Abstract
To evaluate the efficacy of nephrostomy balloon dilation (NBD) for patients who developed vesicourethral anastomotic stricture (VAS) following radical prostatectomy. NBD was performed in patients who developed VAS following radical prostatectomy. Quality of life (QoL), International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) and maximal urinary flow rate (Qmax) were evaluated. Four hundred and sixty-three prostate cancer patients underwent radical retropubic prostatectomy (RRP), and 86 underwent laparoscopic radical prostatectomy (LRP). Most patients (90.3%) had T2 or T3 prostate cancer and a pathological Gleason score of ≤ 7. Forty-five (8.2%) and four (4.7%) patients developed VAS due to radical or LRP, respectively. Forty (89%) patients underwent NBD, including three cases of repeat dilation. The median Qmax was 4 ml s−1 (interquartile range (IQR), 2.3-5.6) before dilation and improved to 16 ml s−1 (IQR, 15–19) and 19 ml s−1 (IQR, 18-21) at the 1- and 12-month follow-up, respectively (P < 0.01). Fifteen (37.5%) patients had urinary incontinence prior to dilation, whereas only three (7.5%) patients had incontinence 12 months following dilation (P < 0.01). The median IPSS score improved from 19 (IQR, 17–24) before dilation to 7 (IQR, 6–8) at 12 months following dilation, and the QoL score improved from 5 (IQR, 4–6) before dilation to 2 (IQR, 2–3) at 12 months following dilation (P < 0.01 in both). VAS occurs in a small but significant proportion of patients following radical prostatectomy. NBD offers an effective remedy for VAS.
Keywords: nephrostomy balloon dilation (NBD), quality of life (QoL), radical prostatectomy, vesicourethral anastomotic stricture (VAS)
INTRODUCTION
Radical prostatectomy remains a common option for clinically localized prostate cancer. A recent competing-risks analysis1 of a large North American population-based cohort indicates that, relative to observation, radical prostatectomy reduces the risk of cancer-specific mortality by half in patients aged ≥65 years. Radical prostatectomy involves removal of the prostate, including its fibrous capsule, the surrounding fat and the seminal vesicles. After removal of the prostate, the bladder neck is reconstructed and tapered to a diameter consistent with that of the urethra, and a vesicourethral anastomosis is created. Surgical experience suggests that the procedure is generally safe, but the development of a stricture at the vesicourethral anastomosis is a significant complication.
The incidence of vesicourethral anastomotic stricture (VAS) varies from 0.48% to 32%.2,3,4 The narrowing may result in significant bladder outlet obstruction symptoms, including poor urine stream, urgency, incomplete bladder emptying and even eventual acute urinary retention in a minority of patients. Urinary extravasation, intraoperative blood loss and a prior history of transurethral surgeries have traditionally been implicated as risk factors for anastomotic stricture. Furthermore, surgical techniques, previous radiotherapy and microvascular diseases may also play a role in the development of anastomotic strictures.5
Currently, various procedures exist for managing anastomotic strictures2,5,6,7,8 after radical prostatectomy, including single sounds or balloon dilation, cold knife incision, transurethral resection or internal urethrotomy with a Holmium laser. However, none of these methods is universally accepted due to the relatively high recurrence rate. In addition, a subset of anastomotic contractures following radical prostatectomy is recurrent and recalcitrant to standard endoscopic therapy. In the current study, we retrospectively reviewed the surgical outcome and safety of 549 clinically localized prostate carcinoma patients who received radical prostatectomy at three tertiary care institutions in China. Furthermore, we evaluated the efficacy of nephrostomy balloon dilation (NBD) for patients who developed a VAS following radical prostatectomy with the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS), quality of life (QoL) score and urinary continence as the primary endpoints.
PATIENTS AND METHODS
Subjects
We retrospectively reviewed the clinicopathologic and surgical data of prostate carcinoma patients who received radical retropubic prostatectomy (RRP) or laparoscopic radical prostatectomy (LRP) between January 2007 and March 2010 at three major metropolitan general hospitals in China. All the institutions had implemented good clinical practice. The study protocol was approved by local ethical committees and institutional review boards at the participating institutions. Informed consent was not required because of the retrospective nature of the study. Prostate cancer was pathologically confirmed and classified by the tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) system according to the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC).9 The major inclusion criteria were a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) value <50 ng ml−1, an age ≤75 years, negative bone scan for metastatic disease, and a life expectancy of at least 10 years from the time of surgery.
