Abstract
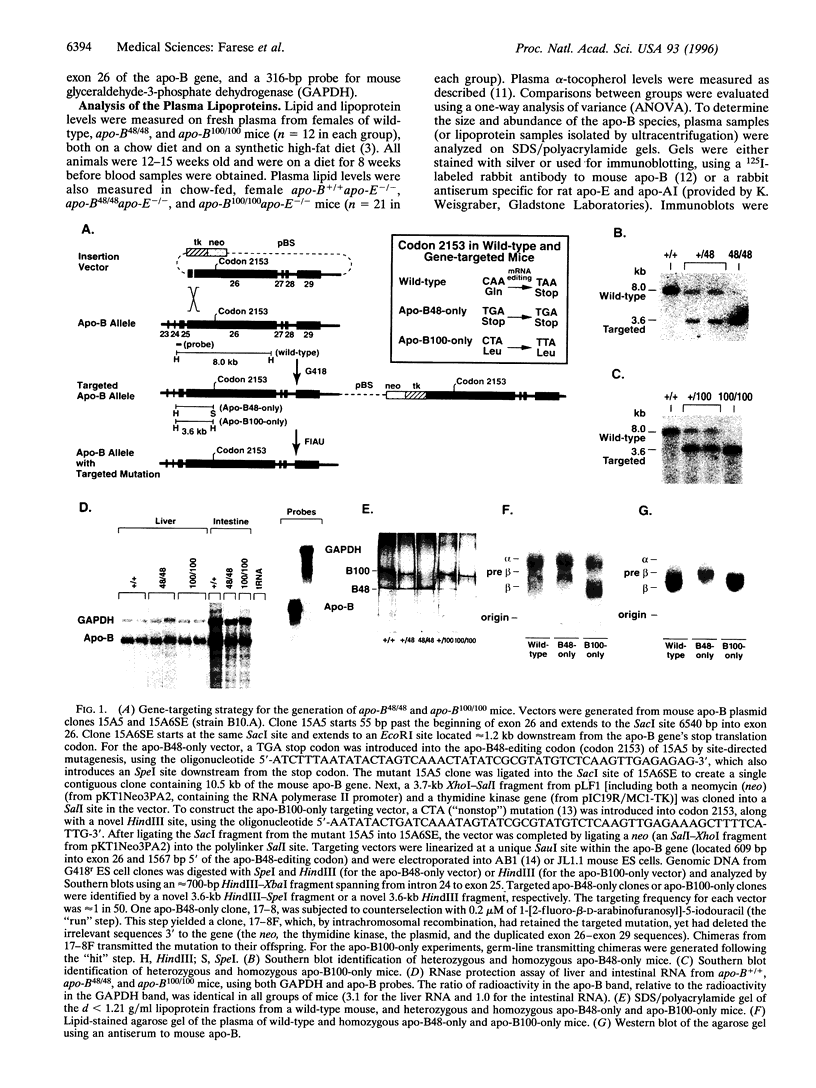
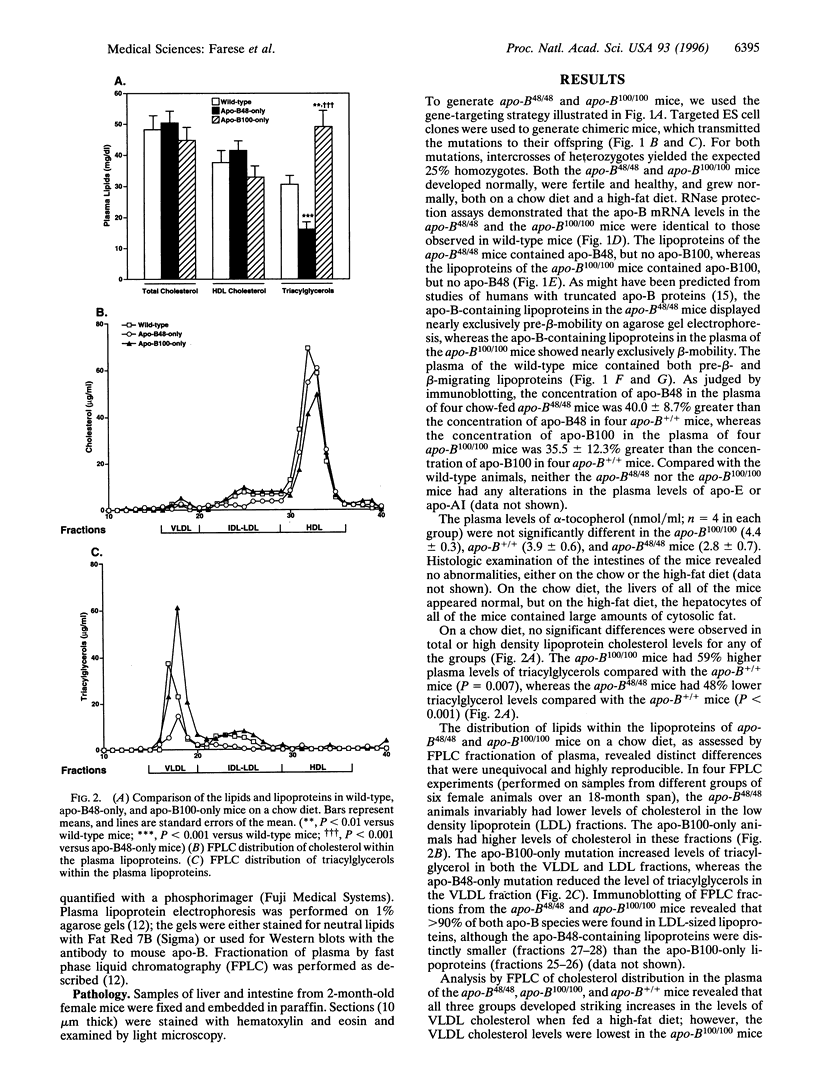
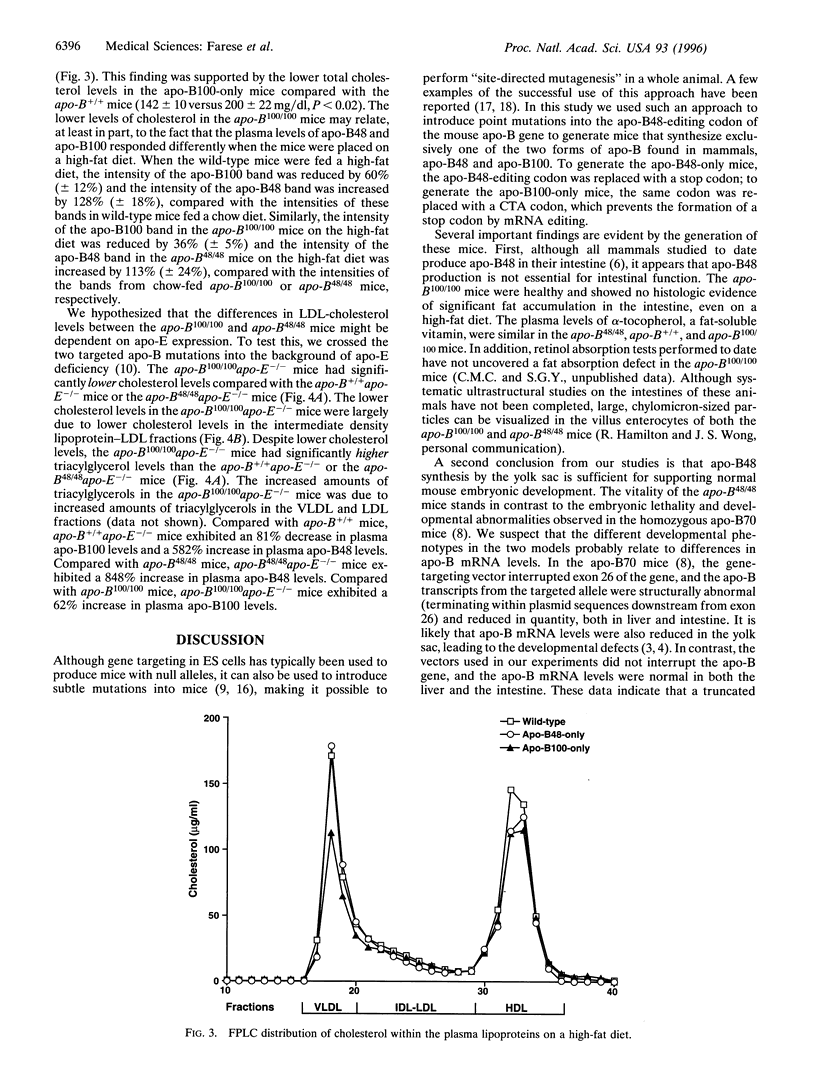
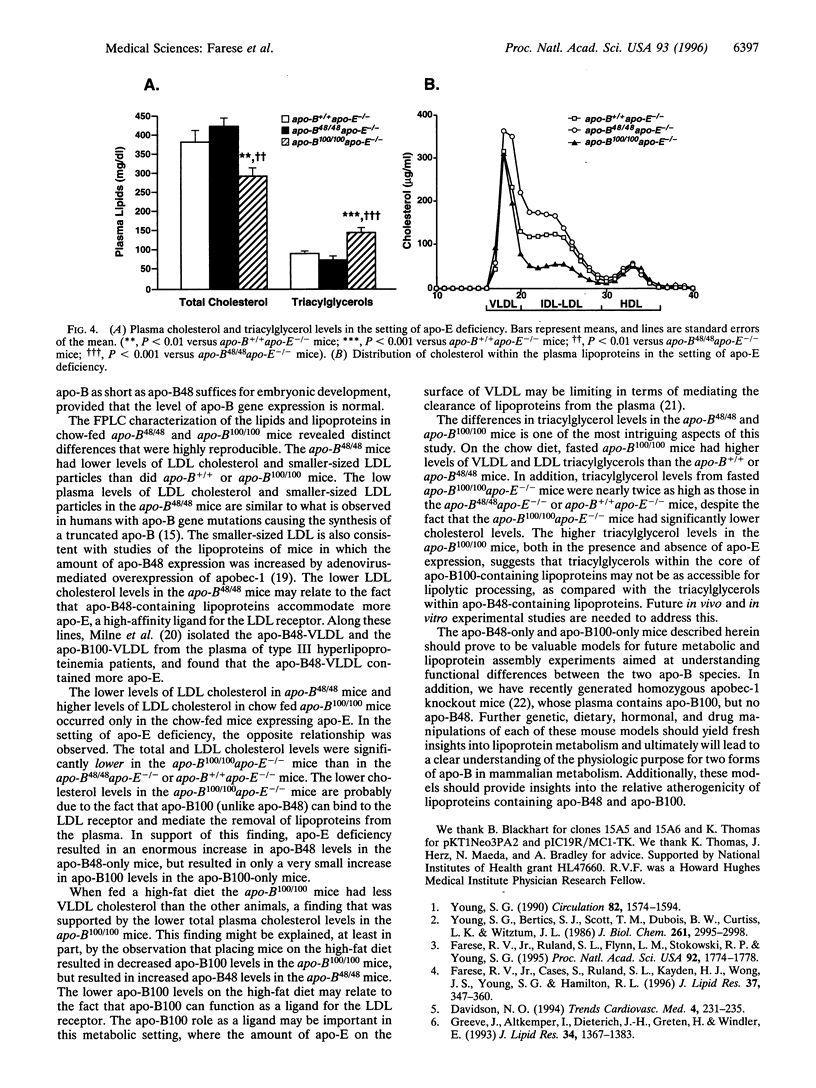
Apolipoprotein (apo)-B is found in two forms in mammals: apo-B100, which is made in the liver and the yolk sac, and apo-B48, a truncated protein made in the intestine. To provide models for understanding the physiologic purpose for the two forms of apo-B, we used targeted mutagenesis of the apo-B gene to generate mice that synthesize exclusively apo-B48 (apo-B48-only mice) and mice that synthesize exclusively apo-B100 (apo-B100-only mice). Both the apo-B48-only mice and apo-B100-only mice developed normally, were healthy, and were fertile. Thus, apo-B48 synthesis was sufficient for normal embryonic development, and the synthesis of apo-B100 in the intestines of adult mice caused no readily apparent adverse effects on intestinal function or nutrition. Compared with wild-type mice fed a chow diet, the levels of low density lipoprotein (LDL)-cholesterol and very low density lipoprotein- and LDL-triacylglycerols were lower in apo-B48-only mice and higher in the apo-B100-only mice. In the setting of apo-E-deficiency, the apo-B100-only mutation lowered cholesterol levels, consistent with the fact that apo-B100-lipoproteins can be cleared from the plasma via the LDL receptor, whereas apo-B48-lipoproteins lacking apo-E cannot. The apo-B48-only and apo-B100-only mice should prove to be valuable models for experiments designed to understand the purpose for the two forms of apo-B in mammalian metabolism.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Farese R. V., Jr, Cases S., Ruland S. L., Kayden H. J., Wong J. S., Young S. G., Hamilton R. L. A novel function for apolipoprotein B: lipoprotein synthesis in the yolk sac is critical for maternal-fetal lipid transport in mice. J Lipid Res. 1996 Feb;37(2):347–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Jr, Ruland S. L., Flynn L. M., Stokowski R. P., Young S. G. Knockout of the mouse apolipoprotein B gene