Abstract
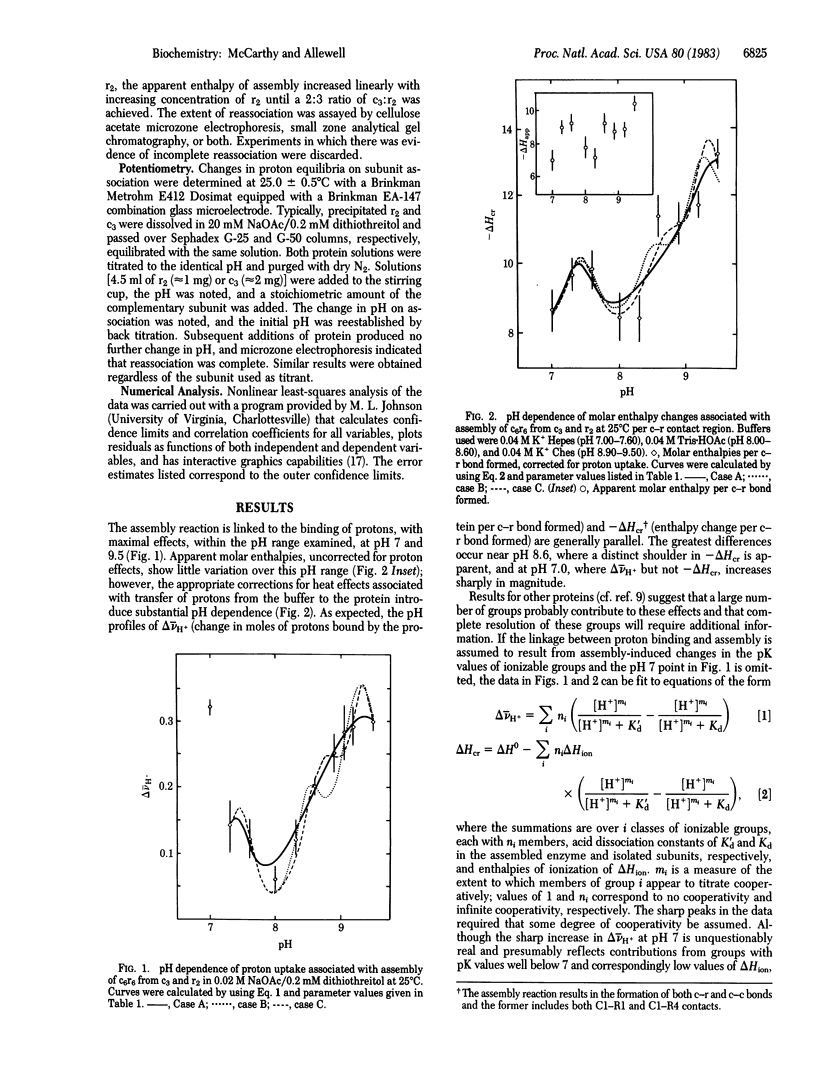
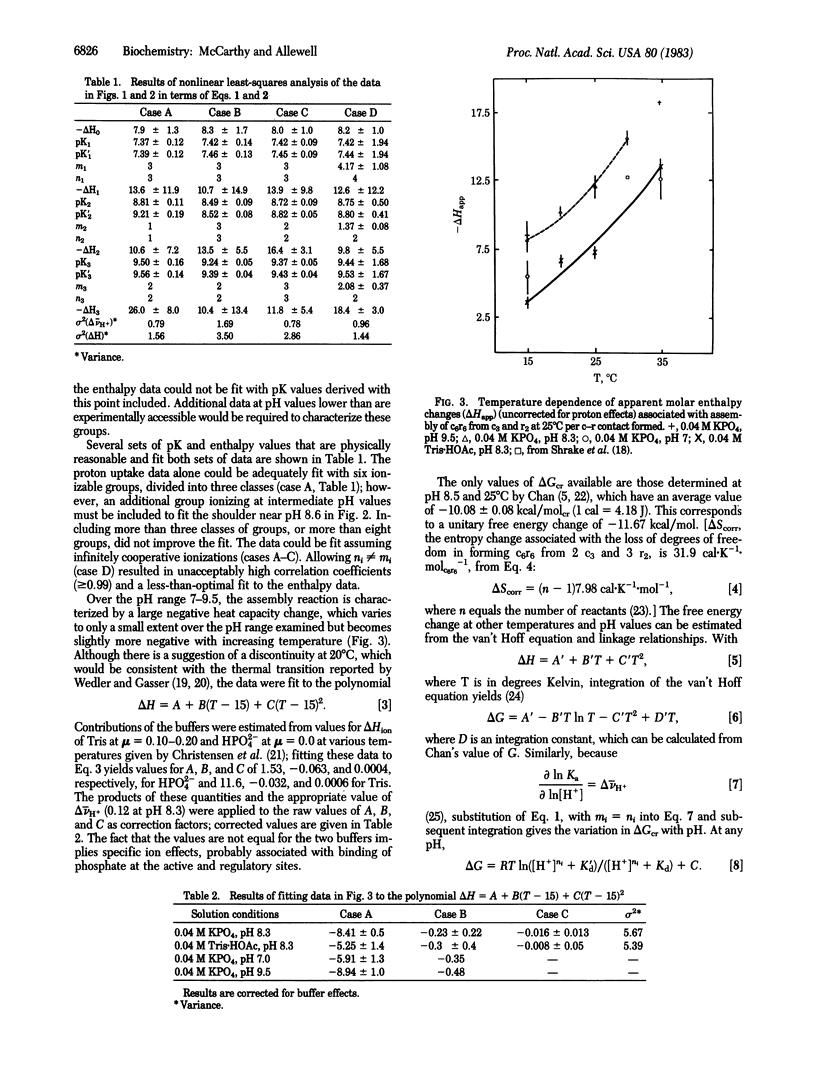
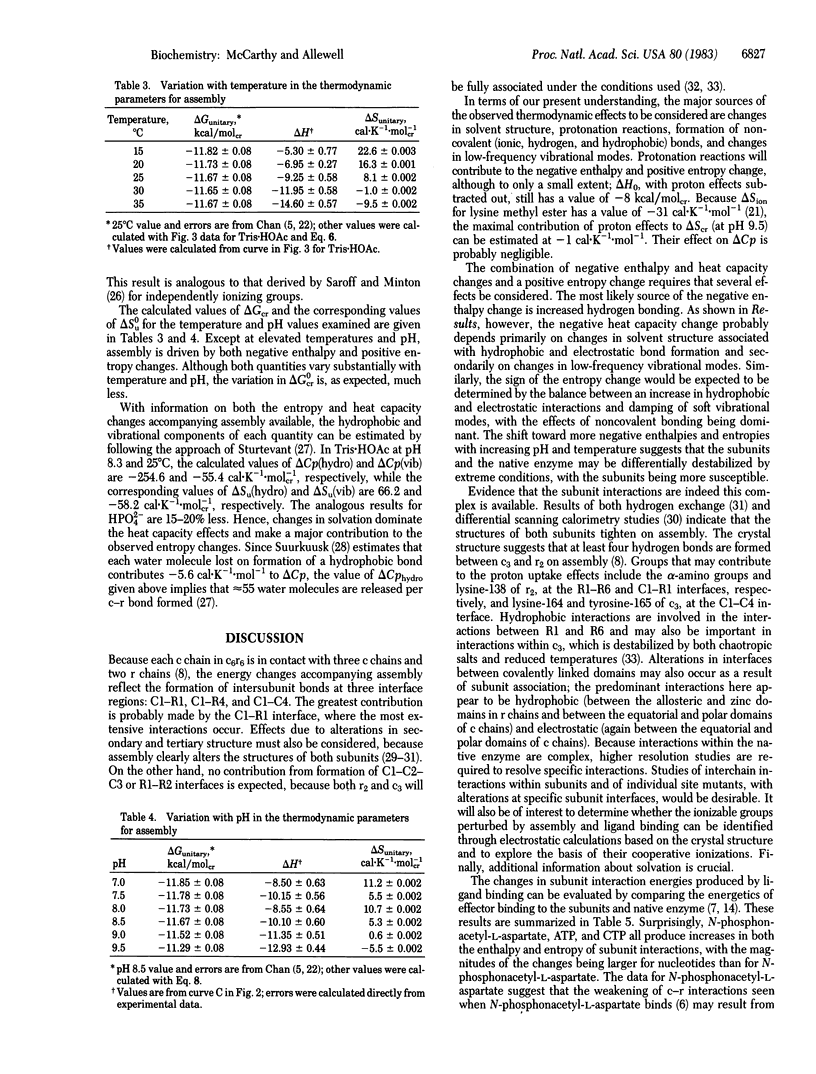
Reaction microcalorimetry and potentiometry have been used to define the thermodynamics of assembly of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase (aspartate carbamoyltransferase, carbamoylphosphate:L-aspartate carbamoyltransferase, EC 2.1.3.2) from its catalytic and regulatory subunits and the linkage between assembly and proton binding. Over the pH range 7-9.5 and the temperature range 15-30 degrees C, assembly is characterized by negative enthalpy and heat capacity changes and positive entropy changes. The dependence of the enthalpy and entropy changes on pH is complex; however, the negative heat capacity change results in both quantities becoming more negative with increasing temperature. Assembly is linked to the binding of protons; the effects observed can be fit to models involving six or more ionizable groups with pK values of 7.3-7.4, 8.5-8.8, and 9.2-9.5, which ionize cooperatively. Contributions from additional groups cannot be ruled out and are in fact expected. The overall pattern of thermodynamic effects implies a complex set of intersubunit interactions. Protonation reactions and increased hydrogen bonding are likely to be the major sources of the negative enthalpy change; however, the negative heat capacity change results primarily from changes in solvent structure associated with hydrophobic and electrostatic bond formation with changes in low-frequency vibrational modes making a secondary contribution. Similarly, the relatively small entropy change observed within the temperature range examined probably reflects the balance between positive contributions from increased hydrophobic and electrostatic bonding and negative contributions from increased hydrogen bonding and damping of low-frequency vibrational modes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackers G. K. Energetics of subunit assembly and ligand binding in human hemoglobin. Biophys J. 1980 Oct;32(1):331–346. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(80)84960-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allwell N. M., Hofmann G. E., Zaug A., Lennick M. Bohr effect in Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamylase. Linkages between substrate binding, proton binding, and conformational transitions. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 10;18(14):3008–3015. doi: 10.1021/bi00581a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns D. L., Schachman H. K. Assembly of the catalytic trimers of aspartate transcarbamoylase from folded monomers. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8638–8647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burz D. S., Allewell N. M. Interactions of ionizable groups in Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamylase with adenosine and cytidine 5'-triphosphates. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6647–6655. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. W. Subunit interactions in aspartate trancarbamylase from Escherichia coli studied using matrix-bound derivatives. FEBS Lett. 1974 Aug 25;44(2):178–181. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80720-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. W. Subunit interactions in aspartate transcarbamylase. A model for the allosteric mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):668–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohlberg J. A., Pigiet V. P., Jr, Schachman H. K. Structure and arrangement of the regulatory subunits in aspartate transcarbamylase. Biochemistry. 