Abstract
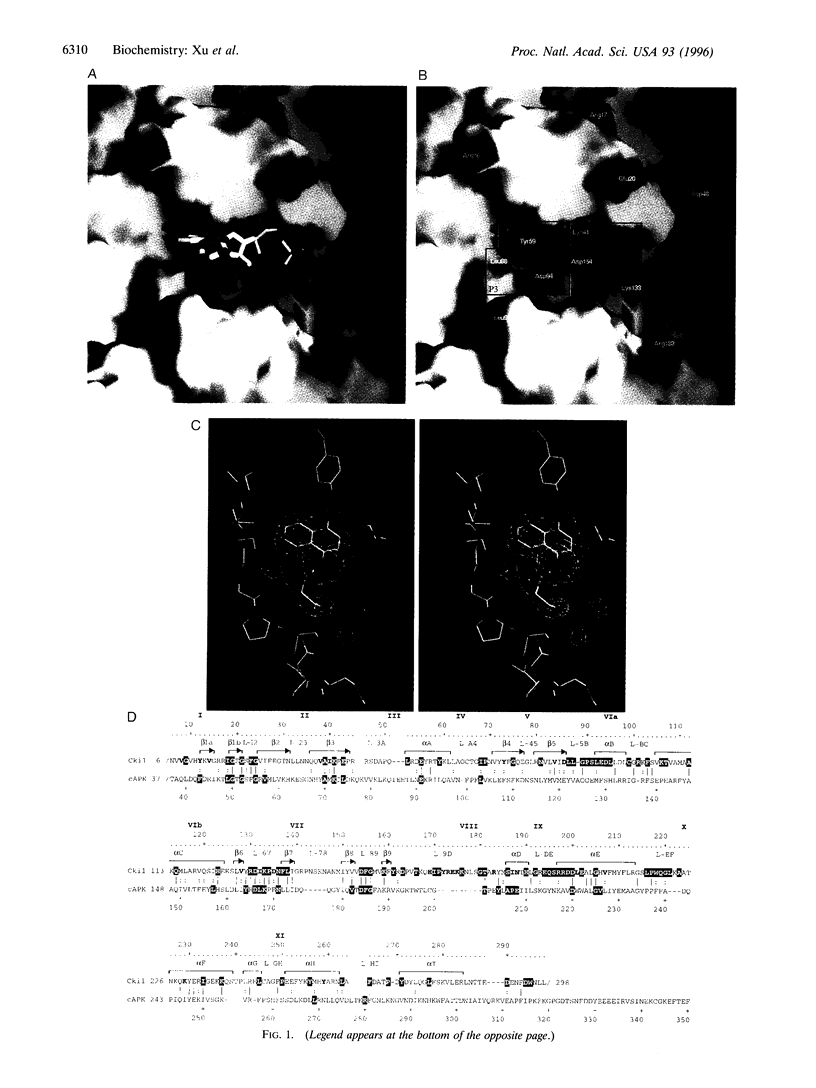
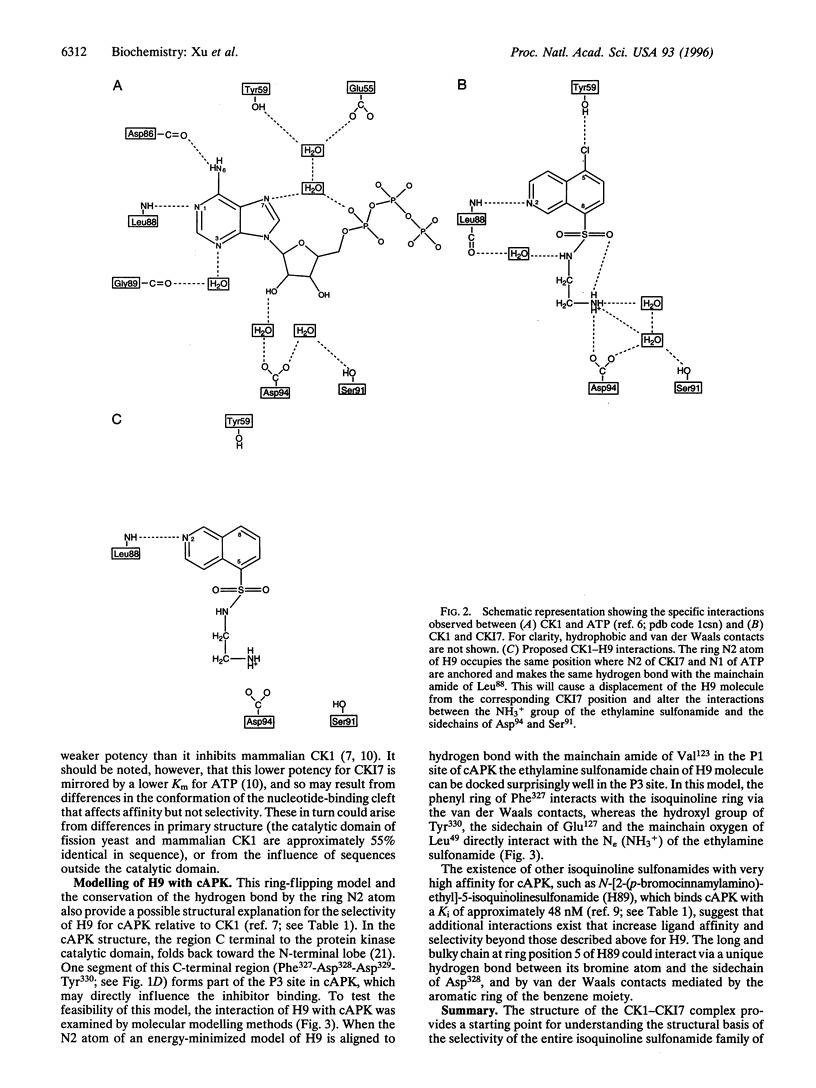
A large family of isoquinoline sulfonamide compounds inhibits protein kinases by competing with adenosine triphosphates(ATP), yet interferes little with the activity of other ATP-using enzymes such as ATPases and adenylate cyclases. One such compound, N-(2-aminoethyl)-5-chloroisoquinoline-8-sulfonamide (CK17), is selective for casein kinase-1 isolated from a variety of sources. Here we report the crystal structure of the catalytic domain of Schizosaccharomyces pombe casein kinase-1 complexed with CK17, refined to a crystallographic R-factor of 17.8% at 2.5 angstrom resolution. The structure provides new insights into the mechanism of the ATP-competing inhibition and the origin of their selectivity toward different protein kinases. Selectivity for protein kinases versus other enzymes is achieved by hydrophobic contacts and the hydrogen bond with isoquinoline ring. We propose that the hydrogen bond involving the ring nitrogen-2 atom of the isoquinoline must be preserved, but that the ring can flip depending on the chemical substituents at ring positions 5 and 8. Selectivity for individual members of the protein kinase family is achieved primarily by interactions with these substituents.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carmel G., Leichus B., Cheng X., Patterson S. D., Mirza U., Chait B. T., Kuret J. Expression, purification, crystallization, and preliminary x-ray analysis of casein kinase-1 from Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7304–7309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casnellie J. E. Protein kinase inhibitors: probes for the functions of protein phosphorylation. Adv Pharmacol. 1991;22:167–205. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cegielska A., Virshup D. M. Control of simian virus 40 DNA replication by the HeLa cell nuclear kinase casein kinase I. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):1202–1211. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.1202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chijiwa T., Hagiwara M., Hidaka H. A newly synthesized selective casein kinase I inhibitor, N-(2-aminoethyl)-5-chloroisoquinoline-8-sulfonamide, and affinity purification of casein kinase I from bovine testis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4924–4927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chijiwa T., Mishima A., Hagiwara M., Sano M., Hayashi K., Inoue T., Naito K., Toshioka T., Hidaka H. Inhibition