Abstract
The initiation of DNA replication of plasmid R6K is triggered by a 35-kilodalton initiator protein. The initiator protein had been elusive because of its lability and the lack of a convenient assay procedure to aid its purification. Using recombinant DNA techniques, we have fused the cistron of the initiator near its COOH-terminal end, in the correct reading frame, to the lacZ cistron of Escherichia coli at the ninth codon from the NH2 terminus. The fused cistron yielded a protein that was not only stable in vivo but also had dual activities: initiation of DNA replication in vivo and in vitro and hydrolysis of beta-galactoside. Using an affinity column that is specific for beta-galactosidase, we have demonstrated the rapid purification of the hybrid protein to near homogeneity. Exploiting the polymeric structure of the initiator, we have also isolated the nonfused form of the initiator protein, associated through subunit interaction with the beta-galactosidase-fused protein, which permits its purification by affinity chromatography. NH2-terminal amino acid sequence analysis of the heteropolymer has not only shown that the fused and nonfused initiators have the same sequence but also confirmed the protein sequence of the initiator as predicted from its nucleotide sequence. The techniques described here should be generally useful for the isolation of other proteins that are difficult to purify by conventional procedures.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Conrad S. E., Campbell J. L. Characterization of an improved in vitro DNA replication system for Escherichia coli plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 25;6(10):3289–3304. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.10.3289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosa J. H. Three origins of replication are active in vivo in the R plasmid RSF1040. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11075–11077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
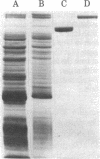
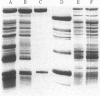
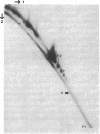
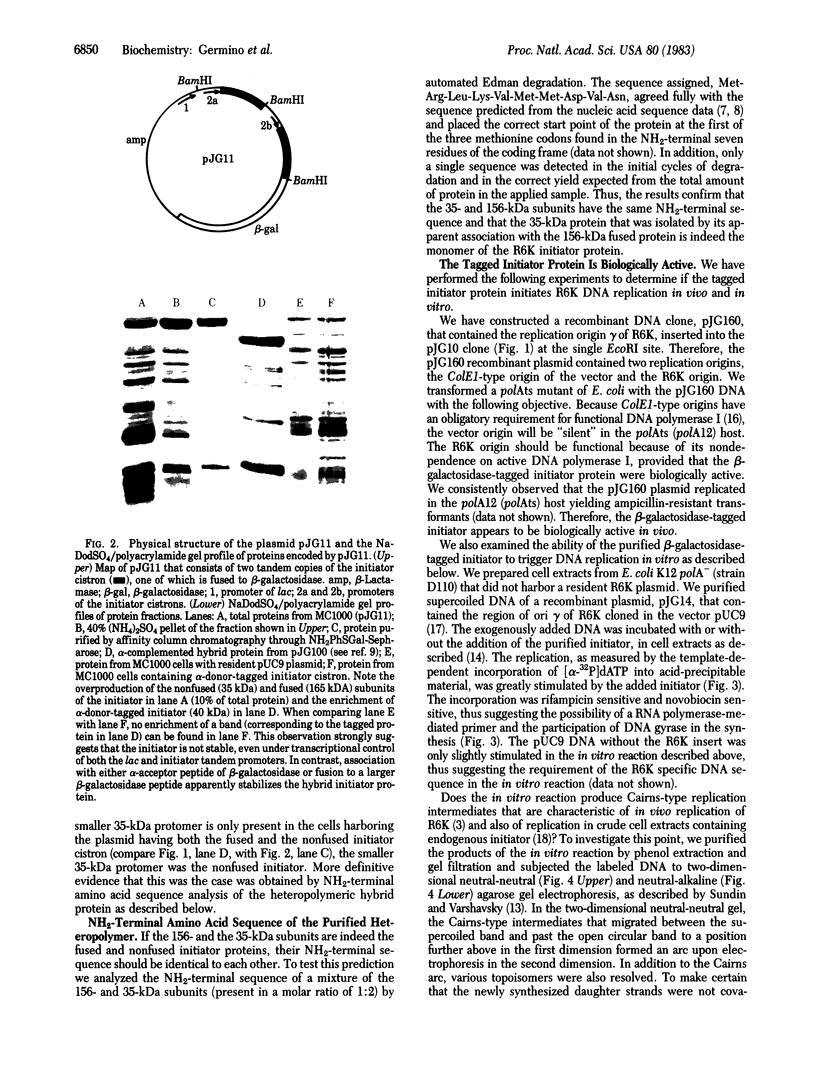
- Germino J., Bastia D. Interaction of the plasmid R6K-encoded replication initiator protein with its binding sites on DNA. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90142-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germino J., Bastia D. Primary structure of the replication initiation protein of plasmid R6K. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5475–5479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germino J., Bastia D. The replication initiator protein of plasmid R6K tagged with beta-galactosidase shows sequence-specific DNA-binding. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):131–140. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90503-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. R., Colot H. V., Guarente L., Rosbash M. Open reading frame cloning: identification, cloning, and expression of open reading frame DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6598–6602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Lauer G., Roberts T. M., Ptashne M. Improved methods for maximizing expression of a cloned gene: a bacterium that synthesizes rabbit beta-globin. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):543–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90640-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inuzuka M., Helinski D. R. Requirement of a plasmid-encoded protein for replication in vitro of plasmid R6K. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5381–5385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inuzuka N., Inuzuka M., Helinski D. R. Activity in vitro of three replication origins of the antibiotic resistance plasmid RSF1040. