Abstract
The influential role of the epigenome in orchestrating genome-wide transcriptional activation instigates the demand for the artificial genetic switches with distinct DNA sequence recognition. Recently, we developed a novel class of epigenetically active small molecules called SAHA-PIPs by conjugating selective DNA binding pyrrole-imidazole polyamides (PIPs) with the histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA. Screening studies revealed that certain SAHA-PIPs trigger targeted transcriptional activation of pluripotency and germ cell genes in mouse and human fibroblasts, respectively. Through microarray studies and functional analysis, here we demonstrate for the first time the remarkable ability of thirty-two different SAHA-PIPs to trigger the transcriptional activation of exclusive clusters of genes and noncoding RNAs. QRT-PCR validated the microarray data, and some SAHA-PIPs activated therapeutically significant genes like KSR2. Based on the aforementioned results, we propose the potential use of SAHA-PIPs as reagents capable of targeted transcriptional activation.
Modern experimental techniques assist us in recognizing genes of therapeutic significance1. Recently, there has been an exponential increase in the number of genes that gets classified as the potential therapeutic targets2,3,4,5. Increasing correlation between aberrant transcription patterns and diseases further stimulate the need for effectors capable of modulating these faulty gene(s)/transcription factors6,7. Artificial transcriptional activators are the preferred tools to achieve such complex feat of rewiring the misregulated transcriptional networks8. To retain the capability of their natural equivalents, the artificial transcriptional activators must encompass both DNA recognition and functional modules to trigger protein-protein intercommunication and recruit transcriptional machinery9,10. Small molecules or naturally occurring DNA binding proteins form the major class of artificial transcriptional activators11,12. Some customized natural proteins like transcription activator-like effector nucleases and zinc fingers have shown success in targeted transcriptional control13. In the small molecule category, hairpin pyrrole-imidazole polyamides (PIPs) are the major class of effectors that could be pre-programmed to target the gene(s) of interest14,15. Epigenetic alterations like covalent modification of core histones play an important role in coordinating genome-wide gene expression, which in turn dictates cell fate specification16,17. Therefore, complementing programmable small molecules with epigenetic activity could lead to an adequate control over the intricate gene networks associated with cell homeostasis, differentiation and development. Moreover, small molecules are mostly non-immunogenic, and they could be made to be readily available14.
In this regard, we have recently developed an advanced version of epigenetically active PIP conjugates called SAHA-PIPs18. Since transcriptional activation of pluripotency genes could reprogram somatic cells to a pluripotent state, we screened and identified SAHA-PIPs capable of inducing endogenous pluripotency factors in mouse embryonic fibroblasts19,20. Previous studies in the mouse cells clearly indicated that among a library of SAHA-PIPs, a certain SAHA-PIP alone could enforce transcriptional activation of pluripotency genes21,22. Recently, a SAHA-PIP got identified to have the ability to impose targeted transcriptional activation of germ cell genes in human dermal fibroblasts (HDFs)23. ChIP-seq studies and subsequent motif analysis suggested that about 39 % of the motifs could be identified with the hit SAHA-PIP binding site. A specificity landscape study indicated that PIPs possess better selectivity than the natural DNA-binding proteins in mouse cells24. Accordingly, distinct DNA binding PIPs could be directing SAHA to a set of silent genes and activate them.
To clarify this notion, we treated a library of thirty-two SAHA-PIPs to HDFs and evaluated their effect on the genome-wide gene expression. Here, we report the results of such extensive analyses to reveal the remarkable ability of unique SAHA-PIPs to impose unusual transcriptional activation of therapeutically important genes in a human somatic cell. Furthermore, we show that these targeted transcriptional activators could activate a different set of noncoding RNAs and suppress an identical set. QRT-PCR studies validated the pattern observed with microarray analysis and some SAHA-PIPs activated the therapeutically important genes including the recently identified KSR2, the obesity gene2 and SEMA6A, the retinal ‘ON’ circuit factor3. These DNA-based epigenetic switches could be developed to have the ability of modulating the transcription of therapeutically important genes and non-coding RNAs in a precise manner.