Surgical techniques
Radical retropubic prostatectomy
RRP was performed as previously described.10,11 The prostate and seminal vesicles were removed, and the bladder neck was preserved at the surgeon's discretion. The bladder neck was reconstructed, the mucosa was everted and a direct mucosa-to-mucosa anastomosis between the bladder neck and urethra was made by six interrupted 3–0 monocryl/polyglactin sutures over a 16F silicone Foley catheter or a 22–24F 3-way Foley catheter. Alternatively, after bladder neck preservation, vesicourethral anastomosis was performed using the running suture technique with 3–0 polyglactin, as was performed in LRP.
Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy
LRP was performed using the antegrade Montsouris technique.12 After the removal of the prostate and seminal vesicles, a posterior running suture of 3–0 polyglactin was used to approximate full-thickness muscularis and mucosa, forming a tennis racket closure when the bladder neck was reconstructed. The neck was narrowed to approximate the diameter of the urethra. Beginning at the posterior wall, a U-shaped suture was placed from the inside to the outside at the bladder level, from the outside to the inside of the lumen of the urethra, from the inside to the outside of the lumen of the urethra and finally from the outside to the inside of the lumen of the bladder. The double-looped knot, placed inside the bladder neck, was spontaneously self-blocked due to tension applied to the threads, allowing the bladder and urethra to be approached simultaneously. Two sets of lateral sutures alternating at the 5, 7, 2 and 10 O’clock position with the knot on the outside were introduced. This U-shape suture was also used to close the bladder neck anteriorly. A silicone 16F Foley catheter was introduced through the anastomosis to reach the bladder.10
Nephrostomy balloon dilation
NBD was performed under local or spinal anesthesia for patients who developed a VAS following radical prostatectomy. A 0.035-inch guide wire (Amplatz Super Stiff; Boston Scientific, Natick, MA, USA) was inserted through a flexible cystourethroscope into the bladder, followed by advancing a 15-cm nephrostomy balloon (Ultraxx Nephrostomy Balloon; Cook Urological, Spencer, IN, USA) over the guide wire. When the balloon reached the bladder distally and the bulbous urethra proximally, as indicated by radiopaque strips on both ends of the balloon, it was inflated to 30F in circumference with a 37% contrast agent by an inflation device (Sphere Inflation Device; Atrion Medical, Arab, AL, USA) (Figure 1). After a 15-min balloon dilation, the anastomosis was examined under a flexible cystourethroscope (Figure 2), and a 24F Foley catheter was left indwelling for 7 days. The operation was performed by four similarly experienced surgeons at the three participating institutions.
Figure 1.
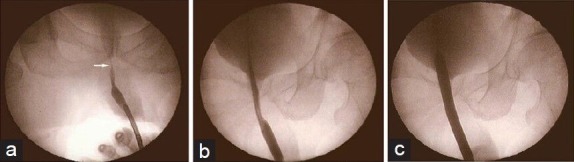
(a) Urethrography shows a vesicourethral anastomotic stricture (white arrow). (b) The dilation balloon was inflated with contrast material. (c) The dilation caliber reaches 30 F when the pressure in the balloon is 20 atm
Figure 2.