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11071–11074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. T., Helinski D. R. DNA polymerase as a requirement for the maintenance of the bacterial plasmid colicinogenic factor E1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Dec 24;41(6):1538–1544. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90562-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolter R., Inuzuka M., Helinski D. R. Trans-complementation-dependent replication of a low molecular weight origin fragment from plasmid R6K. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1199–1208. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontomichalou P., Mitani M., Clowes R. C. Circular R-factor molecules controlling penicillinase synthesis, replicating in Escherichia coli under either relaxed or stringent control. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):34–44. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.34-44.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley K. E., Villarejo M. R., Fowler A. V., Zamenhof P. J., Zabin I. Molecular basis of beta-galactosidase alpha-complementation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1254–1257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Hill B., Kania J. Lac repressor can be fused to beta-galactosidase. Nature. 1974 Jun 7;249(457):561–563. doi: 10.1038/249561a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Koenen M., Sippel A. E., Müller-Hill B. Exon cloning: immunoenzymatic identification of exons of the chicken lysozyme gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6852–6855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shon M., Germino J., Bastia D. The nucleotide sequence of the replication origin beta of the plasmid R6K. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13823–13827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shultz J., Silhavy T. J., Berman M. L., Fiil N., Emr S. D. A previously unidentified gene in the spc operon of Escherichia coli K12 specifies a component of the protein export machinery. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):227–235. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90422-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman H. A., Silhavy T. J., Beckwith J. R. Labeling of proteins with beta-galactosidase by gene fusion. Identification of a cytoplasmic membrane component of the Escherichia coli maltose transport system. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):168–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalker D. M., Kolter R., Helinski D. R. Plasmid R6K DNA replication. I. Complete nucleotide sequence of an autonomously replicating segment. J Mol Biol. 1982 Oct 15;161(1):33–43. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90276-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steers E., Jr, Cuatrecasas P., Pollard H. B. The purification of beta-galactosidase from Escherichia coli by affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 10;246(1):196–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundin O., Varshavsky A. Terminal stages of SV40 DNA replication proceed via multiply intertwined catenated dimers. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):103–114. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watterson D. M., Sharief F., Vanaman T. C. The complete amino acid sequence of the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein (calmodulin) of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):962–975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]