Abstract
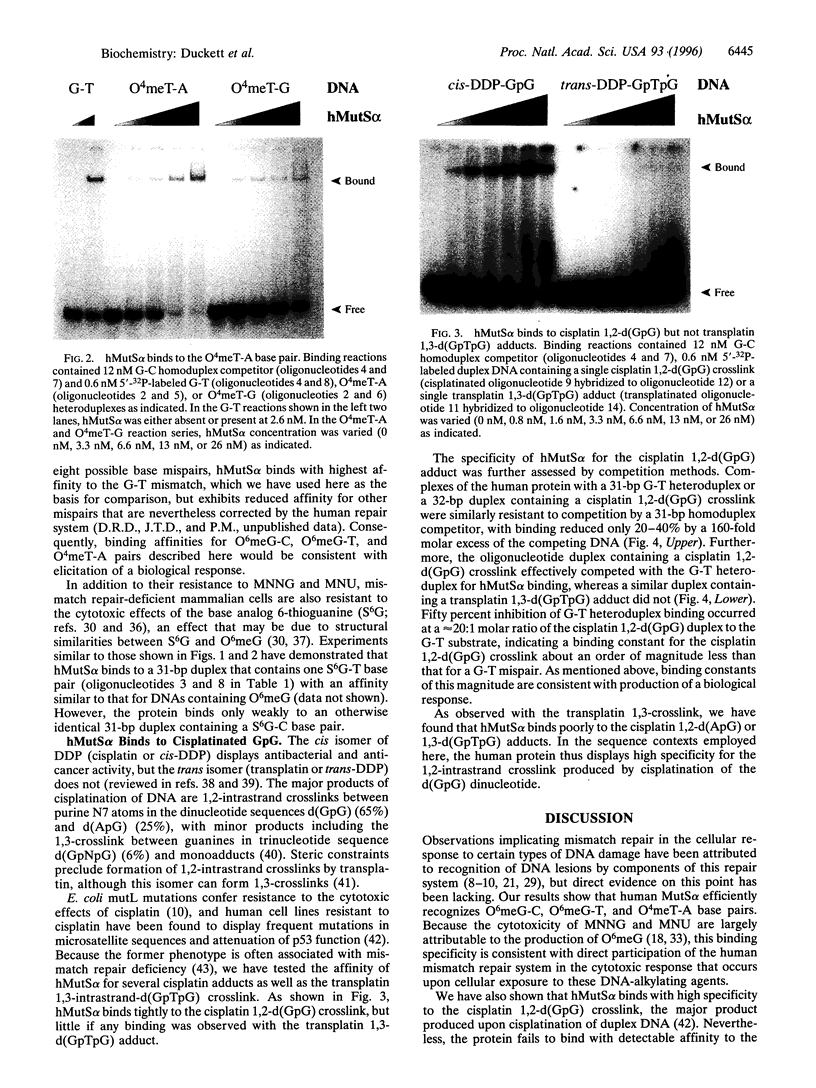
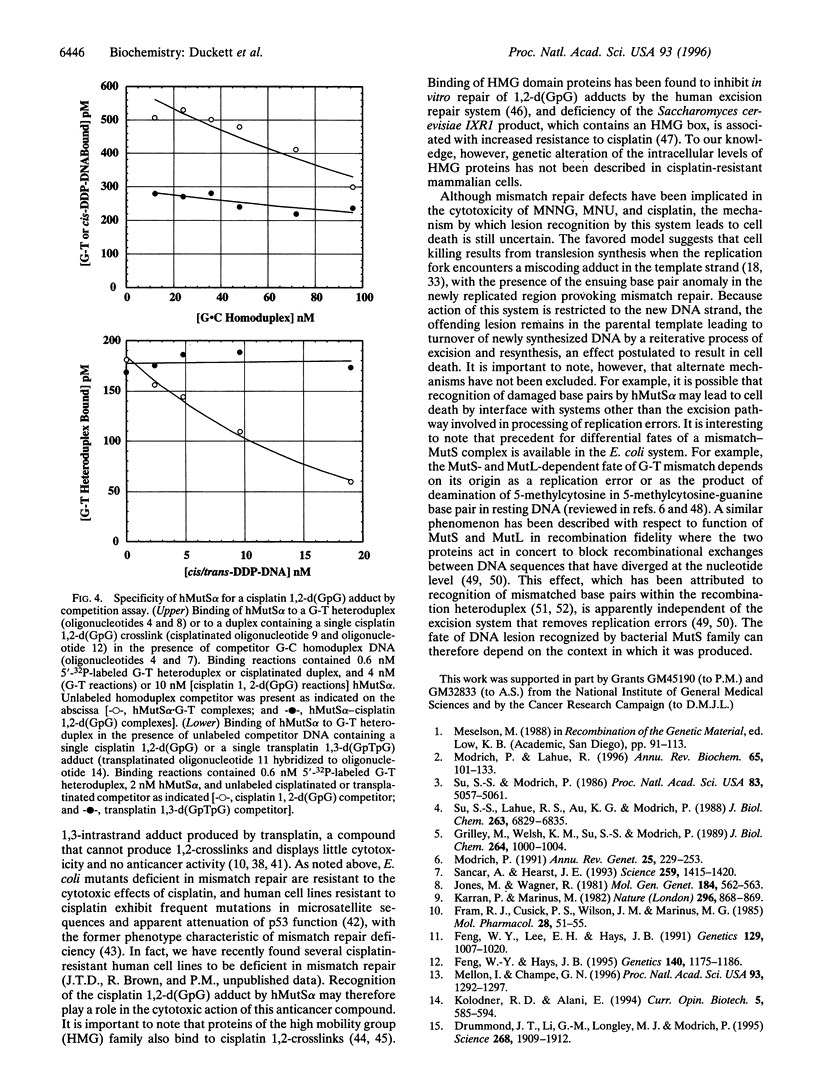
Bacterial and mammalian mismatch repair systems have been implicated in the cellular response to certain types of DNA damage, and genetic defects in this pathway are known to confer resistance to the cytotoxic effects of DNA-methylating agents. Such observations suggest that in addition to their ability to recognize DNA base-pairing errors, members of the MutS family may also respond to genetic lesions produced by DNA damage. We show that the human mismatch recognition activity MutSalpha recognizes several types of DNA lesion including the 1,2-intrastrand d(GpG) crosslink produced by cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II), as well as base pairs between O6-methylguanine and thymine or cytosine, or between O4-methylthymine and adenine. However, the protein fails to recognize 1,3-intrastrand adduct produced by trans-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) at a d(GpTpG) sequence. These observations imply direct involvement of the mismatch repair system in the cytotoxic effects of DNA-methylating agents and suggest that recognition of 1,2-intrastrand cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) adducts by MutSalpha may be involved in the cytotoxic action of this chemotherapeutic agent.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthoney D. A., McIlwrath A. J., Gallagher W. M., Edlin A. R., Brown R. Microsatellite instability, apoptosis, and loss of p53 function in drug-resistant tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1996 Mar 15;56(6):1374–1381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aquilina G., Giammarioli A. M., Zijno A., Di Muccio A., Dogliotti E., Bignami M. Tolerance to O6-methylguanine and 6-thioguanine cytotoxic effects: a cross-resistant phenotype in N-methylnitrosourea-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cancer Res. 1990 Jul 15;50(14):4248–4253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aquilina G., Hess P., Fiumicino S., Ceccotti S., Bignami M. A mutator phenotype characterizes one of two complementation groups in human cells tolerant to methylation damage. Cancer Res. 1995 Jun 15;55(12):2569–2575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branch P., Aquilina G., Bignami M., Karran P. Defective mismatch binding and a mutator phenotype in cells tolerant to DNA damage. Nature. 1993 Apr 15;362(6421):652–654. doi: 10.1038/362652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. J., Kellett P. J., Lippard S. J. Ixr1, a yeast protein that binds to platinated DNA and confers sensitivity to cisplatin. Science. 1993 Jul 30;261(5121):603–605. doi: 10.1126/science.8342024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G. Cellular responses to cisplatin. The roles of DNA-binding proteins and DNA repair. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):787–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond J. T., Li G. M., Longley M. J., Modrich P. Isolation of an hMSH2-p160 heterodimer that restores DNA mismatch repair to tumor cells. Science. 1995 Jun 30;268(5219):1909–1912. doi: 10.1126/science.7604264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eastman A. Reevaluation of interaction of cis-dichloro(ethylenediamine)platinum(II) with DNA. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 1;25(13):3912–3915. doi: 10.1021/bi00361a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eshleman J. R., Markowitz S. D. Microsatellite instability in inherited and sporadic neoplasms. Curr Opin Oncol. 