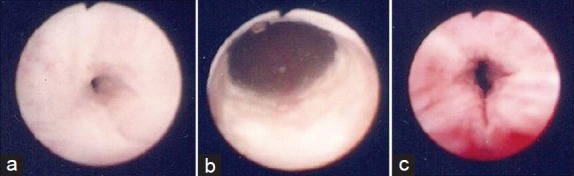
(a) The pinhole stricture of the vesicourethral anastomosis. (b) Vesicourethral anastomosis after dilation with a 30 F balloon. (c) The external sphincter is intact after balloon dilation
Clinical evaluation
A physical examination including a digital rectal examination of the prostate and laboratory studies including PSA were performed at baseline and at subsequent onsite visits at 1, 3, 6 and 12 months postoperatively. Lower urinary tract symptoms, symptom-specific QoL and IPSS (score range: 0-35; mild 0-7, moderate 8-19 and severe >20) were evaluated for efficacy of treatment. Bone metastases were documented on the basis of positive results from bone scanning or skeletal radiography. We also evaluated 30-day perioperative adverse events. VAS was suspected in patients with a significant reduction of the maximal urinary flow rate (Qmax < 10 ml s−1) and a post void residual volume >150 ml and confirmed by flexible cystourethroscopy. Recurrence of the anastomotic stricture was considered when Qmax went below 10 ml s−1 after NBD. Urinary continence status was investigated with the 1-h pad test according to the International Continence Society recommendations.9
Study endpoints
The primary endpoints of this retrospective review were the efficacy of the NBD as evidenced by an improvement in the IPSS and QoL scores, Qmax and urinary continence. Secondary outcomes included PVR and major urinary events. These parameters were measured at baseline and 1, 3, 6 and 12 months postoperatively. Major urinary events included acute urinary retention and gross hematuria. Other adverse events were also recorded at baseline and at subsequent follow-up visits.
Statistical analysis
Data were reported as the mean, interquartile range (IQR), and standard deviation or frequency and percentage for continuous and categorical variables, respectively. We used the two-sided t-test to compare continuous variables and used the Fisher's exact test and Pearson χ2 test to compare categorical variables. Paired differences between the pre- and post-dilation urinary function data were assessed with the Wilcoxon signed rank test. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using Statistical Analysis Software v. 9.2 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA).
RESULTS
Demographic and baseline characteristics of study participants
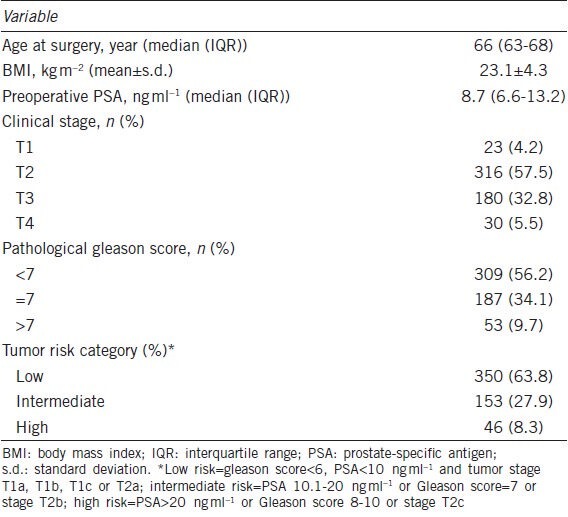
Five hundred and forty-nine prostate cancer patients undergoing RRP or LRP at participating institutions were included in the study. The demographic and disease characteristics are shown in Table 1. The median age at surgery was 66 years (IQR, 63-68 years). Their median preoperative PSA level was 8.7 ng ml−1 (IQR, 6.6-13.2 ng ml−1). Most patients (90.3%) had T2 or T3 prostate cancer, and the great majority of them (90.3%) had a pathological Gleason score of ≤7. In addition, 63.8% of the patients had low-risk, 27.9% had intermediate-risk and 8.3% had high-risk prostate cancer.
Table 1.
Demographic and baseline characteristics of the study participants (n=549)
Surgical outcomes
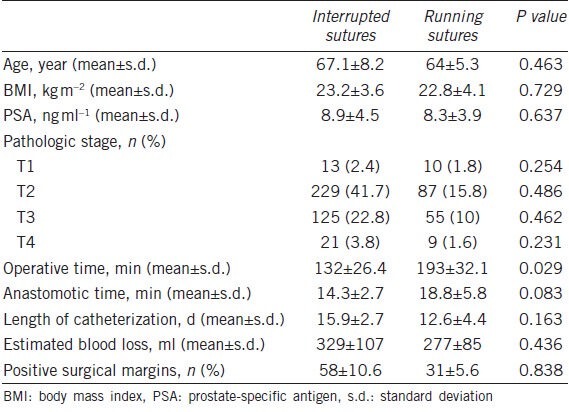
Four hundred and sixty-three patients received RRP and 86 patients underwent LRP. The surgical characteristics of the study cohort are shown in Table 2. The mean operative time was 149 ± 47.1 min, and the estimated volume of blood loss was 313.8 ± 121 ml. The median length of catheterization was 12.2 days (IQR, 8.3-15.7). Eighty-nine (16.2%) patients had positive surgical margins. We further stratified the surgical outcome of these patients by anastomotic sutures. The mean operative time for patients receiving interrupted sutures (132 ± 26.4 min) was noticeably shorter than that for patients receiving running sutures (193 ± 32.1 min) (P < 0.05). Patients receiving interrupted sutures and those receiving running sutures were comparable in demographic and baseline characteristics, length of catheterization, intraoperative blood loss, anastomotic time and the rate of positive surgical margins (Table 3).
