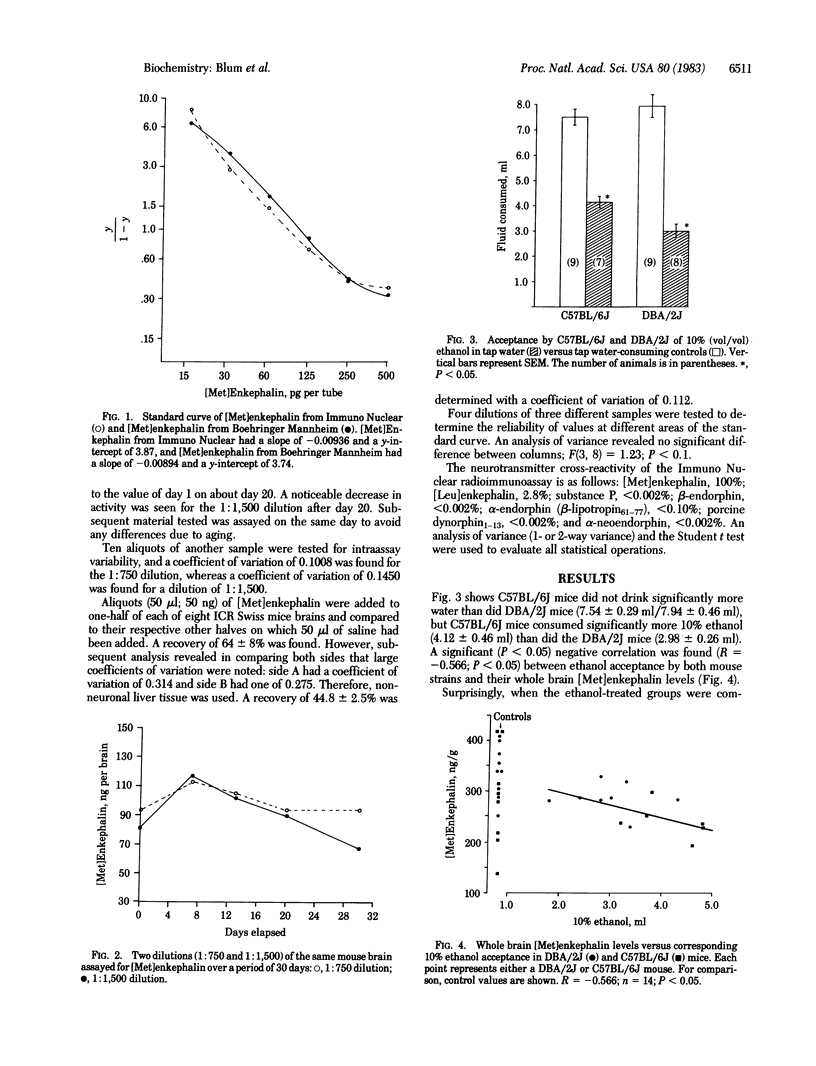
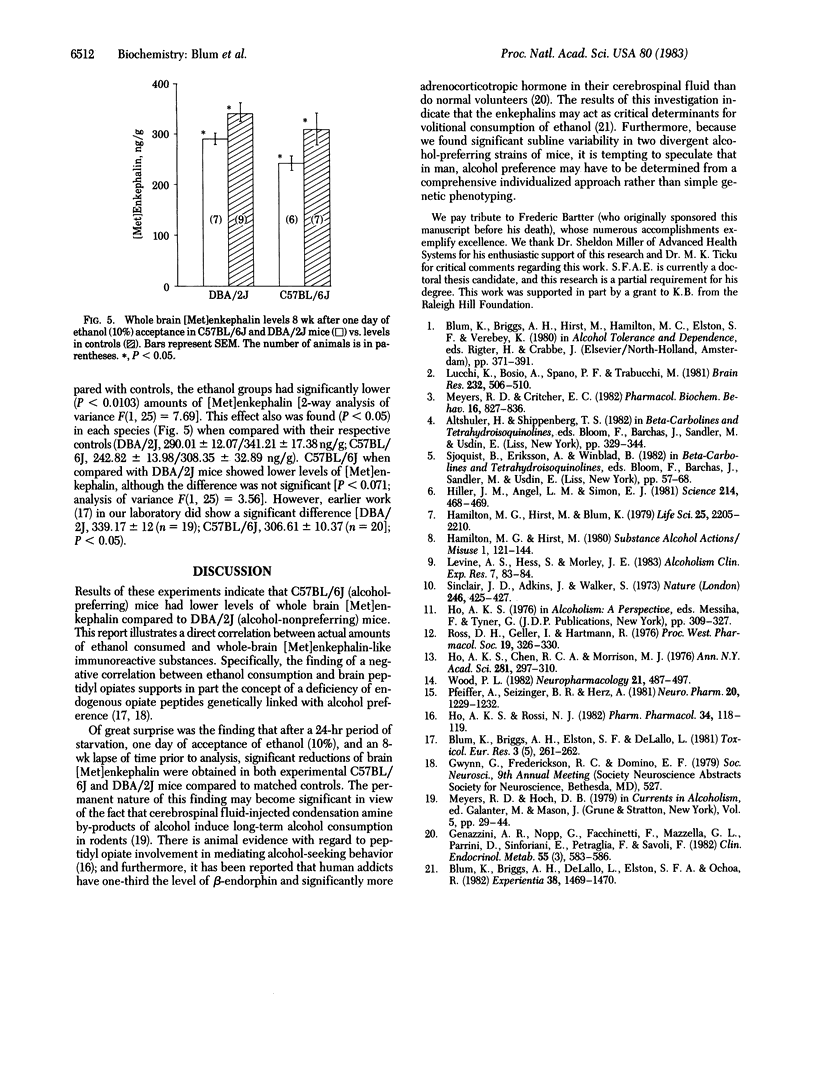
Abstract
Our results indicate a negative correlation between the amount of ethanol (10%) consumed and endogenous levels of brain [Met]enkephalin in C57BL/6J (alcohol-preferring) and DBA/2J (alcohol-nonpreferring) inbred mice strains. Additionally, it was found that 8 wk after 1-day starved groups of both C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mice were challenged with ethanol (10%) for 1-day acceptance, they had significantly lower levels of brain [Met]enkephalin compared with their nonalcohol-treated controls. These results suggest that the brain endogenous peptidyl opiates may play a crucial role in alcohol-seeking behavior.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blum K., Briggs A. H., DeLallo L., Elston S. F., Ochoa R. Whole brain methionine-enkephalin of ethanol-avoiding and ethanol-preferring c57BL mice. Experientia. 1982 Dec 15;38(12):1469–1470. doi: 10.1007/BF01955775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum K., Briggs A. H., Elston S. F., DeLallo L. Ethanol preference as a function of genotypic levels of whole brain enkephalin in mice. Toxicol Eur Res. 1981 Sep;3(5):261–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genazzani A. R., Nappi G., Facchinetti F., Mazzella G. L., Parrini D., Sinforiani E., Petraglia F., Savoldi F. Central deficiency of beta-endorphin in alcohol addicts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Sep;55(3):583–586. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-3-583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton M. G., Hirst M. Alcohol-related tetrahydroisoquinolines: pharmacology and identification. Subst Alcohol Actions Misuse. 1980;1(2):121–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton M. G., Hirst M., Blum K. Opiate-like activity of salsolinol on the electrically stimulated guinea pig ileum. Life Sci. 1979 Dec 24;25(26):2205–2210. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90093-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiller J. M., Angel L. M., Simon E. J. Multiple opiate receptors: alcohol selectively inhibits binding to delta receptors. Science. 