1995 Jan;7(1):83–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng W. Y., Hays J. B. DNA structures generated during recombination initiated by mismatch repair of UV-irradiated nonreplicating phage DNA in Escherichia coli: requirements for helicase, exonucleases, and RecF and RecBCD functions. Genetics. 1995 Aug;140(4):1175–1186. doi: 10.1093/genetics/140.4.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng W. Y., Lee E. H., Hays J. B. Recombinagenic processing of UV-light photoproducts in nonreplicating phage DNA by the Escherichia coli methyl-directed mismatch repair system. Genetics. 1991 Dec;129(4):1007–1020. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.4.1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fram R. J., Cusick P. S., Wilson J. M., Marinus M. G. Mismatch repair of cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II)-induced DNA damage. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Jul;28(1):51–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldmacher V. S., Cuzick R. A., Jr, Thilly W. G. Isolation and partial characterization of human cell mutants differing in sensitivity to killing and mutation by methylnitrosourea and N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12462–12471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grilley M., Welsh K. M., Su S. S., Modrich P. Isolation and characterization of the Escherichia coli mutL gene product. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1000–1004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawn M. T., Umar A., Carethers J. M., Marra G., Kunkel T. A., Boland C. R., Koi M. Evidence for a connection between the mismatch repair system and the G2 cell cycle checkpoint. Cancer Res. 1995 Sep 1;55(17):3721–3725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. C., Zamble D. B., Reardon J. T., Lippard S. J., Sancar A. HMG-domain proteins specifically inhibit the repair of the major DNA adduct of the anticancer drug cisplatin by human excision nuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 25;91(22):10394–10398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes E. N., Engelsberg B. N., Billings P. C. Purification of nuclear proteins that bind to cisplatin-damaged DNA. Identity with high mobility group proteins 1 and 2. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13520–13527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M., Wagner R. N-Methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine sensitivity of E. coli mutants deficient in DNA methylation and mismatch repair. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(3):562–563. doi: 10.1007/BF00352542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karran P., Bignami M. DNA damage tolerance, mismatch repair and genome instability. Bioessays. 1994 Nov;16(11):833–839. doi: 10.1002/bies.950161110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karran P., Bignami M. Self-destruction and tolerance in resistance of mammalian cells to alkylation damage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 25;20(12):2933–2940. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.12.2933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karran P., Marinus M. G. Mismatch correction at O6-methylguanine residues in E. coli DNA. Nature. 