Abstract
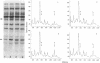
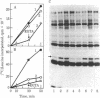
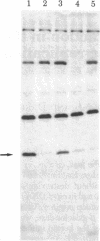
Hemin-supplemented reticulocyte lysates can be activated for translational inhibition by addition of Ca2+ or phospholipid. The fact that this inhibition is prevented or decreased in both cases either by the Ca2+ chelator EGTA or by polymyxin B, an inhibitor of the recently described Ca2+- and phospholipid-dependent protein kinases, suggests the involvement of both Ca2+ and phospholipid in this activation. The inhibition by Ca2+ or phospholipid is accompanied by phosphorylation of the 38-kilodalton subunit of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF-2) and the 90-kilodalton band of the heme-controlled translational inhibitor (HCI) and can be reversed by high concentrations of eIF-2 or GTP. When incubation is conducted at 30 degrees C, the inhibition produced by Ca2+ is not reversed by EGTA after 15 min. However, at 20 degrees C, Ca2+ inhibition can be fully reversed as late as 90 min from the start of incubation and phosphorylation of the eIF-2 alpha-subunit is correspondingly decreased. These results are consistent with the idea that, like heme deprivation, the activation by Ca2+ and phospholipid promotes the first step of the reaction pro-inhibitor in equilibrium reversible inhibitor leads to irreversible inhibitor and suggest that, in the presence of hemin albeit by a different mechanism, this activation affects the same inhibitor that is activated in the absence of heme--namely, HCI. Whether this activation is direct or indirect--e.g., via a separate Ca2+- and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase--remains to be determined.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens M. J., Pain V. M., Henshaw E. C., London I. M. Characterization of a macromolecular inhibitor of polypeptide chain initiation from Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Sep 20;72(2):768–775. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaunay J., Ranu R. S., Levin D. H., Ernst V., London I. M. Characterization of a rat liver factor that inhibits initiation of protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2264–2268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M., Rabinovitz M. Control of globin synthesis by hemin: factors influencing formation of an inhibitor of globin chain initiation in reticulocyte lysates. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 6;287(2):340–352. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90383-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Appelbaum B. D., Vogler W. R., Kuo J. F. Phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase and its substrates in human neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 29;111(3):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91376-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T., Vanderhoff G., London I. M. Control of globin synthesis: the role of heme. J Mol Biol. 1972 May 28;66(3):471–481. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90427-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagus R., Safer B. Activity of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 is modified by processes distinct from phosphorylation. I. Activities of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 and eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha kinase in lysate gel filtered under different conditions. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1317–1323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Inohara S., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase from rat brain. Subcellular distribution, purification, and properties. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13341–13348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto A., Takai Y., Mori T., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Activation of calcium and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by diacylglycerol, its possible relation to phosphatidylinositol turnover. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2273–2276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo J. F., Andersson R. G., Wise B. C., Mackerlova L., Salomonsson I., Brackett N. L., Katoh N., Shoji M., Wrenn R. W. Calcium-dependent protein kinase: widespread occurrence in various tissues and phyla of the animal kingdom and comparison of effects of phospholipid, calmodulin, and trifluoperazine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7039–7043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda Y., Sharma R. K. Bovine adrenocortical self-phosphorylating protein kinase, SPK 380: purification and characterization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Sep;217(2):588–596. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90541-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London I. M., CLemens M. J., Ranu R. S., Levin D. H., Cherbas L. F., Ernst V. The role of hemin in the regulation of protein synthesis in erythroid cells. Fed Proc. 1976 Sep;35(11):2218–2222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzei G. J., Katoh N., Kuo J. F. Polymyxin B is a more selective inhibitor for phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase than for calmodulin-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Dec 31;109(4):1129–1133. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91894-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa S. Regulation of protein synthesis initiation in eucaryotes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jun;223(2):325–349. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90598-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa S., de Haro C. Regulation of protein synthesis in eukaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:549–580. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinphanichakarn P., Kramer G., Hardesty B. Partial purification and characterization of a translational inhibitor from Friend leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2106–2112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano K., Takai Y., Yamanishi J., Nishizuka Y. A role of calcium-activated phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in human platelet activation. Comparison of thrombin and collagen actions. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):2010–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierra J. M., de Haro C., Datta A., Ochoa S. Translational control by protein kinase in Artemia salina and wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4356–4359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahara S. M., Traugh J. A. Cyclic Nucleotide-independent protein kinases from rabbit reticulocytes. Identification and characterization of a protein kinase activated by proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11558–11564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kishimoto A., Iwasa Y., Kawahara Y., Mori T., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-dependent activation of a multifunctional protein kinase by membrane phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3692–3695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise B. C., Glass D. B., Chou C. H., Raynor R. L., Katoh N., Schatzman R. C., Turner R. S., Kibler R. F., Kuo J. F. Phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase from heart. II. Substrate specificity and inhibition by various agents. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8489–8495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise B. C., Raynor R. L., Kuo J. F. Phospholipid-sensitive Ca2+-dependent protein kinase from heart. I. Purification and general properties. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8481–8488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Haro C., Manne V., de Herreros A. G., Ochoa S. Heat-stable inhibitor of translation in reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3134–3137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Haro C., Ochoa S. Further studies on the mode of action of the heme-controlled translational inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1741–1745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]