of forskolin-induced neurite outgrowth and protein phosphorylation by a newly synthesized selective inhibitor of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, N-[2-(p-bromocinnamylamino)ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide (H-89), of PC12D pheochromocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5267–5272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bondt H. L., Rosenblatt J., Jancarik J., Jones H. D., Morgan D. O., Kim S. H. Crystal structure of cyclin-dependent kinase 2. Nature. 1993 Jun 17;363(6430):595–602. doi: 10.1038/363595a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara M., Inagaki M., Hidaka H. Specific binding of a novel compound, N-[2-(methylamino)ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide (H-8) to the active site of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 May;31(5):523–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M. Protein kinase catalytic domain sequence database: identification of conserved features of primary structure and classification of family members. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:38–62. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00126-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra M. F., Liskay R. M., Ou A. C., DeMaggio A. J., Burbee D. G., Heffron F. HRR25, a putative protein kinase from budding yeast: association with repair of damaged DNA. Science. 1991 Aug 30;253(5023):1031–1034. doi: 10.1126/science.1887218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issinger O. G. Casein kinases: pleiotropic mediators of cellular regulation. Pharmacol Ther. 1993;59(1):1–30. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(93)90039-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Zou J. Y., Cowan S. W., Kjeldgaard M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr A. 1991 Mar 1;47(Pt 2):110–119. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390010224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milne D. M., Palmer R. H., Campbell D. G., Meek D. W. Phosphorylation of the p53 tumour-suppressor protein at three N-terminal sites by a novel casein kinase I-like enzyme. Oncogene. 1992 Jul;7(7):1361–1369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls A., Sharp K. A., Honig B. Protein folding and association: insights from the interfacial and thermodynamic properties of hydrocarbons. Proteins. 