1972 Aug 29;11(18):3396–3411. doi: 10.1021/bi00768a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan M. A., Ackers G. K., Matthew J. B., Hanania G. I., Gurd F. R. Electrostatic contributions to the energetics of dimer-tetramer assembly in human hemoglobin: pH dependence and effect of specifically bound chloride ions. Biochemistry. 1981 Dec 22;20(26):7439–7449. doi: 10.1021/bi00529a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formisano S., Johnson M. L., Edelhoch H. Thermodynamics of the self-association of glucagon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3340–3344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart J. C., Holoubek H. The purification of aspartate transcarbamylase of Escherichia coli and separation of its protein subunits. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 25;242(12):2886–2892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. H., Rosenbusch J. P., Blout E. R., Weber K. K. Conformational changes in aspartate transcarbamylase. II. Circular dichroism evidence for the involvement of metal ions in allosteric interactions. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 25;248(14):5057–5062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammes G. G., Wu C. W. Regulation of enzyme activity. The activity of enzymes can be controlled by a multiplicity of conformational equilibria. Science. 1971 Jun 18;172(3989):1205–1211. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3989.1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearn R. P., Richards F. M., Sturtevant J. M., Watt G. D. Thermodynamics of the binding of S-peptide to S-protein to form ribonuclease S.. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 2;10(5):806–817. doi: 10.1021/bi00781a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensley P., Schachman H. K. Communication between dissimilar subunits in aspartate transcarbamoylase: effect of inhibitor and activator on the conformation of the catalytic polypeptide chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3732–3736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho C., Russu I. M. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance investigation of hemoglobins. Methods Enzymol. 1981;76:275–312. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)76128-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honzatko R. B., Crawford J. L., Monaco H. L., Ladner J. E., Ewards B. F., Evans D. R., Warren S. G., Wiley D. C., Ladner R. C., Lipscomb W. N. Crystal and molecular structures of native and CTP-liganded aspartate carbamoyltransferase from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 15;160(2):219–263. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howlett G. J., Blackburn M. N., Compton J. G., Schachman H. K. Allosteric regulation of aspartate transcarbamoylase. Analysis of the structural and functional behavior in terms of a two-state model. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 15;16(23):5091–5100. doi: 10.1021/bi00642a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. L., Ackers G. K. Thermodynamic analysis of human hemoglobins in terms of the Perutz mechanism: extensions of the Szabo--Karplus model to include subunit assembly. Biochemistry. 