Table 2.
Surgical characteristics of the study participants (n=549)
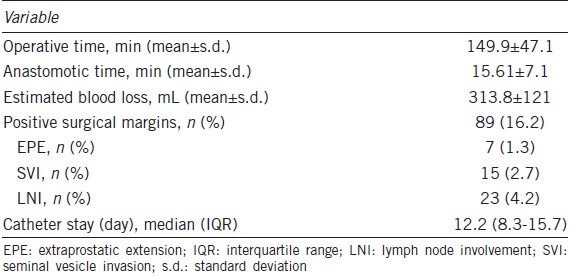
Table 3.
Demographic, baseline and surgical characteristics of the study participants stratified by anastomotic suture techniques
Surgical morbidities
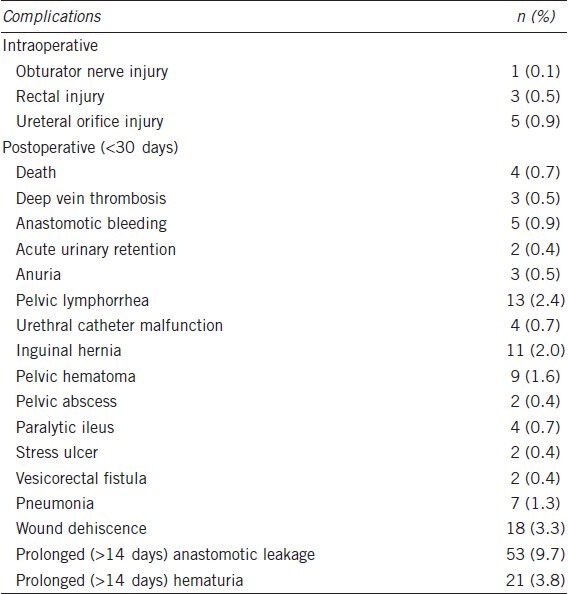
Perioperative complications during the first 30 days after surgery occurred in 31.3% of the patients who underwent radical prostatectomy and included four deaths. The most common complication was prolonged (>14 days) anastomotic leakage (9.7%), followed by prolonged (>14 days) hematuria (3.8%) and wound dehiscence (3.3%) (Table 4). Complications occurring in at least 2% of the patients included pelvic lymphorrhea (2.4%) and inguinal hernia (2.0%). Acute urinary retention occurred in 0.4% of the men.
Table 4.
Adverse events occurring within 30 days after surgery (n=549)
Rates of anastomotic stricture
Forty-five (8.2%) patients developed a VAS with a median time of 4.1 months (IQR, 3.1-6.7 months) from RRP. Four (4.7%) patients receiving LRP developed an anastomotic stricture. Thirty-nine (10.1%) patients with interrupted sutures and six (3.7%) patients with running sutures developed an anastomotic stricture (Figure 3). To determine whether the difference between these two proportions was statistically significant, we used a z-test of independent proportions. This yielded a z-score of 1.78 (P < 0.001), suggesting that patients who have their vesicourethral anastomoses constructed with the interrupted suture technique are more likely to have anastomotic strictures than patients with running sutures.
Figure 3.