1991;11(4):281–296. doi: 10.1002/prot.340110407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen D. J., Noble M. E., Garman E. F., Papageorgiou A. C., Johnson L. N. Two structures of the catalytic domain of phosphorylase kinase: an active protein kinase complexed with substrate analogue and product. Structure. 1995 May 15;3(5):467–482. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00180-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Gahmen U., Brandsen J., Jones H. D., Morgan D. O., Meijer L., Vesely J., Kim S. H. Multiple modes of ligand recognition: crystal structures of cyclin-dependent protein kinase 2 in complex with ATP and two inhibitors, olomoucine and isopentenyladenine. Proteins. 1995 Aug;22(4):378–391. doi: 10.1002/prot.340220408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuazon P. T., Traugh J. A. Casein kinase I and II--multipotential serine protein kinases: structure, function, and regulation. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1991;23:123–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang P. C., Vancura A., Desai A., Carmel G., Kuret J. Cytoplasmic forms of fission yeast casein kinase-1 associate primarily with the particulate fraction of the cell. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 22;269(16):12014–12023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warncke K., Dutton P. L. Experimental resolution of the free energies of aqueous solvation contributions to ligand-protein binding: quinone-QA site interactions in the photosynthetic reaction center protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2920–2924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshel A., Aqvist J., Creighton S. Enzymes work by solvation substitution rather than by desolvation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5820–5824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu R. M., Carmel G., Sweet R. M., Kuret J., Cheng X. Crystal structure of casein kinase-1, a phosphate-directed protein kinase. EMBO J. 1995 Mar 1;14(5):1015–1023. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07082.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang F., Strand A., Robbins D., Cobb M. H., Goldsmith E. J. Atomic structure of the MAP kinase ERK2 at 2.3 A resolution. Nature. 1994 Feb 24;367(6465):704–711. doi: 10.1038/367704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng J., Knighton D. R., ten Eyck L. F., Karlsson R., Xuong N., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase complexed with MgATP and peptide inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 9;32(9):2154–2161. doi: 10.1021/bi00060a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]