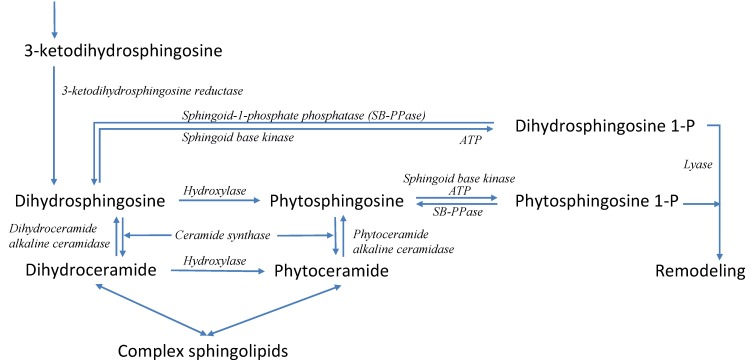
Figure 4.
Simplified pathway system of sphingolipid biosynthesis and usage in yeast. Sphingolipid biosynthesis is initiated with the condensation of palmitoyl-CoA and serine, leading to 3-ketodihydrosphingosine, which is quickly converted into dihydrosphingosine, the first simple sphingolipid in the pathway. Dihydrosphingosine is the starting point for five other key sphingolipids, namely dihydroceramide, dihydrosphingosine 1-phosphate, phytosphingosine, phytoceramide, and phytosphingosine 1-phosphate, which regulate each other’s production and degradation extensively. The system has two exit routes. One is the formation of complex sphingolipids, which become parts of membranes, and the other is the remodeling pathway, which recycles sphingolipids. When heat stress is applied, the six key sphingolipids exhibit strong dynamic changes in concentration. Recordings of these responses over 30 minutes following a shift in temperature serve as our time course data. Pertinent enzymes are shown in italics. Further details are available in [55,56,57,58].