results in embryonic lethality in homozygotes and protection against diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in heterozygotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 28;92(5):1774–1778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greeve J., Altkemper I., Dieterich J. H., Greten H., Windler E. Apolipoprotein B mRNA editing in 12 different mammalian species: hepatic expression is reflected in low concentrations of apoB-containing plasma lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1993 Aug;34(8):1367–1383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasty P., Ramírez-Solis R., Krumlauf R., Bradley A. Introduction of a subtle mutation into the Hox-2.6 locus in embryonic stem cells. Nature. 1991 Mar 21;350(6315):243–246. doi: 10.1038/350243a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano K., Young S. G., Farese R. V., Jr, Ng J., Sande E., Warburton C., Powell-Braxton L. M., Davidson N. O. Targeted disruption of the mouse apobec-1 gene abolishes apolipoprotein B mRNA editing and eliminates apolipoprotein B48. J Biol Chem. 1996 Apr 26;271(17):9887–9890. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.17.9887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homanics G. E., Smith T. J., Zhang S. H., Lee D., Young S. G., Maeda N. Targeted modification of the apolipoprotein B gene results in hypobetalipoproteinemia and developmental abnormalities in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2389–2393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang J. K., Gohil K., Packer L. Simultaneous determination of tocopherols, ubiquinols, and ubiquinones in blood, plasma, tissue homogenates, and subcellular fractions. Anal Biochem. 1986 Aug 15;157(1):106–116. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90203-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton M. F., Farese R. V., Jr, Chiesa G., Grass D. S., Chin P., Hammer R. E., Hobbs H. H., Young S. G. Transgenic mice expressing high plasma concentrations of human apolipoprotein B100 and lipoprotein(a). J Clin Invest. 