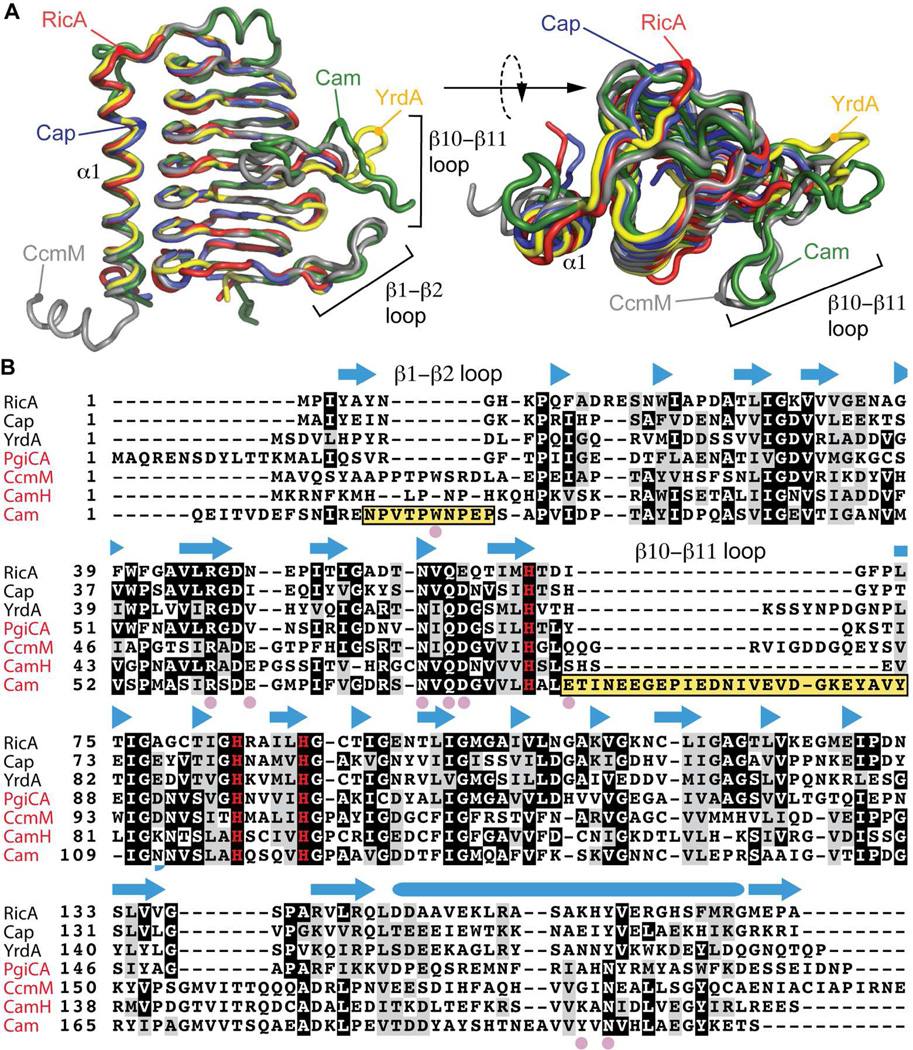
Figure 4.
Structural comparison of RicA to related γ-CA family proteins. A) Structural alignment of RicA (red) to YrdA (yellow, PDB code : 3TIO), Cap (blue, PDB code : 2FKO), CcmM (grey, PDB code : 3KWC) and Cam (green, PDB code : 1QRE). B) Amino acid sequence alignment of RicA to γ-CA proteins from Escherichia coli (YrdA), Pyrococcus horikoshii (Cap), Porphyromonas gingivalis (PgiCA), Thermosynechococcus elongatus (CcmM) and Methanosarcina thermophil (CamH and Cam). Secondary structure of RicA is annotated above the amino acid sequence. β-strands are represented with blue arrows; α-helix by blue cylinder. Pink solid circles highlight residues in Cam present in the active site and important for carbonic anhydrase activity. Yellow boxes highlight the β1–β2 and β10–β11 loops of Cam. The three histidines (H67, H84 and H89) involved in zinc coordination are shown in red. Names of the proteins with a reported carbonic anhydrase activities are in red.