Abstract
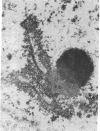
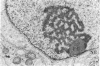
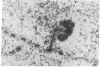
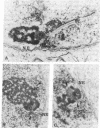
The spatial relationships of acrocentric chromosomes were studied during prophase I of meiosis in human oocytes and spermatocytes by using cytogenetic techniques, electron microscopy, and in situ hybridization. Ultrastructural investigations revealed an ordered arrangement of nucleolar bivalents at the zygotene and pachytene stages. The end of the bivalent corresponding to the cytological satellite was consistently attached to the nuclear envelope. The fibrillar center of the nucleolus always contained rDNA chromatin fibers emanating from the secondary constriction region. Association of ribosomal genes from two bivalents in the same fibrillar center was frequently observed. Ultrastructural studies demonstrated the close proximity of chromatids in the short arm region of the involved nonhomologous acrocentrics. A breakage/reunion model based on our data can explain the formation of all observed types of Robertsonian translocations: monocentrics and dicentrics with or without rDNA.
Full text
PDF

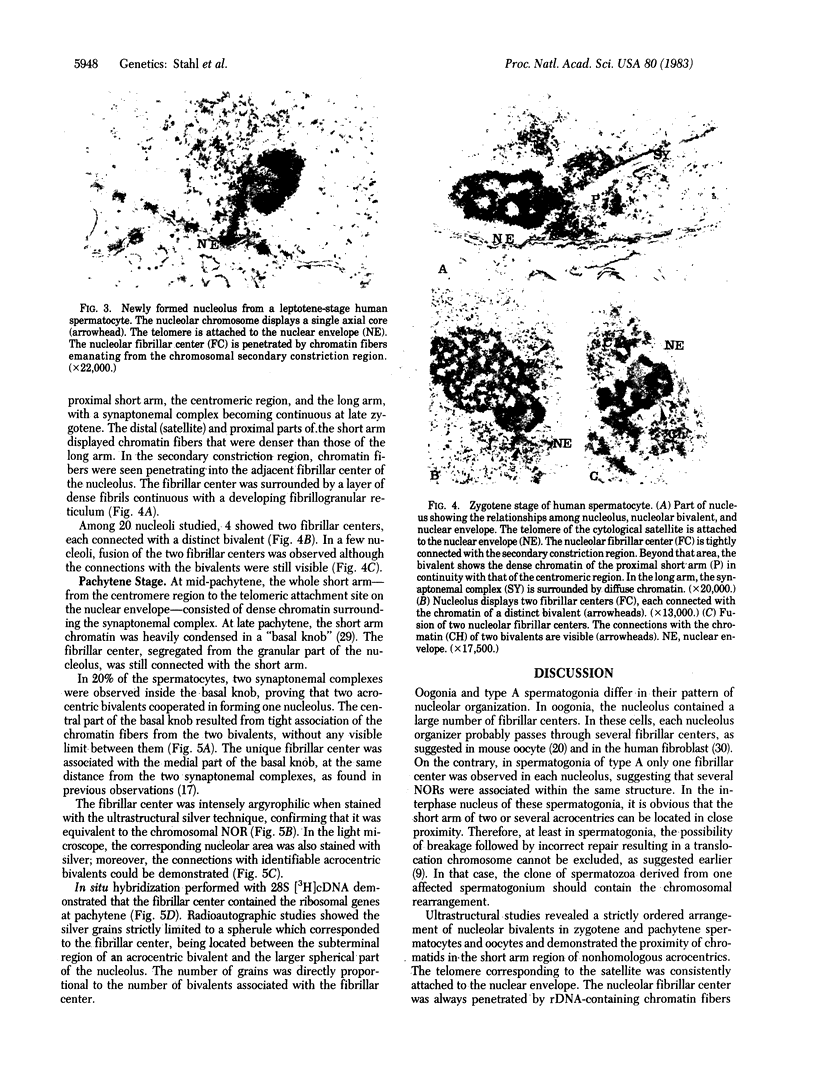
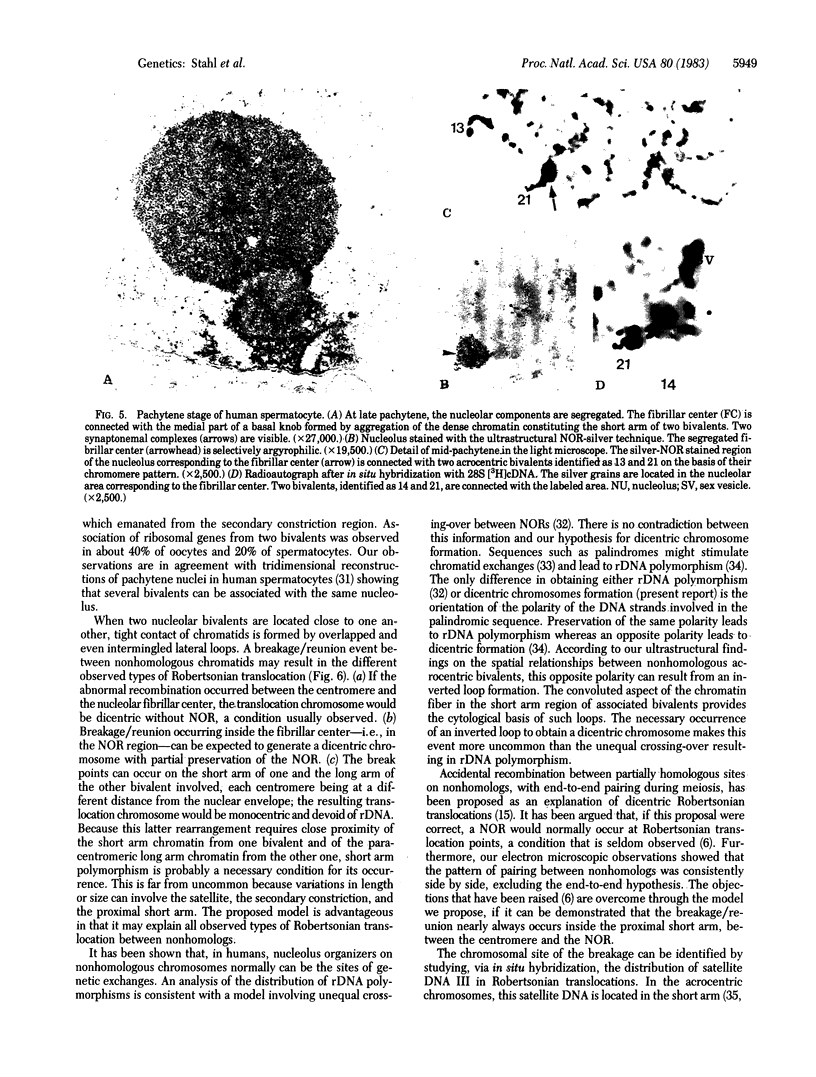
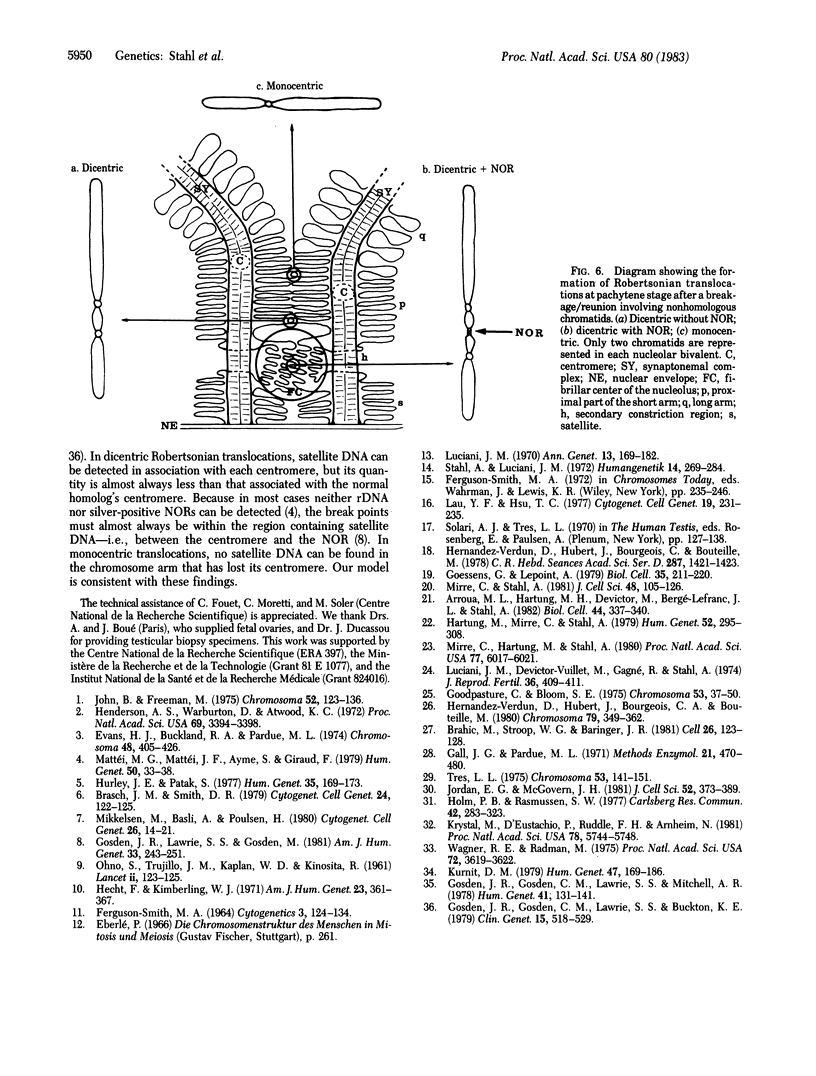
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brahic M., Stroop W. G., Baringer J. R. Theiler's virus persists in glial cells during demyelinating disease. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):123–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasch J. M., Smyth D. R. Absence of silver bands in human Robertsonian translocation chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1979;24(2):122–125. doi: 10.1159/000131365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERGUSON-SMITH M. A. THE SITES OF NUCLEOLUS FORMATION IN HUMAN PACHYTENE CHROMOSOMES. Cytogenetics. 1964;3:124–134. doi: 10.1159/000129803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodpasture C., Bloom S. E. Visualization of nucleolar organizer regions im mammalian chromosomes using silver staining. Chromosoma. 1975 Nov 20;53(1):37–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00329389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosden J. R., Gosden C. M., Lawrie S. S., Buckton K. E. Satellite DNA loss and nucleolar organiser activity in an individual with a de novo chromosome 13,14 translocation. Clin Genet. 1979 Jun;15(6):518–529. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1979.tb00836.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosden J. R., Gosden C., Lawrie S., Mitchell A. R. The fate of DNA satellites I, II, III and ribosomal DNA in a familial dicentric chromosome 13:14. Hum Genet. 