Results
Effect of distinct SAHA-PIPs on genome-wide transcriptional activation in human dermal fibroblasts
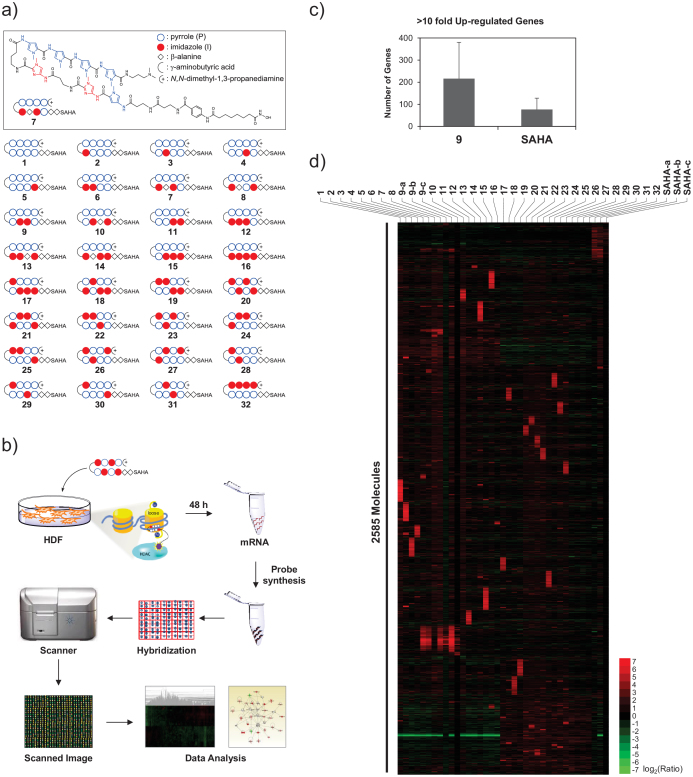
Firstly, distinct DNA sequence recognizing thirty-two different SAHA-PIPs (A to ϕ19,21 termed here as 1 to 32) were synthesized and purified (Figure 1a) through Fmoc solid-phase synthesis using an oxime resin followed by conjugation with SAHA. Since SAHA-PIPs have the ability to permeate the nuclear envelope of the live cells without any transfection agents25, they were simply treated with the HDFs seeded at 1.5 × 105 cells per dish. We chose 1 μM as the working concentration, and 48 h, as the time point to analyze gene expression based on the previous optimization studies23. Global level changes in gene transcription were analyzed after the isolation of total RNAs from the effector (SAHA-PIPs 1 to 32, SAHA and DMSO) treated HDFs (Figure 1b). Screening of the number of genes up or down-regulated by more than ten-fold suggested that most of the PIPs dramatically increased the efficiency of SAHA to induce genome-wide transcriptional activation (Figure S1a and Table S1). In HDFs treated with SAHA-PIPs 1–11, 13–15, and 17–28, about 3 to 10 times more genes got up-regulated than that in SAHA treated HDFs (Figure S1a and Table S1). Interestingly, the analysis of the genes down-regulated by ten-fold indicated that the SAHA-PIP 1 to 32 down-regulate almost the same number (45-69) of genes as SAHA (Figure S1b and Table S1). In some SAHA-PIP (12, 16, 29, 30, 31 and 32) treated HDFs, the number of up-regulated genes were lower than that in SAHA treated HDFs. Although, the reason behind this differential effect is unclear, it could be attributed to the imidazole content, a factor known to hamper the permeability and biological activity of some PIPs26. Interestingly, analysis of the number of genes up-regulated by 2-fold suggested that almost the same number of genes got up- or down-regulated in both SAHA-PIP and SAHA treated HDFs (Table S1). Hence, it is reasonable to assume that most SAHA-PIPs trigger dynamic changes and induce transcriptional activation of developmental gene(s), which are usually conserved in HDFs. Microarray studies carried out with biological triplicate of a representative SAHA-PIP 9, DMSO and SAHA supported this notion and obviated the experimental differences. About twice the number of genes got induced in SAHA-PIP 9 treated HDFs than that in SAHA-treated HDFs (Figure 1c). It is important to note here that a similar pattern could also be observed in SAHA-PIP and SAHA treated MEFs21.
Figure 1. Analysis of global gene expression changes reveals that SAHA-PIPs are capable of triggering differential transcriptional activation.
(a) Chemical structures of the synthetic SAHA - pyrrole-imidazole polyamide conjugates (PIPs) 1–32. PIPs were designed by placing imidazole at various positions in the top and bottom as mentioned before21,23. (b) Workflow of microarray analysis using individual SAHA-PIP treated cells as mentioned in methods. (c) Number of genes up-regulated by more than 10-fold in SAHA and SAHA-PIP 9 treated HDFs. Each bar represents the mean numbers derived from biological triplicates. (d) An unsupervised hierarchical clustering analysis of top 100 up-regulated genes in SAHA-PIP 1–32 treated fibroblasts suggests that each SAHA-PIP activate a unique cluster of genes. Each result represents the sum of two individual culture plates. For SAHA-PIP 9 and SAHA, data derived from additional biological replicates is shown.
SAHA-PIPs trigger differential transcriptional activation and undistinguishable transcriptional repression
A heat map of the top-100 up-regulated genes generated by normalizing the data from SAHA and individual SAHA-PIP (1 to 32) treated HDFs over the data obtained from DMSO treated HDFs revealed a remarkable pattern where each SAHA-PIP activated a unique cluster of genes (Figure 1d). The co-clustered genes observed in the data derived from biological triplicate of the representative SAHA-PIP 9 suggested the robustness of SAHA-PIP to activate unique set of genes (Figure 1d, 9-a-c). Also, the clusters of SAHA activated genes were different from, not just one but also most of the thirty-two SAHA-PIPs, which suggested that the PIP could direct SAHA to different DNA sequences (Figure 1d, SAHA-a-c). To our knowledge, this is the first report to demonstrate the capability of a whole library of transcriptional activators to induce a unique set of genes. Among the SAHA-PIP activated genes, but for 5, 6, 7 and 9, only a minimal number of genes were common between each other (Table S2). On the other hand, in the case of the top-100 down-regulated genes, no such unique cluster of genes could be observed in individual SAHA-PIP treated HDFs (Figure S2). Also, the pattern of down regulation in the case of 1 to 32 was completely opposite to that of up regulation as among them, about 70–90% of down-regulated genes were the same (Figure S2 and Table S3). Few genes got down-regulated in 17 to 32 than that in 1 to 16 treated HDFs, and they were not common. This result could be due to the improved recognition of GC rich sequences by 17 to 32 owing to the presence of imidazole in their top arm12. Nevertheless, the above-mentioned results clearly indicate that SAHA-PIPs only trigger differential transcriptional activation and not transcriptional repression in human fibroblasts. Although, there were commonly up-regulated genes in SAHA-PIPs 5, 6, 7 and 9-treated HDFs, most of them were developmental genes that co-activate each other. Analysis of the possible matching sites of these SAHA-PIPs may lead to the identification of key sequence(s), which are essential for the unusual unlocking of the usually conserved developmental genes.