1982 Jan 19;21(2):201–211. doi: 10.1021/bi00531a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. S., Schachman H. K. Propagation of conformational changes in Ni(II)-substituted aspartate transcarbamoylase: effect of active-site ligands on the regulatory chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1995–1999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantrowitz E. R., Lipscomb W. N. Functionally important arginine residues of aspartate transcarbamylase. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):2873–2880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerbiriou D., Hervé G. An aspartate transcarbamylase lacking catalytic subunit interactions. II. Regulatory subunits are responsible for the lack of co-operative interactions between catalytic sites. Drastic feedback inhibition does not restore these interactions. J Mol Biol. 1973 Aug 25;78(4):687–702. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90289-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knier B. L., Allewell N. M. Calorimetric analysis of aspartate transcarbamylase from Escherichia coli. Binding of substrates and substrate analogues to the native enzyme and catalytic subunit. Biochemistry. 1978 Mar 7;17(5):784–790. doi: 10.1021/bi00598a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langerman N., Sturtevant J. M. Calorimetric studies of quaternary structure and ligand-binding hemerythrin. Biochemistry. 1971 Jul 20;10(15):2809–2815. doi: 10.1021/bi00791a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavialle F., Rogard M., Alfsen A. Calorimetric determination of the enthalpy and heat capacity changes for the association of haptoglobin with hemoglobin. I. Demonstration of two interacting systems. Biochemistry. 1974 May 7;13(10):2231–2234. doi: 10.1021/bi00707a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennick M., Allewell N. M. Changes in the hydrogen exchange kinetics of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamylase produced by effector binding and subunit association. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6759–6763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClintock D. K., Markus G. Conformational changes in aspartate transcarbamylase. I. Proteolysis of the intact enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 10;243(11):2855–2862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettigrew D. W., Romeo P. H., Tsapis A., Thillet J., Smith M. L., Turner B. W., Ackers G. K. Probing the energetics of proteins through structural perturbation: sites of regulatory energy in human hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1849–1853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russu I. M., Ho C. Proton longitudinal relaxation investigation of histidyl residues in human normal adult hemoglobin. Biophys J. 1982 Aug;39(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84509-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saroff H. A., Minton A. P. The Hill plot and the energy of interaction in hemoglobin. Science. 1972 Mar 17;175(4027):1253–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4027.1253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senear D. F., Teller D. C. Thermodynamics of concanavalin A dimer-tetramer self-association: sedimentation equilibrium studies. Biochemistry. 