1978 Mar 17;41(2):131–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00273095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gosden J. R., Lawrie S. S., Gosden C. M. Satellite DNA sequences in the human acrocentric chromosomes: information from translocations and heteromorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1981 Mar;33(2):243–251. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartung M., Mirre C., Stahl A. Nucleolar organizers in human oocytes at meiotic prophase I, studied by the silver-NOR method and electron microscopy. Hum Genet. 1979;52(3):295–308. doi: 10.1007/BF00278679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht F., Kimberling W. J. Patterns of D chromosome involvement in human (DqDq) and (DqGq) Robertsonian rearrangements. Am J Hum Genet. 1971 Jul;23(4):361–367. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A. S., Warburton D., Atwood K. C. Location of ribosomal DNA in the human chromosome complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3394–3398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Verdun D., Hubert J., Bourgeois C. A., Bouteille M. Ultrastructural localization of Ag-NOR stained proteins in the nucleolus during the cell cycle and in other nucleolar structures. Chromosoma. 1980;79(3):349–362. doi: 10.1007/BF00327325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Verdun D., Hubert J., Bourgeois C., Bouteille M. Identification ultrastructurale de l'organisateur nucléolaire par la technique à l'argent. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1978 Dec;287(16):1421–1423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. E., Pathak S. Elimination of nucleolus organizers in a case of 13/14 Robertsonian translocation. Hum Genet. 1977 Feb 11;35(2):169–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00393966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John B., Freeman M. Causes and consequences of Robertsonian exchange. Chromosoma. 1975 Sep 26;52(2):123–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00326262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan E. G., McGovern J. H. The quantitative relationship of the fibrillar centres and other nucleolar components to changes in growth conditions, serum deprivation and low doses of actinomycin D in cultured diploid human fibroblasts (strain MRC-5). J Cell Sci. 1981 Dec;52:373–389. doi: 10.1242/jcs.52.1.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystal M., D'Eustachio P., Ruddle F. H., Arnheim N. Human nucleolus organizers on nonhomologous chromosomes can share the same ribosomal gene variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5744–5748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurnit D. M. Satellite DNA and heterochromatin variants: the case for unequal mitotic crossing over. Hum Genet. 