Abstract
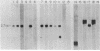
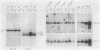
Genetic studies of the white locus have shown that it has a distal region where structural mutations occur and a proximal region where regulatory mutations occur. To better understand the molecular basis of this genetic organization we have analyzed white locus transcription. A 2.7-kilobase transcript comprising 0.0005% of poly(A)-RNA was detected in RNA prepared from pupae or adults. The structure of this transcript helps clarify some unusual genetic properties of the locus. There is a small 5′ exon separated from the majority of the sequences found in the mature RNA by an intron of ≈2.8 kilobases. This 5′ exon is from the proximal region of the locus, whereas the main body of the RNA maps to the distal region. The mutationally silent region between the proximal and distal regions corresponds to the large intron. We have identified the family and determined the exact location of a number of transposable element insertions within the locus. These results show that transposable element insertions within introns can be without phenotypic effect. We have also investigated the effect on the white transcript of the zeste mutation, which represses white locus expression as judged by eye color phenotype. The RNA was unchanged in size or abundance in poly(A)-RNA from adult flies. This demonstrates that the zeste-white interaction does not occur by simply repressing transcription of the white locus in all tissues.
Keywords: zeste, intron, transposable elements, gene regulation, mutational target
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashburner M. Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila. 3. A comparison of the autosomal puffing patterns of the sibling species D. melanogaster and D. simulans. Chromosoma. 1969;27(1):64–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00326111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham P. M., Levis R., Rubin G. M. Cloning of DNA sequences from the white locus of D. melanogaster by a novel and general method. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):693–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90176-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham P. M. The Regulation of White Locus Expression: A Dominant Mutant Allele at the White Locus of DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. Genetics. 1980 Jun;95(2):341–353. doi: 10.1093/genetics/95.2.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M., Rubin G. M. Structure of the Drosophila mutable allele, white-crimson, and its white-ivory and wild-type derivatives. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Nocera P. P., Digan M. E., Dawid I. B. A family of oligo-adenylate-terminated transposable sequences in Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1983 Aug 25;168(4):715–727. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80071-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dretzen G., Bellard M., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. A reliable method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose and acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):295–298. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrberg E. A., Mahaffey J. W., Bond B. J., Davidson N. Transcripts of the six Drosophila actin genes accumulate in a stage- and tissue-specific manner. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):115–123. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90340-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN M. M. Putative non-reciprocal crossing over in Drosophila melanogaster. Z Vererbungsl. 1959;90:375–384. doi: 10.1007/BF00888812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelbart W. M. Synapsis-dependent allelic complementation at the decapentaplegic gene complex in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2636–2640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelbart W. M., Wu C. T. Interactions of zeste mutations with loci exhibiting transvection effects in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1982 Oct;102(2):179–189. doi: 10.1093/genetics/102.2.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. L., Paro R., Gehring W. J. Molecular cloning of the white locus region of Drosophila melanogaster using a large transposable element. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):93–98. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01130.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. L., Sheen J. Y., Gehring W. J., Green M. M. Unequal crossing-over associated with asymmetrical synapsis between nomadic elements in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5017–5021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. M. THE DISCRIMINATION OF WILD-TYPE ISOALLELES AT THE WHITE LOCUS OF DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Apr;45(4):549–553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.4.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JUDD B. H. THE STRUCTURE OF INTRALOCUS DUPLICATION AND DEFICIENCY CHROMOSOMES PRODUCED BY RECOMBINATION IN DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER, WITH EVIDENCE FOR POLARIZED PAIRING. Genetics. 1964 Feb;49:253–265. doi: 10.1093/genetics/49.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J. W., Judd B. H. Allelic pairing and gene regulation: A model for the zeste-white interaction in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1368–1372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judd B H. Studies on Some Position Pseudoalleles at the White Region in Drosophila Melanogaster. Genetics. 1959 Jan;44(1):34–42. doi: 10.1093/genetics/44.1.34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karess R. E., Rubin G. M. A small tandem duplication is responsible for the unstable white-ivory mutation in Drosophila. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):63–69. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korge G. Direct correlation between a chromosome puff and the synthesis of a larval saliva protein in Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma. 1977 Jul 5;62(2):155–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00292637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Bingham P. M., Rubin G. M. Physical map of the white locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):564–568. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Penman S. 5'-terminal structures of poly(A)+ cytoplasmic messenger RNA and of poly(A)+ and poly(A)- heterogeneous nuclear RNA of cells of the dipteran Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1978 Apr 25;120(4):487–515. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90350-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Rubin G. M. The unstable wDZL mutation of Drosophila is caused by a 13 kilobase insertion that is imprecisely excised in phenotypic revertants. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):543–550. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90251-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modolell J., Bender W., Meselson M. Drosophila melanogaster mutations suppressible by the suppressor of Hairy-wing are insertions of a 7.3-kilobase mobile element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1678–1682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirrotta V., Hadfield C., Pretorius G. H. Microdissection and cloning of the white locus and the 3B1-3C2 region of the Drosophila X chromosome. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):927–934. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01523.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rave N., Crkvenjakov R., Boedtker H. Identification of procollagen mRNAs transferred to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper from formaldehyde agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3559–3567. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Kidwell M. G., Bingham P. M. The molecular basis of P-M hybrid dysgenesis: the nature of induced mutations. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):987–994. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90462-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer G., Tschudi C., Perera J., Delius H., Pirrotta V. B104, a new dispersed repeated gene family in Drosophila melanogaster and its analogies with retroviruses. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 25;157(3):435–451. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90470-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Rubin G. M. Drosophila genome organization: conserved and dynamic aspects. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:219–264. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachar Z., Bingham P. M. Regulation of white locus expression: the structure of mutant alleles at the white locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):529–541. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90250-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]