1982 Apr 29;296(5860):868–869. doi: 10.1038/296868a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kat A., Thilly W. G., Fang W. H., Longley M. J., Li G. M., Modrich P. An alkylation-tolerant, mutator human cell line is deficient in strand-specific mismatch repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6424–6428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koi M., Umar A., Chauhan D. P., Cherian S. P., Carethers J. M., Kunkel T. A., Boland C. R. Human chromosome 3 corrects mismatch repair deficiency and microsatellite instability and reduces N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine tolerance in colon tumor cells with homozygous hMLH1 mutation. Cancer Res. 1994 Aug 15;54(16):4308–4312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike G., Maki H., Takeya H., Hayakawa H., Sekiguchi M. Purification, structure, and biochemical properties of human O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14754–14762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodner R. D., Alani E. Mismatch repair and cancer susceptibility. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1994 Dec;5(6):585–594. doi: 10.1016/0958-1669(94)90079-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G. M., Modrich P. Restoration of mismatch repair to nuclear extracts of H6 colorectal tumor cells by a heterodimer of human MutL homologs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 14;92(6):1950–1954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.6.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb L. A. Microsatellite instability: marker of a mutator phenotype in cancer. Cancer Res. 1994 Oct 1;54(19):5059–5063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon I., Champe G. N. Products of DNA mismatch repair genes mutS and mutL are required for transcription-coupled nucleotide-excision repair of the lactose operon in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Feb 6;93(3):1292–1297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.3.1292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modrich P., Lahue R. Mismatch repair in replication fidelity, genetic recombination, and cancer biology. Annu Rev Biochem. 1996;65:101–133. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.65.070196.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modrich P. Mechanisms and biological effects of mismatch repair. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:229–253. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.001305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murchie A. I., Lilley D. M. T4 endonuclease VII cleaves DNA containing a cisplatin adduct. J Mol Biol. 1993 Sep 5;233(1):77–85. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palombo F., Gallinari P., Iaccarino I., Lettieri T., Hughes M., D'Arrigo A., Truong O., Hsuan J. J., Jiricny J. GTBP, a 160-kilodalton protein essential for mismatch-binding activity in human cells. Science. 1995 Jun 30;268(5219):1912–1914. doi: 10.1126/science.7604265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos N., Nicolaides N. C., Liu B., Parsons R., Lengauer C., Palombo F., D'Arrigo A., Markowitz S., Willson J. K., Kinzler K. W. Mutations of GTBP in genetically unstable cells. Science. 1995 Jun 30;268(5219):1915–1917. doi: 10.1126/science.7604266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulos N., Nicolaides N. C., Wei Y. F., Ruben S. M., Carter K. C., Rosen C. A., Haseltine W. A., Fleischmann R. D., Fraser C. M., Adams M. D. Mutation of a mutL homolog in hereditary colon cancer. Science. 