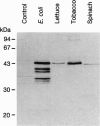
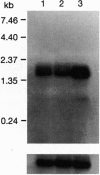
Abstract
Plants need to avoid or dissipate excess light energy to protect photosystem II (PSII) from photoinhibitory damage. Higher plants have a conserved system that dissipates excess energy as heat in the light-harvesting complexes of PSII that depends on the transthylakoid delta pH and violaxanthin de-epoxidase (VDE) activity. To our knowledge, we report the first cloning of a cDNA encoding VDE and expression of functional enzyme in Escherichia coli. VDE is nuclear encoded and has a transit peptide with characteristic features of other lumen-localized proteins. The cDNA encodes a putative polypeptide of 473 aa with a calculated molecular mass of 54,447 Da. Cleavage of the transit peptide results in a mature putative polypeptide of 348 aa with a calculated molecular mass of 39,929 Da, close to the apparent mass of the purified enzyme (43 kDa). The protein has three interesting domains including (i) a cysteine-rich region, (ii) a lipocalin signature, and (iii) a highly charged region. The E. coli expressed enzyme de-epoxidizes violaxanthin sequentially to antheraxanthin and zeaxanthin, and is inhibited by dithiothreitol, similar to VDE purified from chloroplasts. This confirms that the cDNA encodes an authentic VDE of a higher plant and is unequivocal evidence that the same enzyme catalyzes the two-step mono de-epoxidation reaction. The cloning of VDE opens new opportunities for examining the function and evolution of the xanthophyll cycle, and possibly enhancing light-stress tolerance of plants.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bugos R. C., Chiang V. L., Campbell W. H. cDNA cloning, sequence analysis and seasonal expression of lignin-bispecific caffeic acid/5-hydroxyferulic acid O-methyltransferase of aspen. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Dec;17(6):1203–1215. doi: 10.1007/BF00028736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausmeyer S., Klösgen R. B., Herrmann R. G. Protein import into chloroplasts. The hydrophilic lumenal proteins exhibit unexpected import and sorting specificities in spite of structurally conserved transit peptides. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):13869–13876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore A. M., Hazlett T. L., Govindjee Xanthophyll cycle-dependent quenching of photosystem II chlorophyll a fluorescence: formation of a quenching complex with a short fluorescence lifetime. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 14;92(6):2273–2277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.6.2273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore A. M., Yamamoto H. Y. Dark induction of zeaxanthin-dependent nonphotochemical fluorescence quenching mediated by ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1899–1903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hageman J., Baecke C., Ebskamp M., Pilon R., Smeekens S., Weisbeek P. Protein Import into and Sorting inside the Chloroplast Are Independent Processes. Plant Cell. 1990 May;2(5):479–494. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.5.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton P., Ruban A. V., Walters R. G. Regulation of Light Harvesting in Green Plants (Indication by Nonphotochemical Quenching of Chlorophyll Fluorescence). Plant Physiol. 1994 Oct;106(2):415–420. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen J. N., Caceres I., Eliopoulos E. E., Zagalsky P. F., Findlay J. B. Complete sequence and model for the A2 subunit of the carotenoid pigment complex, crustacyanin. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Apr 23;197(2):407–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15925.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko K., Cashmore A. R. Targeting of proteins to the thylakoid lumen by the bipartite transit peptide of the 33 kd oxygen-evolving protein. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3187–3194. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08477.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubauer C., Yamamoto H. Y. Mehler-peroxidase reaction mediates zeaxanthin formation and zeaxanthin-related fluorescence quenching in intact chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1992 Aug;99(4):1354–1361. doi: 10.1104/pp.99.4.1354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pervaiz S., Brew K. Homology and structure-function correlations between alpha 1-acid glycoprotein and serum retinol-binding protein and its relatives. FASEB J. 1987 Sep;1(3):209–214. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.3.3622999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rockholm D. C., Yamamoto H. Y. Violaxanthin de-epoxidase. Plant Physiol. 1996 Feb;110(2):697–703. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.2.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. K., Schloss J. V., Mazur B. J. Functional expression of plant acetolactate synthase genes in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4179–4183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorst O., Oosterhoff-Teertstra R., Vankan P., Smeekens S., Weisbeek P. Plastocyanin of Arabidopsis thaliana; isolation and characterization of the gene and chloroplast import of the precursor protein. Gene. 1988 May 15;65(1):59–69. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90417-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMAMOTO H. Y., NAKAYAMA T. O., CHICHESTER C. O. Studies on the light and dark interconversions of leaf xanthophylls. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Apr;97:168–173. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(62)90060-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto H. Y., Higashi R. M. Violaxanthin de-epoxidase. Lipid composition and substrate specificity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Oct;190(2):514–522. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90305-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto H. Y., Kamite L. The effects of dithiothreitol on violaxanthin de-epoxidation and absorbance changes in the 500-nm region. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jun 23;267(3):538–543. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(72)90182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G., Steppuhn J., Herrmann R. G. Domain structure of mitochondrial and chloroplast targeting peptides. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Apr 1;180(3):535–545. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14679.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]