Abstract
Addition of epidermal growth factor (EGF) to quiescent cultured cells was found to stimulate the activity of glycogen synthase (UDPglucose:glycogen 4-alpha-D-glucosyltransferase, EC 2.4.1.11), an enzyme subjected to regulation by covalent modification. In Swiss mouse 3T3 cells, the activation by EGF paralleled the effect seen with insulin; the time course and dose-response curves of the two polypeptide factors were similar. Stimulation of enzyme activity ratio [(activity in the absence of glucose 6-phosphate)/(activity in the presence of glucose 6-phosphate)] was maximal after 20-30 min of incubation. Both factors caused a maximal stimulation of 2.5-fold in synthase activity ratio at approximately equal to 10 nM, and the half-maximal effect was observed at 0.1-1 nM. Insulin and EGF exhibited partial additivity in effecting this enzyme activation. In contrast, human A431 cells showed no response to insulin. Although quantitatively different, the EGF effect in the latter cells was time dependent, reaching a maximum at 90 min, and dose dependent, with a maximal stimulation of 4-fold in synthase activity ratio at 10 nM. Half-maximal effect was observed at 0.3 nM EGF. Direct quantitation of allosteric effectors (glucose 6-phosphate, adenine nucleotides, and Pi) present in the enzyme assay mixtures indicated that the observed activation was not simply a consequence of changes in metabolite concentrations. These results suggest that EGF may be important in regulating glycogen synthesis through phosphorylation/dephosphorylation mechanisms.
Full text
PDF
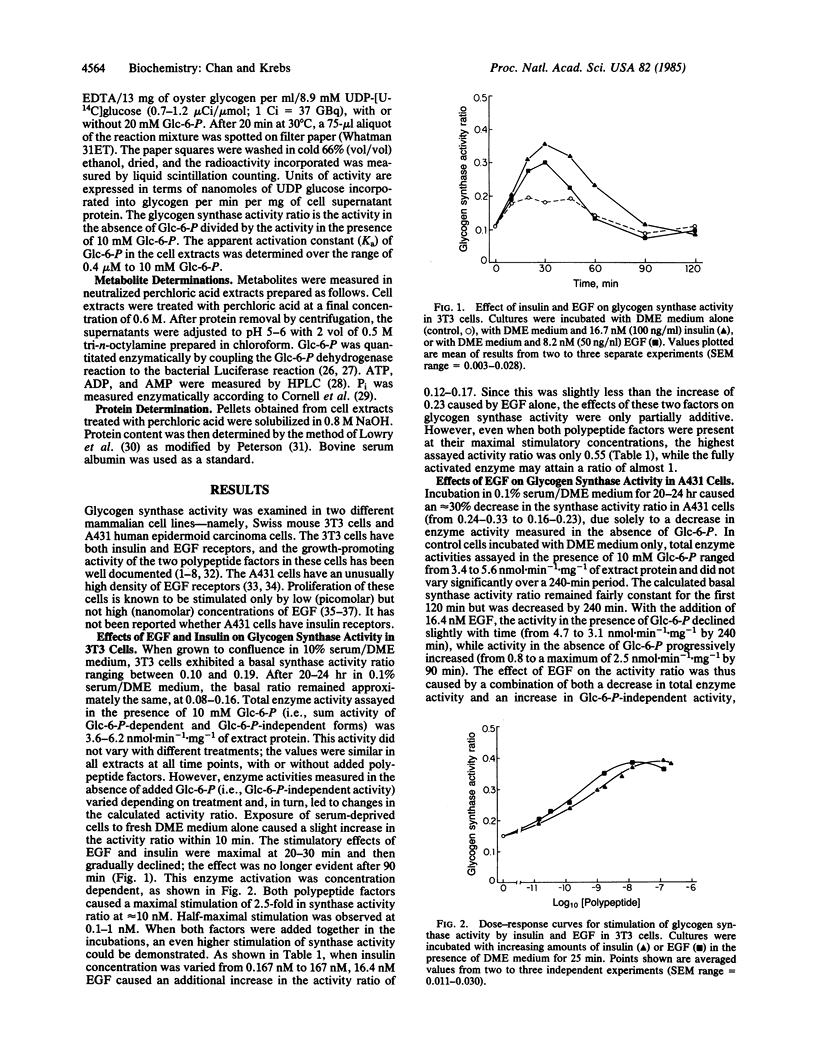
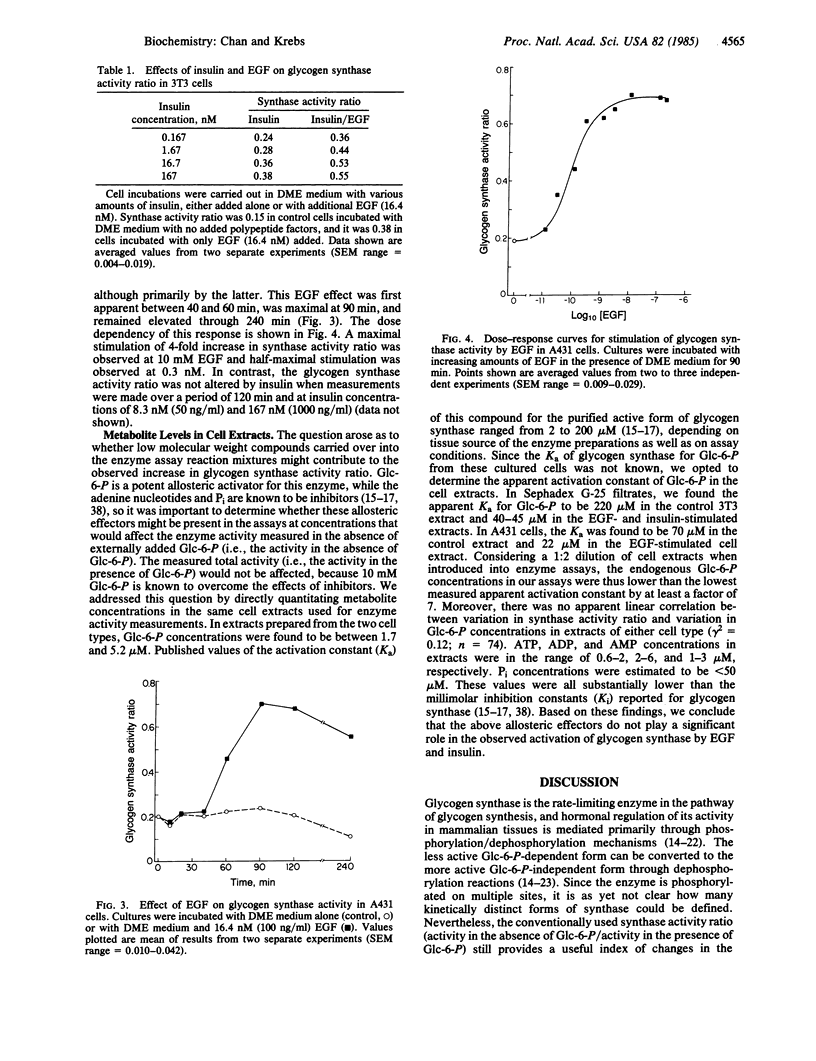


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes D. W. Epidermal growth factor inhibits growth of A431 human epidermoid carcinoma in serum-free cell culture. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):1–4. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes D., Colowick S. P. Stimulation of sugar uptake in cultured fibroblasts by epidermal growth factor (EGF) and EGF-binding arginine esterase. J Cell Physiol. 1976 Dec;89(4):633–639. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040890420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., King L., Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor stimulates phosphorylation in membrane preparations in vitro. Nature. 1978 Nov 23;276(5686):409–410. doi: 10.1038/276409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Bowen-Pope D. F., Raines E., Ross R., Hunter T. Similar effects of platelet-derived growth factor and epidermal growth factor on the phosphorylation of tyrosine in cellular proteins. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):263–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90426-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell N. W., Leadbetter M. G., Veech R. L. Modifications in the enzymatic assay for inorganic phosphate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jun;95(2):524–526. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90766-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond I., Legg A., Schneider J. A., Rozengurt E. Glycolysis in quiescent cultures of 3T3 cells. Stimulation by serum, epidermal growth factor, and insulin in intact cells and persistence of the stimulation after cell homogenization. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):866–871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabricant R. N., De Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Nerve growth factor receptors on human melanoma cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):565–569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. F., Linsley P. S., Wrann M. Receptor remodeling and regulation in the action of epidermal growth factor. Fed Proc. 1982 Nov;41(13):2988–2995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigler H., Ash J. F., Singer S. J., Cohen S. Visualization by fluorescence of the binding and internalization of epidermal growth factor in human carcinoma cells A-431. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3317–3321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiken J. F., Lawrence J. C., Jr Glycogen synthase in rat adipocytes and skeletal muscle is phosphorylated on both serine and threonine. FEBS Lett. 1984 Sep 17;175(1):55–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80568-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg M. D., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin and epidermal growth factor. Human fibroblast receptors related to deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis and amino acid uptake. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):3845–3853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Epidermal growth factor induces rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of proteins in A431 human tumor cells. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto T., Mendelsohn J., Le A., Sato G. H., Lazar C. S., Gill G. N. Relation of epidermal growth factor receptor concentration to growth of human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7761–7766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto T., Sato J. D., Le A., Polikoff J., Sato G. H., Mendelsohn J. Growth stimulation of A431 cells by epidermal growth factor: identification of high-affinity receptors for epidermal growth factor by an anti-receptor monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1337–1341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kricka L. J., Wienhausen G. K., Hinkley J. E., De Luca M. Automated bioluminescent assays for NADH, glucose 6-phosphate, primary bile acids, and ATP. Anal Biochem. 1983 Mar;129(2):392–397. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90567-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner J., Lawrence J. C., Walkenbach R. J., Roach P. J., Hazen R. J., Huang L. C. Insulin control of glycogen synthesis. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1978;9:425–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. C., Jr, Larner J. Activation of glycogen synthase in rat adipocytes by insulin and glucose involves increased glucose transport and phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 10;253(7):2104–2113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen-Hamilton M., Hamilton R. T., Allen W. R., Potter-Perigo S. Synergistic stimulation of S6 ribosomal protein phosphorylation and DNA synthesis by epidermal growth factor and insulin in quiescent 3T3 cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):237–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90423-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Caudwell F. B., Cohen P. Glycogen synthase from rabbit skeletal muscle; effect of insulin on the state of phosphorylation of the seven phosphoserine residues in vivo. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jan 17;130(1):227–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike L. J., Kuenzel E. A., Casnellie J. E., Krebs E. G. A comparison of the insulin- and epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein kinases from human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9913–9921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piras R., Rothman L. B., Cabib E. Regulation of muscle glycogen synthetase by metabolites. Differential effects on the I and D forms. Biochemistry. 1968 Jan;7(1):56–66. doi: 10.1021/bi00841a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss R. M., Herschman H. R. Variants of 3T3 cells lacking mitogenic response to epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3918–3921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss P. D., Zuurendonk P. F., Veech R. L. Measurement of tissue purine, pyrimidine, and other nucleotides by radial compression high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jul;140(1):162–171. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90148-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roach P. J. Glycogen synthase and glycogen synthase kinases. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1981;20:45–105. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152820-1.50006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roach P. J., Larner J. Rabbit skeletal muscle glycogen synthase. II. Enzyme phosphorylation state and effector concentrations as interacting control parameters. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):1920–1925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roach P. J., Takeda Y., Larner J. Rabbit skeletal muscle glycogen synthase. I. Relationship between phosphorylation state and kinetic properties. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 10;251(7):1913–1919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Heppel L. A. Serum rapidly stimulates ouabain-sensitive 86-RB+ influx in quiescent 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4492–4495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheorain V. S., Khatra B. S., Soderling T. R. Hormonal regulation of skeletal muscle glycogen synthase through covalent phosphorylation. Fed Proc. 1982 Aug;41(10):2618–2622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. L., Lawrence J. C., Jr Insulin action in denervated rat hemidiaphragms. Decreased hormonal stimulation of glycogen synthesis involves both glycogen synthase and glucose transport. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2201–2207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Martin-Pérez J., Siegmann M., Otto A. M. The effect of serum, EGF, PGF2 alpha and insulin on S6 phosphorylation and the initiation of protein and DNA synthesis. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Schlender K. K., Larner J. A rapid filter paper assay for UDPglucose-glycogen glucosyltransferase, including an improved biosynthesis of UDP-14C-glucose. Anal Biochem. 1968 Oct 24;25(1):486–499. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90127-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VILLAR-PALASI C., LARNER J. Insulin treatment and increased UDPG-glycogen transglucosylase activity in muscle. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Sep;94:436–442. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


