Abstract
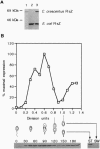
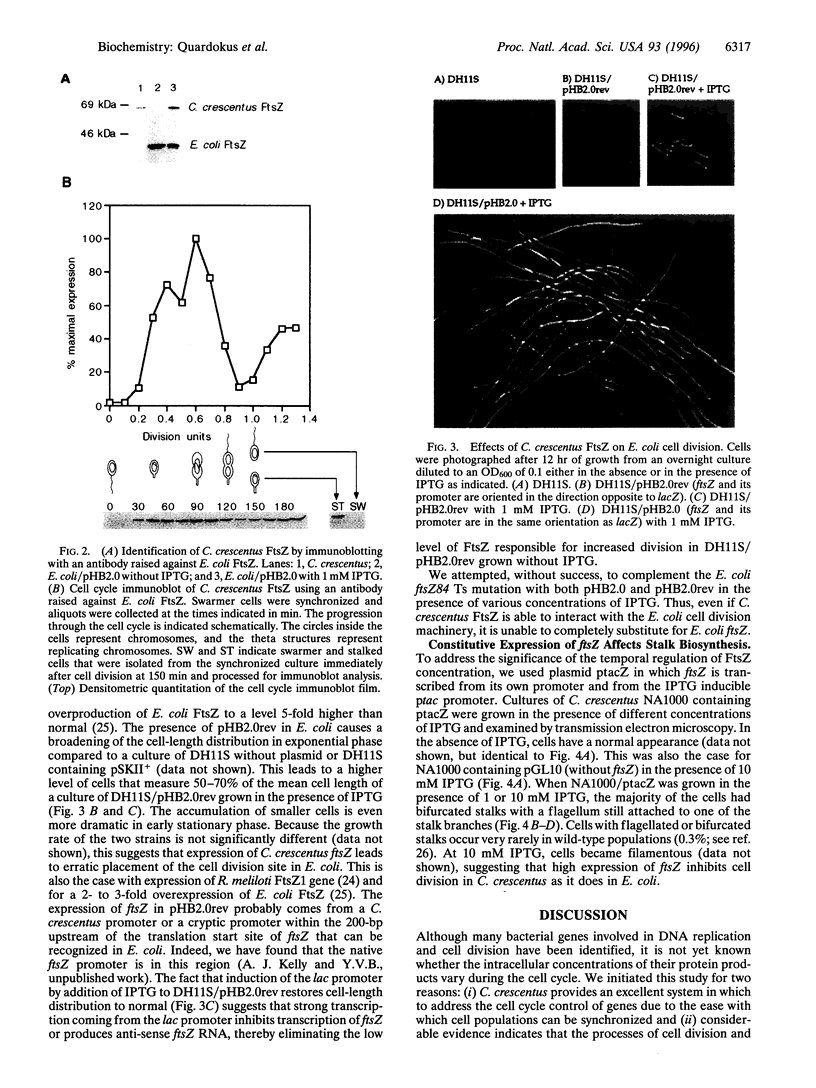
Many genes involved in cell division and DNA replication and their protein products have been identified in bacteria; however, little is known about the cell cycle regulation of the intracellular concentration of these proteins. It has been shown that the level of the tubulin-like GTPase FtsZ is critical for the initiation of cell division in bacteria. We show that the concentration of FtsZ varies dramatically during the cell cycle of Caulobacter crescentus. Caulobacter produce two different cell types at each cell division: (i) a sessile stalked cell that can initiate DNA replication immediately after cell division and (ii) a motile swarmer cell in which DNA replication is blocked. After cell division, only the stalked cell contains FtsZ. FtsZ is synthesized slightly before the swarmer cells differentiate into stalked cells and the intracellular concentration of FtsZ is maximal at the beginning of cell division. Late in the cell cycle, after the completion of chromosome replication, the level of FtsZ decreases dramatically. This decrease is probably mostly due to the degradation of FtsZ in the swarmer compartment of the predivisional cell. Thus, the variation of FtsZ concentration parallels the pattern of DNA synthesis. Constitutive expression of FtsZ leads to defects in stalk biosynthesis suggesting a role for FtsZ in this developmental process in addition to its role in cell division.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alley M. R., Gomes S. L., Alexander W., Shapiro L. Genetic analysis of a temporally transcribed chemotaxis gene cluster in Caulobacter crescentus. Genetics. 1991 Oct;129(2):333–341. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.2.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alley M. R., Maddock J. R., Shapiro L. Requirement of the carboxyl terminus of a bacterial chemoreceptor for its targeted proteolysis. Science. 1993 Mar 19;259(5102):1754–1757. doi: 10.1126/science.8456303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beall B., Lutkenhaus J. FtsZ in Bacillus subtilis is required for vegetative septation and for asymmetric septation during sporulation. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):447–455. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernander R., Akerlund T., Nordström K. Inhibition and restart of initiation of chromosome replication: effects on exponentially growing Escherichia coli cells. J Bacteriol. 1995 Apr;177(7):1670–1682. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.7.1670-1682.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bi E. F., Lutkenhaus J. FtsZ ring structure associated with division in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1991 Nov 14;354(6349):161–164. doi: 10.1038/354161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramhill D., Thompson C. M. GTP-dependent polymerization of Escherichia coli FtsZ protein to form tubules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):5813–5817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.5813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun Y. V., Marczynski G., Shapiro L. The expression of asymmetry during Caulobacter cell differentiation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:419–450. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.002223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun Y. V., Shapiro L. A temporally controlled sigma-factor is required for polar morphogenesis and normal cell division in Caulobacter. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2395–2408. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corton J. C., Ward J. E., Jr, Lutkenhaus J. Analysis of cell division gene ftsZ (sulB) from gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.1-7.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degnen S. T., Newton A. Chromosome replication during development in Caulobacter crescentus. J Mol Biol. 1972 Mar 14;64(3):671–680. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmatilake A. J., Kendrick K. E. Expression of the division-controlling gene ftsZ during growth and sporulation of the filamentous bacterium Streptomyces griseus. Gene. 1994 Sep 15;147(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donachie W. D. The cell cycle of Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1993;47:199–230. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.47.100193.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driks A., Schoenlein P. V., DeRosier D. J., Shapiro L., Ely B. A Caulobacter gene involved in polar morphogenesis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):2113–2123. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.2113-2123.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson H. P. FtsZ, a prokaryotic homolog of tubulin? Cell. 1995 Feb 10;80(3):367–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90486-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evinger M., Agabian N. Envelope-associated nucleoid from Caulobacter crescentus stalked and swarmer cells. J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):294–301. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.294-301.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrido T., Sánchez M., Palacios P., Aldea M., Vicente M. Transcription of ftsZ oscillates during the cell cycle of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3957–3965. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06073.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gober J. W., Champer R., Reuter S., Shapiro L. Expression of positional information during cell differentiation of Caulobacter. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90646-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gober J. W., Marques M. V. Regulation of cellular differentiation in Caulobacter crescentus. Microbiol Rev. 1995 Mar;59(1):31–47. doi: 10.1128/mr.59.1.31-47.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huguenel E. D., Newton A. Localization of surface structures during procaryotic differentiation: role of cell division in Caulobacter crescentus. Differentiation. 1982;21(2):71–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1982.tb01199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Kunkel L. M. Detailed analysis of the repeat domain of dystrophin reveals four potential hinge segments that may confer flexibility. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4560–4566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. J., Smith M., Jessee J., Bloom F. DH11S: an Escherichia coli strain for preparation of single-stranded DNA from phagemid vectors. Biotechniques. 1992 May;12(5):718–721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutkenhaus J. FtsZ ring in bacterial cytokinesis. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Aug;9(3):403–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01701.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddock J. R., Shapiro L. Polar location of the chemoreceptor complex in the Escherichia coli cell. Science. 1993 Mar 19;259(5102):1717–1723. doi: 10.1126/science.8456299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marczynski G. T., Dingwall A., Shapiro L. Plasmid and chromosomal DNA replication and partitioning during the Caulobacter crescentus cell cycle. J Mol Biol. 1990 Apr 20;212(4):709–722. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90232-B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolin W., Corbo J. C., Long S. R. Cloning and characterization of a Rhizobium meliloti homolog of the Escherichia coli cell division gene ftsZ. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5822–5830. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5822-5830.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee A., Lutkenhaus J. Guanine nucleotide-dependent assembly of FtsZ into filaments. J Bacteriol. 1994 May;176(9):2754–2758. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.9.2754-2758.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton A., Ohta N. Regulation of the cell division cycle and differentiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:689–719. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.003353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radford S. E., Laue E. D., Perham R. N., Martin S. R., Appella E. Conformational flexibility and folding of synthetic peptides representing an interdomain segment of polypeptide chain in the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):767–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo M. F., Shapiro L., Gober J. Asymmetric expression of the gyrase B gene from the replication-competent chromosome in the Caulobacter crescentus predivisional cell. J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(21):6970–6981. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.21.6970-6981.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Hedge P. J., te Heesen S., Edelman A., Broome-Smith J. K. Kanamycin-resistant vectors that are analogues of plasmids pUC8, pUC9, pEMBL8 and pEMBL9. Gene. 1986;41(2-3):337–342. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens C., Reisenauer A., Wright R., Shapiro L. A cell cycle-regulated bacterial DNA methyltransferase is essential for viability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Feb 6;93(3):1210–1214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.3.1210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X., Lutkenhaus J. The FtsZ protein of Bacillus subtilis is localized at the division site and has GTPase activity that is dependent upon FtsZ concentration. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Aug;9(3):435–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01705.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. E., Jr, Lutkenhaus J. Overproduction of FtsZ induces minicell formation in E. coli. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):941–949. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90290-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingrove J. A., Gober J. W. A sigma 54 transcriptional activator also functions as a pole-specific repressor in Caulobacter. Genes Dev. 1994 Aug 1;8(15):1839–1852. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.15.1839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingrove J. A., Mangan E. K., Gober J. W. Spatial and temporal phosphorylation of a transcriptional activator regulates pole-specific gene expression in Caulobacter. Genes Dev. 1993 Oct;7(10):1979–1992. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.10.1979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweiger G., Marczynski G., Shapiro L. A Caulobacter DNA methyltransferase that functions only in the predivisional cell. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jan 14;235(2):472–485. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]