1994 Mar 18;263(5153):1625–1629. doi: 10.1126/science.8128251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons R., Li G. M., Longley M. J., Fang W. H., Papadopoulos N., Jen J., de la Chapelle A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B., Modrich P. Hypermutability and mismatch repair deficiency in RER+ tumor cells. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1227–1236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90331-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit M. A., Dimpfl J., Radman M., Echols H. Control of large chromosomal duplications in Escherichia coli by the mismatch repair system. Genetics. 1991 Oct;129(2):327–332. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pil P. M., Lippard S. J. Specific binding of chromosomal protein HMG1 to DNA damaged by the anticancer drug cisplatin. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):234–237. doi: 10.1126/science.1566071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport H. P. The 6-thioguanine/5-methyl-2-pyrimidinone base pair. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7253–7267. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayssiguier C., Thaler D. S., Radman M. The barrier to recombination between Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium is disrupted in mismatch-repair mutants. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):396–401. doi: 10.1038/342396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risinger J. I., Umar A., Barrett J. C., Kunkel T. A. A hPMS2 mutant cell line is defective in strand-specific mismatch repair. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 4;270(31):18183–18186. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.31.18183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hearst J. E. Molecular matchmakers. Science. 1993 Mar 5;259(5100):1415–1420. doi: 10.1126/science.8451638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer B., Chavez F., Goodman M. F., Essigmann J. M., Dosanjh M. K. Effect of 3' flanking neighbors on kinetics of pairing of dCTP or dTTP opposite O6-methylguanine in a defined primed oligonucleotide when Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I is used. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8271–8274. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su S. S., Lahue R. S., Au K. G., Modrich P. Mispair specificity of methyl-directed DNA mismatch correction in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6829–6835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su S. S., Modrich P. Escherichia coli mutS-encoded protein binds to mismatched DNA base pairs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5057–5061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umar A., Boyer J. C., Thomas D. C., Nguyen D. C., Risinger J. I., Boyd J., Ionov Y., Perucho M., Kunkel T. A. Defective mismatch repair in extracts of colorectal and endometrial cancer cell lines exhibiting microsatellite instability. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 20;269(20):14367–14370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worth L., Jr, Clark S., Radman M., Modrich P. Mismatch repair proteins MutS and MutL inhibit RecA-catalyzed strand transfer between diverged DNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3238–3241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]