Remarkable ability of SAHA-PIPs and not SAHA to activate therapeutically important gene(s)
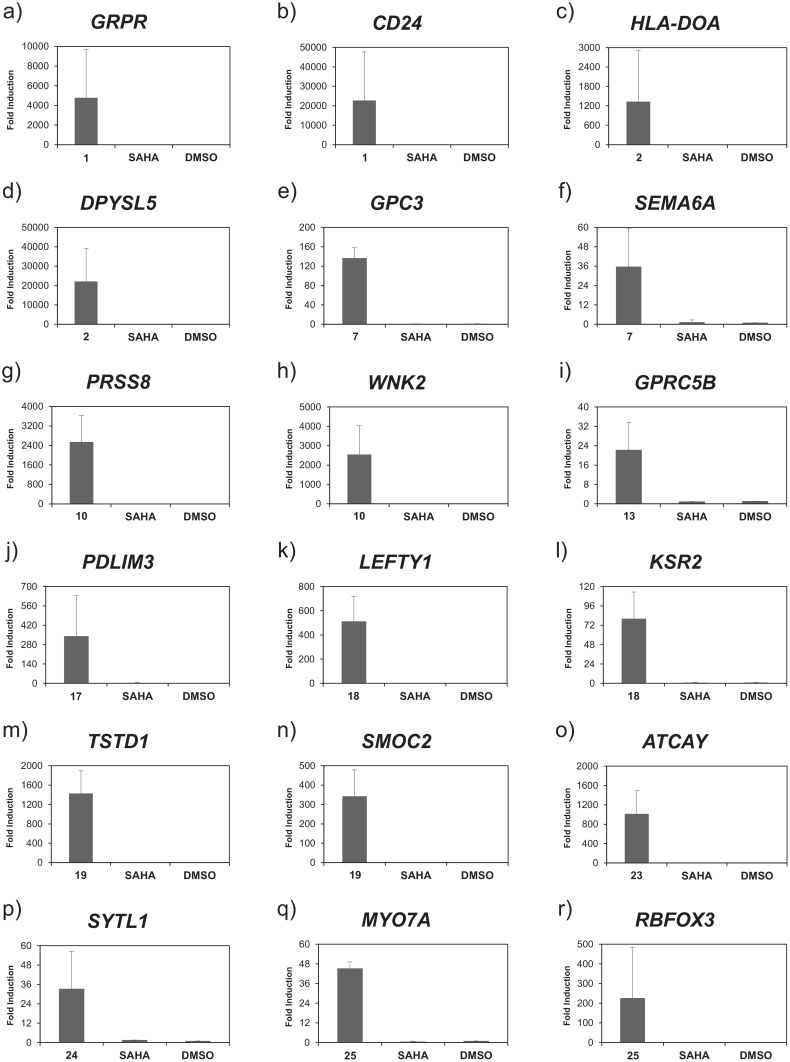
Functional analysis was performed using ingenuity pathway analysis (IPA™) a web-based functional analysis tool with four-fold as the cut-off value to evaluate the comprehensive effect of SAHA-PIP. Consistent with our expectation, each SAHA-PIP displayed differential and significant (p < 0.005) functional annotations that were unique to themselves but those that are different from SAHA (Table 1). Although it is difficult to achieve targeted activation of singular transcription machinery with these 6 bp recognizing ligands, some SAHA-PIPs activated a distinctive set of genes. For example, SAHA-PIPs 1, 7 and 19 modulated a set of genes associated with glucose metabolism, heart, and ear development, respectively (Figure S3). Also, SAHA-PIPs 2, 13, 17, 18, 24 and 25 activated gene networks associated with hematological system, nervous system, hair and skin, respiratory, sensory system and digestive system, respectively (Figure S4). Since SAHA-PIPs distinctively activated some therapeutically important genes, we chose them as the candidate genes to validate the microarray data using qRT-PCR analysis. In accordance to the functional analysis of microarray data (Figure S3), SAHA-PIP 1 dramatically activated GRPR, a gene associated with insulin secretion27 and CD24, a surface marker for PDX1-positive pancreatic progenitors28 (Figure 2a and b). Likewise, SAHA-PIP 2 activated chronic lymphocytic leukaemia associated HLA-DOA29 and DPYSL5 (Figure 2c and d). Interestingly, SAHA-PIP 7 activated GPC3, a factor associated with cardiac and coronary vascular development30 and SEMA6A, which recently got identified as a critical gene for retinal development and motion sensing3 (Figure 2e and f). SAHA-PIP 10 activated PRSS8 and WNK2, a positive regulator of canonical Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway31 (Figure 2g and h). SAHA-PIP 13 activated GPRC5B that got recently identified to contribute to neurogenesis5 (Figure 2i). In the case of second generation SAHA-PIPs, 17 activated PDLIM3, a gene belonging to the network shown in Figure S4c and 18 activated LEFTY1 and KSR2, the factors known to be associated with lung development32 (Figure 2j–l). Likewise, 19 activated TSTD1 and SMOC2, a factor known to be associated with hearing impairment33 (Figure 2m and n). Interestingly, ATCAY, a gene known to cause cerebellar ataxia got activated with 23 treatment34 (Figure 2o). Similarly, 24 activated the sensory system associated SYTL14 and 25 activated digestive system associated MYO7A35 and RBFOX3 (Figure 2p–r). Control studies carried out by treating HDFs with SAHA-alone did not activate any of these therapeutically important genes (Figure 2 a–r, Bars SAHA). It is important to note here that the fold induction appeared very high with all SAHA-PIPs but not with SAHA treatment. This remarkable induction is attributed to the outstanding difference in the threshold cycle values of the analyzed genes (Table S4). Nevertheless, it is reasonable to state that SAHA-PIP distinctively unlock the silent developmental gene(s) in a human somatic cell. Recently, mutations in KSR2 were associated with obesity and insulin resistance in humans2. In this regard, small molecules capable of triggering transcriptional activation of such key genes open up new vistas of opportunities in therapeutic gene modulation.