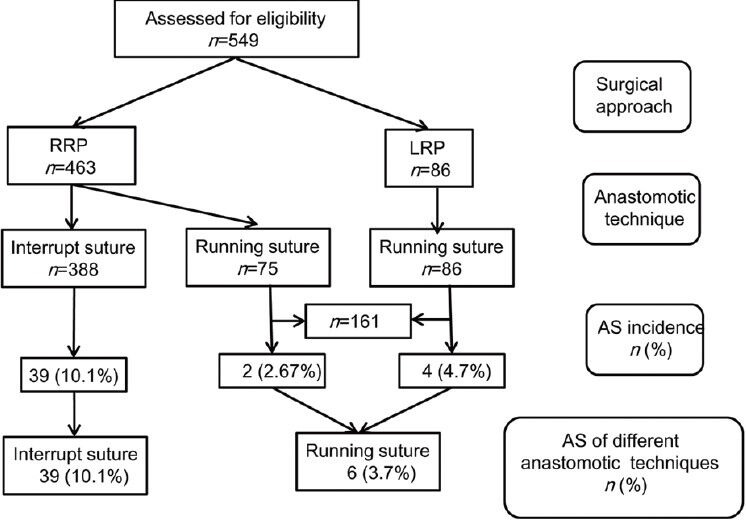
Incidence of vesicourethral anastomotic strictures following radical prostatectomy
Outcome of NBD for VASs
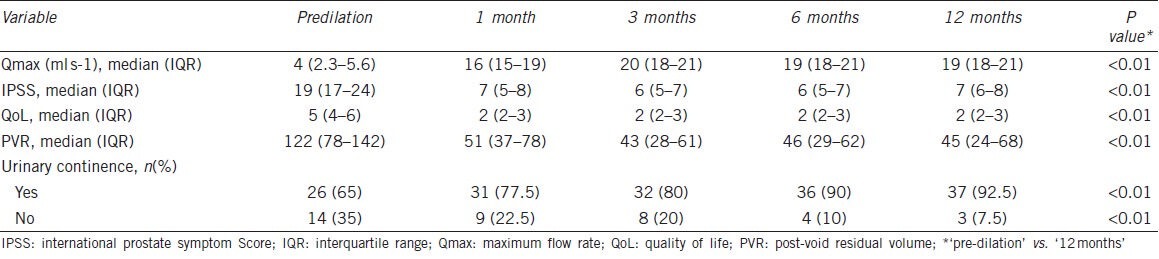
Forty (89%) patients underwent NBD, and three (7.5%) of them had repeat dilation due to weak voiding 4, 5 and 9 months after the first dilation. Thereafter, no repeat dilation was required. Three (7.5%) patients received transurethral resection with electrocautery and two (5%) patients had simple dilation only. The median Qmax of patients undergoing NBD was 4 ml s−1 (IQR, 2.3-5.6 ml s−1) before dilation, which improved to 16 ml s−1 (IQR, 15-19 ml s−1) 1 month following surgery (P < 0.01). At the last 12-month follow-up, the median Qmax was maintained at 19 ml s−1 (IQR, 18-21 ml s−1) (P < 0.01) (Table 5). Fifteen (35%) patients had urinary incontinence prior to dilation, and the number was reduced to three (7.5%) patients 12 months following NBD (P < 0.01). Anastomotic stricture patients also experienced a marked improvement in QoL as a result of NBD: the median IPSS score improved from 19 (IQR, 17-24) before dilation to 7 (IQR, 6-8) at 12 months following dilation, and the QoL score improved from 5 (IQR, 4-6) before dilation to 2 (IQR, 2-3) at 12 months following dilation (P < 0.01 in both).
Table 5.
