Abstract
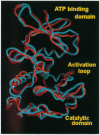
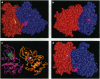
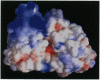
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and p185c-neu proteins associate as dimers to create an efficient signaling assembly. Overexpression of these receptors together enhances their intrinsic kinase activity and concomitantly results in oncogenic cellular transformation. The ectodomain is able to stabilize the dimer, whereas the kinase domain mediates biological activity. Here we analyze potential interactions of the cytoplasmic kinase domains of the EGFR and p185c-neu tyrosine kinases by homology molecular modeling. This analysis indicates that kinase domains can associate as dimers and, based on intermolecular interaction calculations, that heterodimer formation is favored over homodimers. The study also predicts that the self-autophosphorylation sites located within the kinase domains are not likely to interfere with tyrosine kinase activity, but may regulate the selection of substrates, thereby modulating signal transduction. In addition, the models suggest that the kinase domains of EGFR and p185c-neu can undergo higher order aggregation such as the formation of tetramers. Formation of tetrameric complexes may explain some of the experimentally observed features of their ligand affinity and hetero-receptor internalization.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argos P. An investigation of protein subunit and domain interfaces. Protein Eng. 1988 Jul;2(2):101–113. doi: 10.1093/protein/2.2.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blundell T. L., Sibanda B. L., Sternberg M. J., Thornton J. M. Knowledge-based prediction of protein structures and the design of novel molecules. 1987 Mar 26-Apr 1Nature. 326(6111):347–352. doi: 10.1038/326347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougall W. C., Qian X., Peterson N. C., Miller M. J., Samanta A., Greene M. I. The neu-oncogene: signal transduction pathways, transformation mechanisms and evolving therapies. Oncogene. 1994 Aug;9(8):2109–2123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Parker P., Waterfield M. D. Autophosphorylation sites on the epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):483–485. doi: 10.1038/311483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R., Levy R. B., Peles E., Yarden Y. Heterodimerization of the erbB-1 and erbB-2 receptors in human breast carcinoma cells: a mechanism for receptor transregulation. Biochemistry. 1990 Dec 18;29(50):11024–11028. doi: 10.1021/bi00502a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H. Dimerization of cell surface receptors in signal transduction. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90404-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Bleasby A. J., Fuchs R. CLUSTAL V: improved software for multiple sequence alignment. Comput Appl Biosci. 1992 Apr;8(2):189–191. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/8.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. H., Parker M. W., Lei J. Y., Wilce M. C., Benian G. M., Kemp B. E. Insights into autoregulation from the crystal structure of twitchin kinase. Nature. 1994 Jun 16;369(6481):581–584. doi: 10.1038/369581a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard S. R., Wei L., Ellis L., Hendrickson W. A. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the human insulin receptor. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):746–754. doi: 10.1038/372746a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janin J., Chothia C. The structure of protein-protein recognition sites. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16027–16030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S., Thornton J. M. Protein-protein interactions: a review of protein dimer structures. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1995;63(1):31–65. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(94)00008-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Thirup S. Using known substructures in protein model building and crystallography. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):819–822. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04287.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Zou J. Y., Cowan S. W., Kjeldgaard M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr A. 1991 Mar 1;47(Pt 2):110–119. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390010224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Cadena D. L., Zheng J., Ten Eyck L. F., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M., Gill G. N. Structural features that specify tyrosine kinase activity deduced from homology modeling of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5001–5005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Zheng J. H., Ten Eyck L. F., Ashford V. A., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):407–414. doi: 10.1126/science.1862342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokai Y., Cohen J. A., Drebin J. A., Greene M. I. Stage- and tissue-specific expression of the neu oncogene in rat development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8498–8501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokai Y., Myers J. N., Wada T., Brown V. I., LeVea C. M., Davis J. G., Dobashi K., Greene M. I. Synergistic interaction of p185c-neu and the EGF receptor leads to transformation of rodent fibroblasts. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):287–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90843-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax I., Mitra A. K., Ravera C., Hurwitz D. R., Rubinstein M., Ullrich A., Stroud R. M., Schlessinger J. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) induces oligomerization of soluble, extracellular, ligand-binding domain of EGF receptor. A low resolution projection structure of the ligand-binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13828–13833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemmon M. A., Schlessinger J. Regulation of signal transduction and signal diversity by receptor oligomerization. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Nov;19(11):459–463. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüthy R., Bowie J. U., Eisenberg D. Assessment of protein models with three-dimensional profiles. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):83–85. doi: 10.1038/356083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori S., Akiyama T., Yamada Y., Morishita Y., Sugawara I., Toyoshima K., Yamamoto T. C-erbB-2 gene product, a membrane protein commonly expressed on human fetal epithelial cells. Lab Invest. 1989 Jul;61(1):93–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers J. N., LeVea C. M., Smith J. E., Kallen R. G., Tung L., Greene M. I. Expression, purification, and characterization of Bacneu. A soluble protein tyrosine kinase domain encoded by the neu-oncogene. Receptor. 1992 Spring;2(1):1–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls A., Sharp K. A., Honig B. Protein folding and association: insights from the interfacial and thermodynamic properties of hydrocarbons. Proteins. 1991;11(4):281–296. doi: 10.1002/prot.340110407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponder J. W., Richards F. M. Tertiary templates for proteins. Use of packing criteria in the enumeration of allowed sequences for different structural classes. J Mol Biol. 1987 Feb 20;193(4):775–791. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90358-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Press M. F., Cordon-Cardo C., Slamon D. J. Expression of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in normal human adult and fetal tissues. Oncogene. 1990 Jul;5(7):953–962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian X., Dougall W. C., Hellman M. E., Greene M. I. Kinase-deficient neu proteins suppress epidermal growth factor receptor function and abolish cell transformation. Oncogene. 1994 May;9(5):1507–1514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian X., LeVea C. M., Freeman J. K., Dougall W. C., Greene M. I. Heterodimerization of epidermal growth factor receptor and wild-type or kinase-deficient Neu: a mechanism of interreceptor kinase activation and transphosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 15;91(4):1500–1504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quian X. L., Decker S. J., Greene M. I. p185c-neu and epidermal growth factor receptor associate into a structure composed of activated kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1330–1334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sali A., Overington J. P., Johnson M. S., Blundell T. L. From comparisons of protein sequences and structures to protein modelling and design. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jun;15(6):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90036-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samanta A., LeVea C. M., Dougall W. C., Qian X., Greene M. I. Ligand and p185c-neu density govern receptor interactions and tyrosine kinase activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 1;91(5):1711–1715. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.5.1711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by allosteric receptor oligomerization. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Nov;13(11):443–447. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segatto O., King C. R., Pierce J. H., Di Fiore P. P., Aaronson S. A. Different structural alterations upregulate in vitro tyrosine kinase activity and transforming potency of the erbB-2 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5570–5574. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada T., Qian X. L., Greene M. I. Intermolecular association of the p185neu protein and EGF receptor modulates EGF receptor function. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1339–1347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90697-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner D. B., Kokai Y., Wada T., Cohen J. A., Williams W. V., Greene M. I. Linkage of tyrosine kinase activity with transforming ability of the p185neu oncoprotein. Oncogene. 1989 Oct;4(10):1175–1183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner D. B., Liu J., Cohen J. A., Williams W. V., Greene M. I. A point mutation in the neu oncogene mimics ligand induction of receptor aggregation. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):230–231. doi: 10.1038/339230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wodak S. J., De Crombrugghe M., Janin J. Computer studies of interactions between macromolecules. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1987;49(1):29–63. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(87)90008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Schlessinger J. Self-phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor: evidence for a model of intermolecular allosteric activation. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 10;26(5):1434–1442. doi: 10.1021/bi00379a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang F., Strand A., Robbins D., Cobb M. H., Goldsmith E. J. Atomic structure of the MAP kinase ERK2 at 2.3 A resolution. Nature. 1994 Feb 24;367(6465):704–711. doi: 10.1038/367704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng J., Knighton D. R., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M., Ten Eyck L. F. Crystal structures of the myristylated catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase reveal open and closed conformations. Protein Sci. 1993 Oct;2(10):1559–1573. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560021003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]