Table 1. Top 6 Functions of SAHA-PIP modulated genes.
| SAHA-PIP | Functions Annotation (p-Value) |
|---|---|
| 1 | Glucose Metabolism Disorder (9.72E-05), Quantity Of Bilirubin (1.22E-04), Diabetes Mellitus (1.55E-04), Familial Hyperaldosteronism (3.18E-04), Synthesis Of Triacylglycerol (4.26E-04), Lung Tumor (5.04E-04) |
| 2 | Angina Pectoris (1.04E-04), Olfactory Response Of Organism (1.28E-04), Lamellar Ichthyosis (1.62E-04), Bodily Balance (1.95E-04), Efflux Of L-Glutamic Acid (8.57E-04), Hyperplasia Of Stroma (8.57E-04) |
| 3 | Metabolism Of 9-Cis-Retinoic Acid (5.46E-06), Cytolysis Of Antigen Presenting Cells (8.56E-06), Cytolysis Of Phagocytes (2.12E-05), Expansion Of Tumor Cell Lines (2.50E-05), Metabolism Of Retinoid (4.40E-05), Cytolysis Of Fibroblast Cell Lines (7.28E-05) |
| 4 | Degeneration Of Cholinergic Neurons (6.89E-06), Priming Of Cells (1.52E-05), Quantity Of Striatal Neurons (1.91E-05), Glucose Metabolism Disorder (3.77E-05), Growth Of Perikaryon (5.01E-05), Reduction Of Cholesterol (5.01E-05) |
| 5 | Uterine Cancer (3.56E-07), Uterine Serous Papillary Cancer (1.34E-06), Endometrial Cancer (2.33E-06), Abnormal Morphology Of Xiphoid Process (6.81E-06), Endometrial Carcinoma (6.85E-06), Uterine Tumor (8.90E-06) |
| 6 | Uterine Cancer (4.05E-05), Endometrial Carcinoma (4.46E-05), Lamellar Ichthyosis (1.30E-04), Cervical Carcinoma (2.38E-04), Abnormal Morphology Of Melanosomes (2.49E-04), Aggregation Of Melanoma Cell Lines (2.49E-04) |
| 7 | Formation Of Endothelial Tube (8.31E-05), Morphology Of Radius (2.17E-04), Morphology Of Anterior Pituitary Cells (2.25E-04), Formation Of Endothelial Cells (2.61E-04), Formation Of Epithelial Tissue (5.94E-04), Anodontia (7.56E-04) |
| 8 | Development Of Terminal End Bud (4.32E-06), Endometrial Carcinoma (1.19E-05), Uterine Cancer (1.40E-05), Lung Development (1.43E-05), Contraction Of Myofiber (2.90E-05), Transmigration Of Cancer Cells (2.90E-05) |
| 9 | Uterine Serous Papillary Cancer (7.02E-08), Endometrial Cancer (8.78E-07), Formation Of Tight Junctions (7.02E-06), Morphogenesis Of Gastrointestinal Tract (7.02E-06), Differentiation Of Cells (7.14E-06), Uterine Cancer (7.32E-06) |
| 10 | Stimulation Of Lymphatic System Cells (9.85E-05), Th2 Immune Response Of Natural Killer T Lymphocytes (1.96E-04), Reduction Of Cholesterol (1.96E-04), Activation Of Ganglion Cells (3.03E-04), Growth Of Nervous Tissue (3.03E-04), Binding Of Interferon-Gamma Activated Sequence (3.77E-04) |
| 11 | Conversion Of Cerivastatin (7.37E-05), Lysis Of Liposome (7.37E-05), Metabolism Of Cerivastatin (7.37E-05), Neurogenesis Of Subventricular Zone (1.30E-04), Catabolism Of Cyclic AMP (1.68E-04), Killing Of Hematopoietic Cells (1.68E-04) |
| 12 | Hyperplasia Of Stroma (6.57E-05), Morphology Of Anterior Pituitary Cells (2.18E-04), Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxic Reaction Of Cells (4.54E-04), Absorption Of Ca2+ (9.64E-04), Ploidy Of Hepatocytes (1.17E-03), Quantity Of Lactotropes (1.41E-03) |
| 13 | Cell-Cell Adhesion Of Neurons (1.45E-05), Self-Administration Of Cocaine (4.43E-05), Self-Administration (4.73E-05), Abnormal Morphology Of Aorta (6.02E-05), Lung Adenocarcinoma (2.14E-04), Binding Of Cellular Membrane (2.44E-04) |
| 14 | Lung Adenocarcinoma (6.66E-06), Bipolar Disorder (8.85E-06), Lung Tumor (1.24E-05), Lung Cancer (1.35E-05), Carcinoma In Lung (2.79E-05), Morphology Of Anterior Pituitary Cells (3.80E-05) |
| 15 | Cocaine-Related Disorder (7.35E-06), Malignant Hypertension (9.93E-06), Lung Cancer (1.09E-05), Lung Adenocarcinoma (1.15E-05), Adenocarcinoma (1.43E-05), Carcinoma In Lung (4.30E-05) |
| 16 | Uptake Of Retinoid (4.21E-04), Metabolism Of D-Fructose (6.29E-04), Signaling Of Inositol Phosphate (6.29E-04), Absorption Of Phosphate (8.77E-04), Development Of Diaphragm (1.49E-03), Proliferation Of Cerebral Cortex Cells (3.69E-03) |
| 17 | Progression Of Atherosclerotic Lesion (1.20E-04), Lung Tumor (4.48E-04), Neuritogenesis Of Pheochromocytoma Cell Lines (4.76E-04), Mitogenesis Of Skin Cell Lines (5.02E-04), Pachyonychia Congenital (5.02E-04), Lung Cancer (6.12E-04) |