Urinary function of patients with anastomotic strictures at diagnosis and at subsequent follow-up visits after the last stricture treatment (n=40)
DISCUSSION
Excessive intraoperative blood loss, local urinary extravasation and a history of prior transurethral prostatic surgeries are the most often cited predisposing factors for VASs.13 Comorbidities such as hypertension, coronary artery disease, diabetes mellitus and cigarette smoking appear to be significant risk factors for the development of anastomotic strictures after radical prostatectomy because these diseases are associated with malfunctioning of the microvascular system and cause local ischemia and scar formation at the anastomosis.5 The surgical technique used for bladder neck preservation and the suture material used to create the vesicourethral anastomosis may also contribute to anastomotic strictures.14 Most authors are prone to adopting bladder neck preservation to prevent anastomotic strictures.15,16,17,18,19
In our series, the incidence of anastomotic strictures was 8.2%, which falls within the range of 1%–9.4% reported by others.15,16,17,18,19 In addition, we found that the incidence of anastomotic strictures was significantly higher in patients with an anastomosis constructed by the interrupted suture technique than in those with the running suture technique. This finding is consistent with those reported by Ozu et al.,6 who found that the use of running sutures in these patients is safer compared with the use of four to six interrupted sutures, allowing safe early catheter removal in most patients. We speculate that the running suture technique decreases prolonged anastomotic urinary leakage and bleeding, which may lead to local ischemia or blood clot accumulation, delay mucosa healing and result in urinary extravasation. The latter is now considered a potential risk factor for developing an anastomotic stricture.7,13
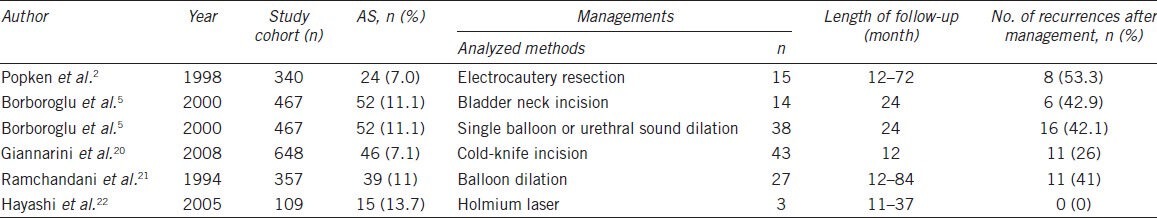
Currently, there is no commonly accepted therapeutic option for anastomotic strictures. There have been no clinical studies on anastomotic strictures with a large patient sample, and only two studies enrolled more than 50 patients (Table 6). Recommended treatments include simple dilation, transurethral incision or resection of the bladder neck with electrocautery. However, the recurrence rate after the use of these methods is high (Table 6) (42.1%–53.3%),2,5 and some patients undergo repeated treatments before they are cured. Scant literature is available on balloon dilation for anastomotic strictures following radical prostatectomy. Kumar and Nargund8 used an F15 ureteral balloon catheter as the first-line treatment for anastomotic strictures following radical prostatectomy in nine cases with a balloon inflation pressure of 60 mmHg. The Ultraxx™ Nephrostomy Balloon is commonly used to dilate the musculofascial tract and renal capsule, establishing a nephrostomy tract during a percutaneous procedure. For access, the balloon has a short transitional taper from the balloon to the catheter shaft at the tip. In our study, this short tip provides a close approximation of the dilating tract to pass the stricture site along the guide wire. Furthermore, depending on the design of the screwed pushing inflation device with a pressure gauge and valve, the pressure inside the balloon could reach 20 atm (15 000 mmHg) and promise success of dilation even if the stricture is quite rigid. In this respect, the nephrostomy balloon set seems more effective than other approaches.8,21 Although the external urinary sphincter is close to the vesicourethral anastomosis, with 30F dilation, urinary incontinence is not likely to occur as a potential complication. In our study, we confirmed the integrity of the external sphincter by flexible cystoscope after dilation. As an inherent advantage, balloon dilation creates only a radical force at the stricture site, whereas standard dilation catheters cause parallel shearing forces. For this reason, the mucosa and elastic sphincter are not easy to injure when the balloon is inflated. Balloon dilation did not impair the urinary continence of our patients in this study. In addition, balloon dilation caused an apparent improvement in the Qmax, IPSS and QoL score.
Table 6.
