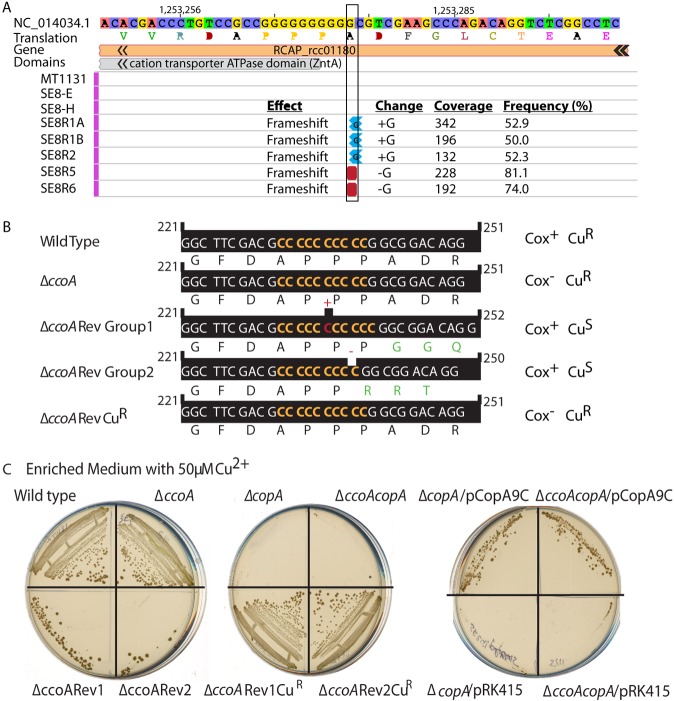
FIG 3 .
The ΔccoA revertants contain a single cytosine indel mutation in the copA gene that inactivates CopA protein. (A) NGS results show the R. capsulatus genome region that contains the RCC01180 (copA) gene encoding CopA. The strains are listed to the left. MT1131 is the wild-type strain. SE8-E and SE8-H are two different isolates of SE8 (ΔccoA). SE8R1A and SE8R1B are two different isolates of SE8R1 (ΔccoARev1). SE8R2 (ΔccoARev2), SE8R5 (ΔccoARev5), and SE8R6 (ΔccoARev6) strains are shown last. The whole genomes of the strains were sequenced and compared. The base pair changes and their effects and the related statistical data (coverage and frequency) are shown on the right. (B) The nucleotide sequence of copA between positions 221 and 251, together with the encoded amino acid sequence are shown for the wild type (MT1131), ΔccoA (SE8E or -H), ΔccoARev group 1 (SE8R1A or -B or SE8R2), ΔccoARev group 2 (SE8R5 or SER6) and ΔccoARev Cur (SE8R1CuR or SE8R2CuR) strains. The same sequence and reading frame are found in the wild-type, ΔccoA, and ΔccoARevCuR strains, which contain a wild-type copA allele with 10 consecutive cytosines. An insertion of one cytosine in ΔccoARev group 1 (e.g., SE8R1) and a deletion of one cytosine in ΔccoARev group 2 (e.g., SE8R5), resulting in 11 or 9 consecutive cytosines, respectively, and the frameshift mutations are also shown. (C) Cur and Cus phenotypes of wild-type (MT1131), ΔccoA (SE8), ΔcopA (SE24), ΔccoA ΔcopA (SE25), ΔccoARev1 (SE8R1), ΔccoARev2 (SE8R2), ΔccoARev1CuR (SE8R1CuR), and ΔccoARev2CuR (SE8R2CuR) strains were determined by their ability to grow on enriched MPYE medium supplemented with 50 µM CuSO4. Under these conditions, Cus strains are unable to form colonies. Among the Cus strains, the ΔccoARev1 (SE8R1) and ΔccoARev2 (SE8R2) strains frequently yield Cur derivatives, whereas ΔcopA (SE24) and ΔccoA ΔcopA (SE25) strains do not (compare the bottom of the left plate to the top of the middle plate). Similarly, the ΔcopA/pCopA9C and ΔcopA ΔccoA/pCopA9C strains yield Cur derivatives, whereas the same strains with a plasmid lacking a copA allele (pRK415) do not yield any Cur derivatives (right plate).