| 18 | Fibrosis Of Muscle (1.83E-05), Concentration Of Lipid (8.60E-05), Crohn's Disease (1.87E-04), Fibrosis Of Skeletal Muscle (2.26E-04), Mass Of Liver (2.42E-04), Inflammation Of Intestine (4.67E-04) |
| 19 | Shape Change Of Skin Cancer Cell Lines (8.85E-05), Nonsyndromic Hearing Impairment (1.72E-04), Length Of Filaments (2.20E-04), Development Of Inner Ear (5.79E-04), Release Of Neurotransmitter (6.18E-04), Cell Death Of Neural Stem Cells (8.68E-04) |
| 20 | Quantity Of Monoamines (6.48E-05), Quantity Of Catecholamine (2.17E-04), Olfaction (2.28E-04), Abnormal Morphology Of Lung (2.91E-04), Peroxidation Of Lipid (3.49E-04), Development Of Cecum (3.77E-04) |
| 21 | Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (3.82E-05), Formation Of Calvaria (4.82E-05), Abnormal Morphology Of Dilated Distal Convoluted Tubule (1.44E-04), Modification Of Octanoic Acid (.44E-04), Sick Sinus Syndrome (2.87E-04), Morphogenesis Of Muscle (3.16E-04) |
| 22 | Chemotaxis Of Lymphatic Endothelial Cells (1.09E-04), Isomerization Of Lipid (1.09E-04), Regeneration Of Gastrocnemius (1.09E-04), Pyroptosis Of Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages (2.18E-04), Thyroid Cancer (4.75E-04), Amyloidosis (5.47E-04) |
| 23 | Proliferation Of BMMC Cells (3.00E-05), Cough (4.94E-05), Proliferation Of Blood-Derived Mast Cells (6.79E-05), Whooping Cough (6.79E-05), Development Of Neuroglia (1.71E-04), Acute Otitis Media (2.03E-04) |
| 24 | Abnormal Morphology Of Mossy Fibers (3.15E-04), Tonic Seizure (6.34E-04), Function Of CD4+ T-Lymphocytes (6.53E-04), Rheumatic Disease (7.12E-04), Quantity Of Methotrexate (7.94E-04), Morphogenesis Of Embryonic Organ (9.32E-04) |
| 25 | Damage Of Septal Neurons (7.97E-05), Development Of Tectorial Membrane (7.97E-05), Proliferation Of Stromal Cell Lines (7.97E-05), Imprinting (1.61E-04), Congenital Anomaly Of Mouth (1.93E-04), Growth Of Otic Vesicle (2.38E-04) |
| 26 | Adenocarcinoma (8.24E-05), Renal-Cell Carcinoma (9.62E-05), Efflux Of Halide (2.26E-04), Efflux Of Monovalent Inorganic Anion (2.26E-04), Development Of Cecum (3.20E-04), Morphology Of Jaw (3.69E-04) |
| 27 | Chemotaxis Of Helper T Lymphocytes (1.46E-04), Abnormal Morphology Of Body Cavity (2.60E-04), Cell Movement Of Helper T Lymphocytes (3.59E-04), Proliferation Of Gamma-Delta T Lymphocytes (4.36E-04), Accumulation Of Very Long Chain Fatty Acid (4.72E-04), Sick Sinus Syndrome (4.72E-04) |
| 28 | Papillary Thyroid Cancer (1.91E-05), Autosomal Recessive Deafness (2.53E-04), Contraction Of Striated Muscle (2.76E-04), Autosomal Recessive Nonsyndromic Hearing Loss (3.39E-04), Thyroid Cancer (4.28E-04), Sick Sinus Syndrome (7.04E-04) |
| 29 | Fate Determination Of Cells (4.32E-04), Extension Of Axons (6.97E-04), Delay In Puberty (1.14E-03), Olfactory Response Of Organism (1.33E-03), Spondylarthritis (1.44E-03), Cytotoxicity Of Lymphocytes (1.57E-03) |
| 30 | Generation Of Plasma Cells (3.44E-04), Quantity Of Follicular T Helper Cells (3.44E-04), Activation Of Purkinje Cells (3.15E-03), Autosomal Recessive GLUT1 Deficiency Syndrome Type 1 (3.15E-03), Biogenesis Of Lateral Plasma Membrane (3.15E-03), Clustering Of Clathrin-Coated Pits (3.15E-03) |
| 31 | Bleeding Of Kidney (5.10E-04), Chronic Large Plaque Psoriasis (1.27E-03), Chronic Small Plaque Psoriasis (1.27E-03), Induction Of Helper T Lymphocytes (1.47E-03), Swelling Of Ear (1.47E-03), Birthweight (1.64E-03) |
| 32 | Diameter Of Blood Vessel (9.72E-04), Morphology Of Lung (1.16E-03), Alveologenesis Of Lung (2.19E-03), Abnormal Morphology Of Lung (2.26E-03), Antley-Bixler Syndrome Without Genital Anomalies Or Disordered Steroidogenesis (2.33E-03), Beare-Stevenson Cutis Gyrata Syndrome (2.33E-03) |
| SAHA | Migration Of Tumor Cells (2.27E-08), Colorectal Cancer (5.80E-08), Gastrointestinal Tract Cancer (4.79E-07), Cell Movement Of Tumor Cells (7.70E-07), Cell Movement Of Cancer Cells (6.34E-06), Neoplasia Of Colon (1.75E-05) |
*Each result represents the sum of two individual culture plates. >4 fold up/down-regulated genes were analyzed using IPA as mentioned in methods. Top 6 functions are based on p-value derived from Fischer's test.