1979 Mar 12;47(2):169–186. doi: 10.1007/BF00273199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Y. F., Hsu T. C. Variable modes of Robertsonian fusions. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1977;19(4):231–235. doi: 10.1159/000130813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luciani J. M., Devictor-Vuillet M., Gagné R., Stahl A. An air-drying method for first meiotic prophase preparations from mammalian ovaries. J Reprod Fertil. 1974 Feb;36(2):409–411. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0360409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luciani J. M. Les chromosomes méiotiques de l'homme. II. Le nucléole. Les chiasmas. 3. La stérilité masculine. Ann Genet. 1970 Sep;13(3):169–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F., Ayme S., Giraud F. Dicentric Robertsonian translocation in man. 17 cases studied by R,C, and N banding. Hum Genet. 1979;50(1):33–38. doi: 10.1007/BF00295586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen M., Basli A., Poulsen H. Nucleolus organizer regions in translocations involving acrocentric chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1980;26(1):14–21. doi: 10.1159/000131416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirre C., Hartung M., Stahl A. Association of ribosomal genes in the fibrillar center of the nucleolus: a factor influencing translocation and nondisjunction in the human meiotic oocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6017–6021. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirre C., Stahl A. Ultrastructural organization, sites of transcription and distribution of fibrillar centres in the nucleolus of the mouse oocyte. J Cell Sci. 1981 Apr;48:105–126. doi: 10.1242/jcs.48.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OHNO S., TRUJILLO J. M., KAPLAN W. D., KINOSITA R. Nucleolus-organisers in the causation of chromosomal anomalies in man. Lancet. 1961 Jul 15;2(7194):123–126. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)92647-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl A., Luciani J. M. Nucleoli and chromosomes: their relationships during the meiotic prophase of the human fetal oocyte. Humangenetik. 1972;14(4):269–284. doi: 10.1007/BF00290169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tres L. L. Nucleolar RNA synthesis of meiotic prophase spermatocytes in the human testis. Chromosoma. 1975 Nov 24;53(2):141–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00333042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner R. E., Jr, Radman M. A mechanism for initiation of genetic recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3619–3622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]