FIG 4 .
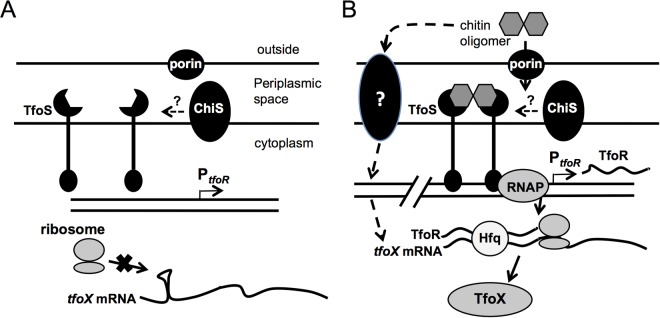
Proposed model for the role of TfoS in activating competence in V. cholerae. (A) In the absence of chitin oligomers, TfoS cannot dimerize and activate TfoR transcription. Alternatively, in the absence of chitin oligimers, dimerized TfoS is in an inactive state and the DNA-binding domains of the protein are unable to upregulate TfoR. In the absence of TfoR, TfoX translation is inhibited by a stem-loop structure in the tfoX mRNA 5′ UTR that occludes the Shine-Dalgarno sequence required for translation initiation (18). (B) In the presence of chitin, tfoX mRNA is upregulated by an unknown mechanism. Also, short chitin oligomers enter the periplasm by nonspecific porins or via the V. cholerae chitporin (VC0972) (9). These chitin oligomers interact with and dimerize TfoS protein (and/or induce a conformational change in TfoS dimers) in the inner membrane, which allows the cytoplasmic DNA-binding domains to bind to the tfoR promoter, recruit RNAP, and positively regulate TfoR transcription. ChiS may also act to enhance TfoS activity by an unknown mechanism (16). TfoR then interacts with Hfq and the 5′ UTR of tfoX mRNA to expose the Shine-Dalgarno sequence of the tfoX mRNA to positively regulate tfoX translation. TfoX then goes on to activate the genes necessary for competence.