Data were analyzed through the use of IPA (Ingenuity Systems, www.ingenuity.com).
Figure 2. Remarkable ability of SAHA-PIPs and not SAHA to trigger dynamic transcriptional activation of therapeutically important genes.
Based on the microarray data, we chose therapeutically important genes distinctively activated by individual SAHA-PIPs. SAHA and DMSO were used as the control. The concentration of the effectors and incubation conditions were as mentioned in methods. QRT-PCR analysis of the expression level of (a) GRPR, (b) CD24, (c) HLA-DOA, (d) DPYSL5, (e) GPC3, (f) SEMA6A, (g) PRSS8, (h) WNK2, (i) GPRC5B, (j) PDLIM3, (k) LEFTY1, (l) KSR2, (m) TSTD1, (n) SMOC2, (o) ATCAY, (p) SYTL1, (q) MYO7A and (r) RBFOX3. Fold changes relative to non-treated control (DMSO) are presented as induction values. Each bar represents the mean ± SD from 6 wells. Original Ct values are presented in Table S4.
Individual SAHA-PIPs trigger transcriptional activation of distinctive noncoding RNAs in HDFs
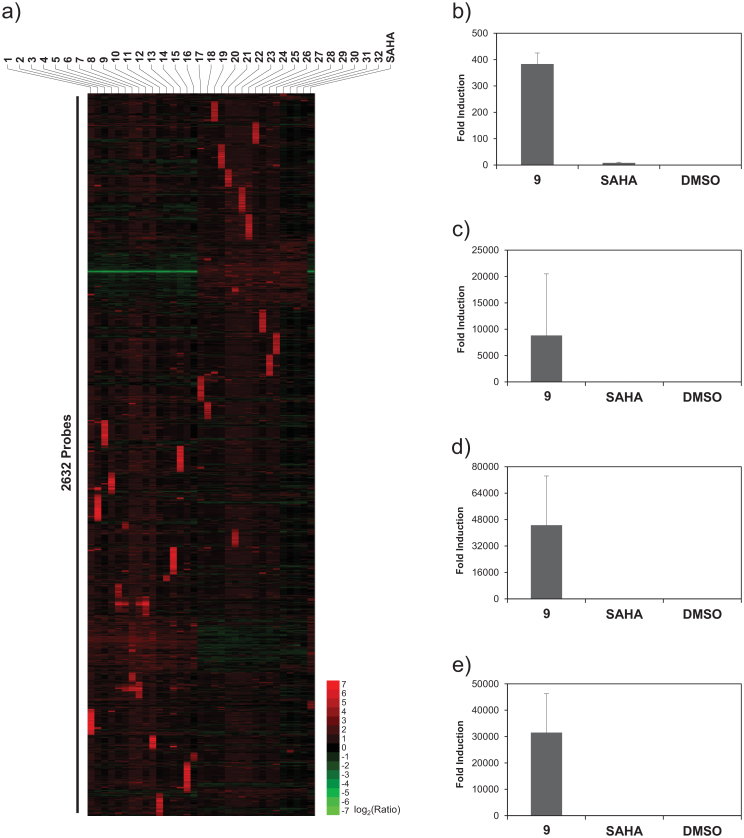
Recent studies reveal that only one fifth of the transcription across the human genome gets associated with protein-coding genes, and a significant amount of the remaining fraction includes non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), most of whose function remains unknown36. The ncRNAs express in a development-specific manner, and they could also induce epigenetic regulation37. Many functional revelations get attributed to the ever-increasing volume of newly characterized ncRNAs38. For example, a long ncRNA termed ‘Brave heart’ was shown to activate the core cardiovascular gene network by functioning upstream of MesP1, a master regulator that establishes the cardiovascular lineage during mammalian development39. Since transcriptional reorganization of ncRNAs could be linked to some common functional characteristics, we generated a heat map of the top 100 up-regulated ncRNAs. Consistent with the pattern observed with global changes in gene expression, unique clusters of ncRNAs were differentially up-regulated by individual SAHA-PIPs (Figure 3a). Again, a heat map of the top 100 ncRNAs down-regulated by individual SAHA-PIPs did not show such a unique cluster of ncRNAs (Figure S5). QRT-PCR studies again validated the microarray data and four of the uncharacterized noncoding RNAs got activated in HDFs after treatment with SAHA-PIP 9 and not SAHA (Figure 3b–e). SAHA-PIPs activating distinctive ncRNAs could be instrumental in assigning functional roles to uncharacterized segment of the human genome. Cytotoxicity did not influence the gene expression profile obtained with SAHA-PIP treatment as while SAHA alone killed about 50% of the cells, none of the SAHA-PIPs had cytotoxic effect on HDFs at 1 μM working concentration even after 48 h (Figure S6a). Interestingly, even at 10 μM working concentration none of the SAHA-PIPs were cytotoxic, which suggests their potential use as therapeutic reagents (Figure S6b).
Figure 3. Individual SAHA-PIPs trigger transcriptional activation of distinctive non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs).
(a) An unsupervised hierarchical clustering analysis of top 100 ncRNAs in SAHA, SAHA-PIP 1–32 treated fibroblasts suggests that each SAHA-PIP also activate unique cluster of ncRNAs. Each result represents the sum of two individual culture plates. QRT-PCR analysis of the expression level of the uncharacterized gene probes (b) A_21_P0000813, (c) A_21_P0000821, (d) A_21_P0014207 and e) A_19_P00319154 were carried out as mentioned in Figure 2 with SAHA and DMSO as control. Fold changes relative to non-treated control (DMSO) are presented as induction values. Each bar represents the mean ± SD from 6 wells. Original Ct values are presented in Table S4.