1993 Dec;92(6):3029–3037. doi: 10.1172/JCI116927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton M. F., Farese R. V., Jr, Young S. G. Familial hypobetalipoproteinemia. J Lipid Res. 1993 Apr;34(4):521–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon A. P., Bradley A. The Wnt-1 (int-1) proto-oncogene is required for development of a large region of the mouse brain. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1073–1085. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90385-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milne R. W., Weech P. K., Blanchette L., Davignon J., Alaupovic P., Marcel Y. L. Isolation and characterization of apolipoprotein B-48 and B-100 very low density lipoproteins from type III hyperlipoproteinemic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):816–823. doi: 10.1172/JCI111276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piedrahita J. A., Zhang S. H., Hagaman J. R., Oliver P. M., Maeda N. Generation of mice carrying a mutant apolipoprotein E gene inactivated by gene targeting in embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4471–4475. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph U., Brabet P., Hasty P., Bradley A., Birnbaumer L. Disruption of the G(i2) alpha locus in embryonic stem cells and mice: a modified hit and run strategy with detection by a PCR dependent on gap repair. Transgenic Res. 1993 Nov;2(6):345–355. doi: 10.1007/BF01976176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimano H., Yamada N., Katsuki M., Shimada M., Gotoda T., Harada K., Murase T., Fukazawa C., Takaku F., Yazaki Y. Overexpression of apolipoprotein E in transgenic mice: marked reduction in plasma lipoproteins except high density lipoprotein and resistance against diet-induced hypercholesterolemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1750–1754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalenhoef A. F., Malloy M. J., Kane J. P., Havel R. J. Metabolism of apolipoproteins B-48 and B-100 of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins in normal and lipoprotein lipase-deficient humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1839–1843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng B., Blumenthal S., Forte T., Navaratnam N., Scott J., Gotto A. M., Jr, Chan L. Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of rat apolipoprotein B mRNA-editing protein in mice virtually eliminates apolipoprotein B-100 and normal low density lipoprotein production. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 25;269(47):29395–29404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valancius V., Smithies O. Testing an "in-out" targeting procedure for making subtle genomic modifications in mouse embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1402–1408. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao Z. M., Blackhart B. D., Johnson D. F., Taylor S. M., Haubold K. W., McCarthy B. J. Elimination of apolipoprotein B48 formation in rat hepatoma cell lines transfected with mutant human apolipoprotein B cDNA constructs. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1175–1182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. G., Bertics S. J., Scott T. M., Dubois B. W., Curtiss L. K., Witztum J. L. Parallel expression of the MB19 genetic polymorphism in apoprotein B-100 and apoprotein B-48. Evidence that both apoproteins are products of the same gene. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):2995–2998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. G. Recent progress in understanding apolipoprotein B. Circulation. 1990 Nov;82(5):1574–1594. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.82.5.1574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiher B. G., Eichwald E., Zabner J., Smith J. J., Puga A. P., McCray P. B., Jr, Capecchi M. R., Welsh M. J., Thomas K. R. A mouse model for the delta F508 allele of cystic fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1995 Oct;96(4):2051–2064. doi: 10.1172/JCI118253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