Management of anastomotic strictures (AS) following radical retropubic prostatectomy reported in the literature
In conclusion, anastomotic strictures occur in a small but significant proportion (8.2%) of patients following radical prostatectomy. NBD offers an effective remedy for anastomotic strictures with a marked improvement in urinary function and QoL.22
REFERENCES
- 1.Abdollah F, Sun M, Schmitges J, Tian Z, Jeldres C, et al. Cancer-specific and other-cause mortality after radical prostatectomy versus observation in patients with prostate cancer: competing-risks analysis of a large North American population-based cohort. Eur Urol. 2011;60:920–30. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2011.06.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Popken G, Sommerkamp H, Schultze-Seemann W, Wetterauer U, Katzenwadel A. Anastomotic stricture after radical prostatectomy: incidence, findings and treatment. Eur Urol. 1998;33:382–6. doi: 10.1159/000019620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Besarani D, Amoroso P, Kirby R. Bladder neck contracture after radical retropubic prostatectomy. BJU Int. 2004;94:1245–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2004.05151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Augustin H, Pummer K, Daghofer F, Habermann H, Primus G, et al. Patient self-reporting questionnaire on urological morbidity and bother after radical retropubic prostatectomy. Eur Urol. 2002;42:112–7. doi: 10.1016/s0302-2838(02)00259-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Borboroglu PG, Sands JP, Roberts JL, Amling CL. Risk factors for vesicourethral anastomotic stricture after radical prostatectomy. Urology. 2000;56:96–100. doi: 10.1016/s0090-4295(00)00556-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ozu C, Hagiuda J, Nakagami Y, Hamada R, Horiguchi Y, et al. Radical retropubic prostatectomy with running vesicourethral anastomosis and early catheter removal: our experience. Int J Urol. 2009;16:487–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2009.02281.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kostakopoulos A, Argiropoulos V, Protogerou V, Tekerlekis P, Melekos M. Vesicourethral anastomotic strictures after radical retropubic prostatectomy: the experience of a single institution. Urol Int. 2004;72:17–20. doi: 10.1159/000075267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kumar P, Nargund VH. Management of post-radical prostatectomy anastomotic stricture by endoscopictransurethral balloon dilatation. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 2007;41:314–5. doi: 10.1080/00365590601017030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, Griffiths D, Rosier P, et al. The standardization of terminology of lower urinary tract function: report from the Standardization Sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Neurourol Urodyn. 2002;21:167–78. doi: 10.1002/nau.10052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Walsh PC. Anatomic radical prostatectomy. Evolution of the surgical technique. J Urol. 1998;160:2418–24. doi: 10.1097/00005392-199812020-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Walsh PC, Mostwin JL. Radical prostatectomy and cystoprostatectomy with preservation of potency. Results using a new nerve-sparing technique. Br J Urol. 1984;56:694–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1984.tb06149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Guillonneau B, Vallancien G. Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: the Montsouris technique. J Urol. 2000;163:1643–9. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(05)67512-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Surya BV, Provet J, Johanson KE, Brown J. Anastomotic strictures following radical prostatectomy: risk factors and management. J Urol. 1990;143:755–8. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)40082-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Williams SB, Alemozaffar M, Lei Y, Hevelone N, Lipsitz SR, et al. Randomized controlled trial of barbed polyglyconate versus polyglactin suture for robot-assisted laparoscopic prostatectomy anastomosis: technique and outcomes. Eur Urol. 2010;58:875–81. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2010.07.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Soloway MS, Neulander E. Bladder-neck preservation during radical retropubic prostatectomy. Semin Urol Oncol. 2000;18:51–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kaye KW, Creed KE, Wilson GJ, D’Antuono M, Dawkins HJ. Urinary continence after radical retropubic prostatecprostatectomy. Analysis and synthesis of contributing factors: a unified concept. Br J Urol. 1997;80:444–51. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410x.1997.00373.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Poon M, Ruckle H, Bamshad BR, Tsai C, Webster R, et al. Radical retropubic prostatectomy: bladder neck preservation versus reconstruction. J Urol. 2000;163:194–8. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(05)68003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gaker DL, Steel BL. Radical prostatectomy with preservation of urinary continence: pathology and long-term results. J Urol. 2004;172:2549–52. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000144071.24113.1c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ramsden AR, Chodak GW. Can leakage at the vesicourethral anastomosis be predicted after radical retropubic prostatectomy? BJU Int. 2004;93:503–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.2003.04668.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Giannarini G, Manassero F, Mogorovich A, Valent F, De Maria M, et al. Cold-Knife Incision of Anastomotic Strictures after Radical Retropubic Prostatectomy with Bladder Neck Preservation: efficacy and Impact on Urinary Continence Status. Eur Urol. 2008;54:647–56. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2007.12.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ramchandani P, Banner MP, Berlin JW, Dannenbaum MS, Wein AJ. Vesicourethral anastomotic stricture after radical prostatectomy: efficacy of transurethral balloon dilatation. Radiology. 1994;193:345–9. doi: 10.1148/radiology.193.2.7972741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hayashi T, Yoshinaga A, Ohno R, Ishii N, Watanabe T, et al. Successful treatment of recurrent vesicourethral stricture after radical prostatectomy with holmium laser: report of three cases. Int J Urol. 2005;12:414–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2005.01053.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