Discussion
Programmed control over gene expression in a human somatic cell could lead to the development of innovative strategies to treat some uncured defect-transcriptional machinery associated disorders7. So far, the known programmable DNA binding small molecules and/or natural proteins often overlook the ability to remodel the chromatin architecture, which is an essential module in achieving targeted transcriptional activation13,20. Chromatin immune precipitation analysis clearly indicated that SAHA-PIPs distinctively activate certain genes in both mouse and human somatic cells through site-specific hyperacetylation in their promoter region19,21,23. Hence, the transcriptional activator like SAHA-PIPs capable in binding a certain DNA sequence could modify the local chromatin architecture and initiate dramatic changes in the original transcriptional state of a cell. Transcriptional activation of some therapeutically important genes described in this report may also lead to undesired effects. However, the tunable nature of these DNA-based epigenetic switches facilitates the attachment of gene-suppressing effectors. Nevertheless, this is the first ever report on the small molecules, which are capable of activating these key developmental genes. Although SAHA-PIPs employed in this study recognizes only 6 base pairs, previous reports suggest that it is possible to expand the recognition ability of PIP40. Hence, it is reasonable to assume that each of these DNA-based epigenetic switches could be developed to induce targeted transcriptional activation of a singular biologically significant pathway. Unlike other programmable transcriptional activators, PIPs could bind with methylated DNA sequences. Also, it is possible to conjugate different enzyme inhibitor and/or fluorescent molecules for versatile applications12,41. Tuning the chemical architecture of SAHA in a SAHA-PIP for inducing differential gene expression is also possible42. Multi-target small molecule such as SAHA-PIP may potentially achieve programmed control of developmental genes, which in-turn could reprogram any cell to a desired cell type14. These chemical biology tools could also be developed to gain essential insights into some unresolved mechanisms and annotate functional relevance of the uncharacterized genes. For precise targeting, cell permeability and accessibility of the SAHA-PIPs and stochastic variations in epigenome should be considered during their design and development23. Nevertheless, the remarkable ability of SAHA-PIPs to induce rapid transcriptional activation of the silent developmental genes may encourage researchers to integrate multi-functional molecules and develop versatile transcriptional activators.
Methods
Microarray studies and functional analysis with SAHA-PIPs
As mentioned before23, HDFs were treated with 1 μM of SAHA, SAHA-PIPs 1–32 and 0.1% DMSO. After 48 h incubation, total RNA was isolated using RNeasy MINI Kit (Qiagen, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The quality of the RNA samples was examined using the Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies, USA). The mRNA from total RNA samples was amplified into dsDNA. T7 polymerase was used to generate Cyanine 3-labeled cRNA. The labeled cRNA was purified using RNeasy Mini kits and concentration was measured using Nanodrop ND1000 v3.5.2 (Thermo Scientific). The cRNA (825 ng) was fragmented and subsequently hybridized to SurePrint G3 Human GE v2 8 × 60K Microarray (Agilent Technologies, USA). The raw data and associated sample information were processed by GeneSpring GX v12.1.0 (Agilent Technologies, USA). For the biological replicate study using SAHA-PIP 9 and SAHA, Whole Human Genome Microarray 4 × 44 v2 (Agilent Technologies, USA) and Human Gene 2.1 ST Array Strip (Affymetrix, USA) were used. The microarray data and complete description of experimental procedure have been deposited in NCBI's Gene Expression Omnibus and are accessible through GEO Series accession number GSE53319 (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE53319). The interpretation of the microarray data obtained from three individual plates is carried out by cluster 3.0 and Ingenuity pathway analysis (IPA™), which uses the dataset containing the gene identifiers and its respective fold change values. Fischer's exact test is employed to measure the p-value that determines the association between the genes in the dataset and their functional annotation. The biological networks were generated based on these focus genes. QRT-PCR studies were done after cDNA synthesis using a ReverTra Ace qPCR RT Master Mix with gDNA Remover and amplifications with THUNDERBIRD SYBR qPCR Mix (Toyobo, Japan) as mentioned before21,23 with the designed primers (Table S5). Data presented is derived from the experiments using biological replicates.
Other experimental details, methods, supplementary figures and tables, are submitted as supplementary material along with this manuscript.
Author Contributions
Experiments were designed by H.S., J.T., T.B., H.N. and G.N.P.J.T., G.N.P., S.J. and S.S. performed research. G.N.P., S.J., H.L., C.A., T.V. and A.S. analysed the data. The manuscript was written by G.N.P., R.D.T. and J.T.
Supplementary Material
Supporting Information
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) of Japan. The iCeMS is supported by World Premier International Research Center Initiative, MEXT, Japan. We thank Nagase Science and Technology foundation for their support. We thank iCeMS exploratory grant and Grants-in-aid for Young Scientists-B for support to G.N.P.