1981 May 26;20(11):3076–3083. doi: 10.1021/bi00514a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrake A., Ginsburg A., Schachman H. K. Calorimetric estimate of the enthalpy change for the substrate-promoted conformational transition of aspartate transcarbamoylase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5005–5015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturtevant J. M. Heat capacity and entropy changes in processes involving proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2236–2240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramani S., Bothwell M. A., Gibbons I., Yang Y. R., Schachman H. K. Ligand-promoted weakening of intersubunit bonding domains in aspartate transcarbamolylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3777–3781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suurkuusk J. Specific heat measurements on lysozyme, chymotrypsinogen, and ovalbumin in aqueous solution and in solid state. Acta Chem Scand B. 1974;28(4):409–417. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.28b-0409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiry L., Hervé G. The stimulation of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamylase activity by adenosine triphosphate. Relation with the other regulatory conformational changes; a model. J Mol Biol. 1978 Nov 15;125(4):515–534. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90314-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B. W., Pettigrew D. W., Ackers G. K. Measurement and analysis of ligand-linked subunit dissociation equilibria in human hemoglobins. Methods Enzymol. 1981;76:596–628. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)76147-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdes R., Jr, Ackers G. K. Thermodynamic studies on subunit assembly in human hemoglobin. Self-association of oxygenated chains (alphaSH and betaSH): determination of stoichiometries and equilibrium constants as a function of temperature. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):74–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickers L. P., Donovan J. W., Schachman H. K. Differential scanning calorimetry of asparate transcarbamoylase and its isolate subunits. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 10;253(23):8493–8498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYMAN J., Jr LINKED FUNCTIONS AND RECIPROCAL EFFECTS IN HEMOGLOBIN: A SECOND LOOK. Adv Protein Chem. 1964;19:223–286. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Yang Y. R., Hu C. Y., Schachman H. K. Communication between subunits in aspartate transcarbamoylase. Effect of active site ligands on the tertiary structure of regulatory chains. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):7028–7034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedler F. C., Gasser F. J. Modes of modifier action in E. coli aspartate transcarbamylase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jul;163(1):69–78. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90455-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedler F. C., Gasser F. J. Ordered substrate binding and evidence for a thermally induced change in mechanism for E. coli aspartate transcarbamylase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jul;163(1):57–68. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90454-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. R., Kirschner M. W., Schachman H. K. Aspartate transcarbamoylase (Escherichia coli): preparation of subunits. Methods Enzymol. 1978;51:35–41. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)51007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. R., Schachman H. K. Communication between catalytic subunits in hybrid aspartate transcarbamoylase molecules: effect of ligand binding to active chains on the conformation of unliganded, inactive chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5187–5191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