1981 Oct 23;214(4519):468–469. doi: 10.1126/science.6270788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho A. K., Chen R. C. Interactions of narcotics, narcotic antagonists, and ethanol during acute, chronic, and withdrawal states. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;281:297–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb27940.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho A. K., Rossi N. Suppression of ethanol consumption by MET-enkephalin in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1982 Feb;34(2):118–119. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1982.tb04199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. S., Hess S., Morley J. E. Alcohol and the opiate receptor. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1983 Winter;7(1):83–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1983.tb05416.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. D., Critcher E. C. Naloxone alters alcohol drinking induced in the rat by tetrahydropapaveroline (THP) infused ICV. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1982 May;16(5):827–836. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(82)90243-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer A., Seizinger B. R., Herz A. Chronic ethanol imbibition interferes with delta-, but not with mu-opiate receptors. Neuropharmacology. 1981 Dec;20(12A):1229–1232. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(81)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross D., Hartmann R. J., Geller I. Ethanol preference in the hamster: effects of morphine sulfate and naltrexone, a long-acting morphine antagonist. Proc West Pharmacol Soc. 1976;19:326–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair J. D., Adkins J., Walker S. Morphine-induced suppression of voluntary alcohol drinking in rats. Nature. 1973 Dec 14;246(5433):425–427. doi: 10.1038/246425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. L. Multiple opiate receptors: support for unique mu, delta and kappa sites. Neuropharmacology. 1982 Jun;21(6):487–497. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(82)90038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



