L., Kelleher D. J., Johnson G. L. Purification of the receptor for nerve growth factor from A875 melanoma cells by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3370–3375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter A. L., Bothwell M. A. Nerve growth factor receptors on PC12 cells: evidence for two receptor classes with differing cytoskeletal association. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):867–874. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter A., Riopelle R. J., Harris-Warrick R. M., Shooter E. M. Nerve growth factor receptors. Characterization of two distinct classes of binding sites on chick embryo sensory ganglia cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5972–5982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D., Shooter E. M. Alteration of binding properties and cytoskeletal attachment of nerve growth factor receptors in PC12 cells by wheat germ agglutinin. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):710–717. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]