References
- Yang L. et al. Identifying unexpected therapeutic targets via chemical-protein interactome. PLoS ONE 5, e9568 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, Laura R. et al. KSR2 mutations are associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and impaired cellular fuel oxidation. Cell 155, 765–777 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun L. O. et al. On and off retinal circuit assembly by divergent molecular mechanisms. Science 342, 1241974, 10.1126/science.1241974 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Shlomo G. et al. Microarray-based gene expression analysis during retinal maturation of albino rats. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 246, 693–702 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurabayashi N., Nguyen M. D. & Sanada K. The G protein-coupled receptor GPRC5B contributes to neurogenesis in the developing mouse neocortex. Development 140, 4335–4346 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thandavarayan R. A. et al. Depletion of 14-3-3 protein exacerbates cardiac oxidative stress, inflammation and remodeling process via modulation of MAPK/NF-kB signaling pathways after streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 28, 911–922 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandian G. & Sugiyama H. Strategies to modulate heritable epigenetic defects in cellular machinery: Lessons from Nature. Pharmaceuticals 6, 1–24 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majmudar C. Y., Lum J. K., Prasov L. & Mapp A. K. Functional specificity of artificial transcriptional activators. Chem. Biol. 12, 313–321 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. & Gann A. Transcriptional activation by recruitment. Nature 386, 569–577 (1997). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansari A. Z., Mapp A. K., Nguyen D. H., Dervan P. B. & Ptashne M. Towards a minimal motif for artificial transcriptional activators. Chem. Biol. 8, 583–592 (2001). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Moore R., Guinn M. & Bleris L. Transcription activator-like effector hybrids for conditional control and rewiring of chromosomal transgene expression. Sci. Rep. 2, 897; 10.1038/srep00897 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandian G. N. & Sugiyama H. Programmable genetic switches to control transcriptional machinery of pluripotency. Biotechnol. J. 7, 798–809 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogdanove A. J. & Voytas D. F. TAL effectors: customizable proteins for DNA targeting. Science 333, 1843–1846 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y.-L. et al. Clinical grade iPS cells: need for versatile small molecules and optimal cell sources. Chem. Biol. 20, 1311–1322 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashiwazaki G. et al. Synthesis and biological properties of highly sequence-specific-alkylating N-methylpyrrole–N-methylimidazole polyamide conjugates. J. Med. Chem. 55, 2057–2066 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrero M. J., Boué S. & Izpisúa Belmonte J. C. Epigenetic mechanisms that regulate cell identity. Cell Stem Cell 7, 565–570 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iizuka M. & Smith M. M. Functional consequences of histone modifications. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 13, 154–160 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsuki A. et al. Synthesis and properties of PI polyamide–SAHA conjugate. Tetrahedron Lett. 50, 7288–7292 (2009). [Google Scholar]
- Pandian G. N. et al. Synthetic small molecules for epigenetic activation of pluripotency genes in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. ChemBioChem 12, 2822–2828 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandian G. N. et al. Development of programmable small DNA-binding molecules with epigenetic activity for induction of core pluripotency genes. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 20, 2656–2660 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandian G. N. et al. A synthetic small molecule for rapid induction of multiple pluripotency genes in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2, e544 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda S. et al. Chemically induced pluripotent stem cells (CiPSCs): a transgene-free approach. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 5, 354–355 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han L. et al. A synthetic small molecule for targeted transcriptional activation of germ cell genes in a human somatic cell. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52, 13410–13413 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson C. D. et al. Specificity landscapes of DNA binding molecules elucidate biological function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 107, 4544–4549 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaijayanthi T., Bando T., Hashiya K., Pandian G. N. & Sugiyama H. Design of a new fluorescent probe: pyrrole/imidazole hairpin polyamides with pyrene conjugation at their γ-turn. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 21, 852–855 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishijima S. et al. Cell permeability of Py-Im-polyamide-fluorescein conjugates: Influence of molecular size and Py/Im content. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 18, 978–983 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson K., Pacini G., Sundler F. & Ahrén B. Islet function phenotype in gastrin-releasing peptide receptor gene-deficient mice. Endocrinology 143, 3717–3726 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang W. et al. CD24: a novel surface marker for PDX1-positive pancreatic progenitors derived from human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 29, 609–617 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souwer Y. et al. Detection of aberrant transcription of major histocompatibility complex class II antigen presentation genes in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia identifies HLA-DOA mRNA as a prognostic factor for survival. Br. J. Haematol. 145, 334–343 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng A. et al. Loss of glypican-3 function causes growth factor-dependent defects in cardiac and coronary vascular development. Dev. Biol. 335, 208–215 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serysheva E. et al. Wnk kinases are positive regulators of canonical Wnt/β-catenin signalling. EMBO. Rep. 14, 718–725 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan D. F. et al. A Raf-induced allosteric transition of KSR stimulates phosphorylation of MEK. Nature 472, 366–369 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamani S. C. S. et al. Interstitial deletion of 6q25.2-q25.3: a novel microdeletion syndrome associated with microcephaly, developmental delay, dysmorphic features and hearing loss. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 17, 573–581 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikora K. M. et al. Expression of Caytaxin protein in Cayman Ataxia mouse models correlates with phenotype severity. PLoS ONE 7, e50570 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quintana-Bustamante O. et al. Cell fusion reprogramming leads to a specific hepatic expression pattern during mouse bone marrow derived hepatocyte formation in vivo. PLoS ONE 7, e33945 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapranov P. et al. RNA maps reveal new RNA classes and a possible function for pervasive transcription. Science 316, 1484–1488 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. T. Epigenetic regulation by long noncoding RNAs. Science 338, 1435–1439 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilusz J. E., Sunwoo H. & Spector D. L. Long noncoding RNAs: functional surprises from the RNA world. Genes Dev. 23, 1494–1504 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klattenhoff Carla A. et al. Braveheart, a long noncoding RNA required for cardiovascular lineage commitment. Cell 152, 570–583 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trauger J. W., Baird E. E. & Dervan P. B. Recognition of 16 base pairs in the minor groove of DNA by a pyrrole−imidazole polyamide dimer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120, 3534–3535 (1998). [Google Scholar]
- Vaijayanthi T., Bando T., Pandian G. N. & Sugiyama H. Progress and prospects of pyrrole-imidazole polyamide–fluorophore conjugates as sequence-selective DNA probes. ChemBioChem 13, 2170–2185 (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha A. et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of a targeted DNA-binding transcriptional activator with HDAC8 inhibitory activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 21, 4201–4209 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supporting Information